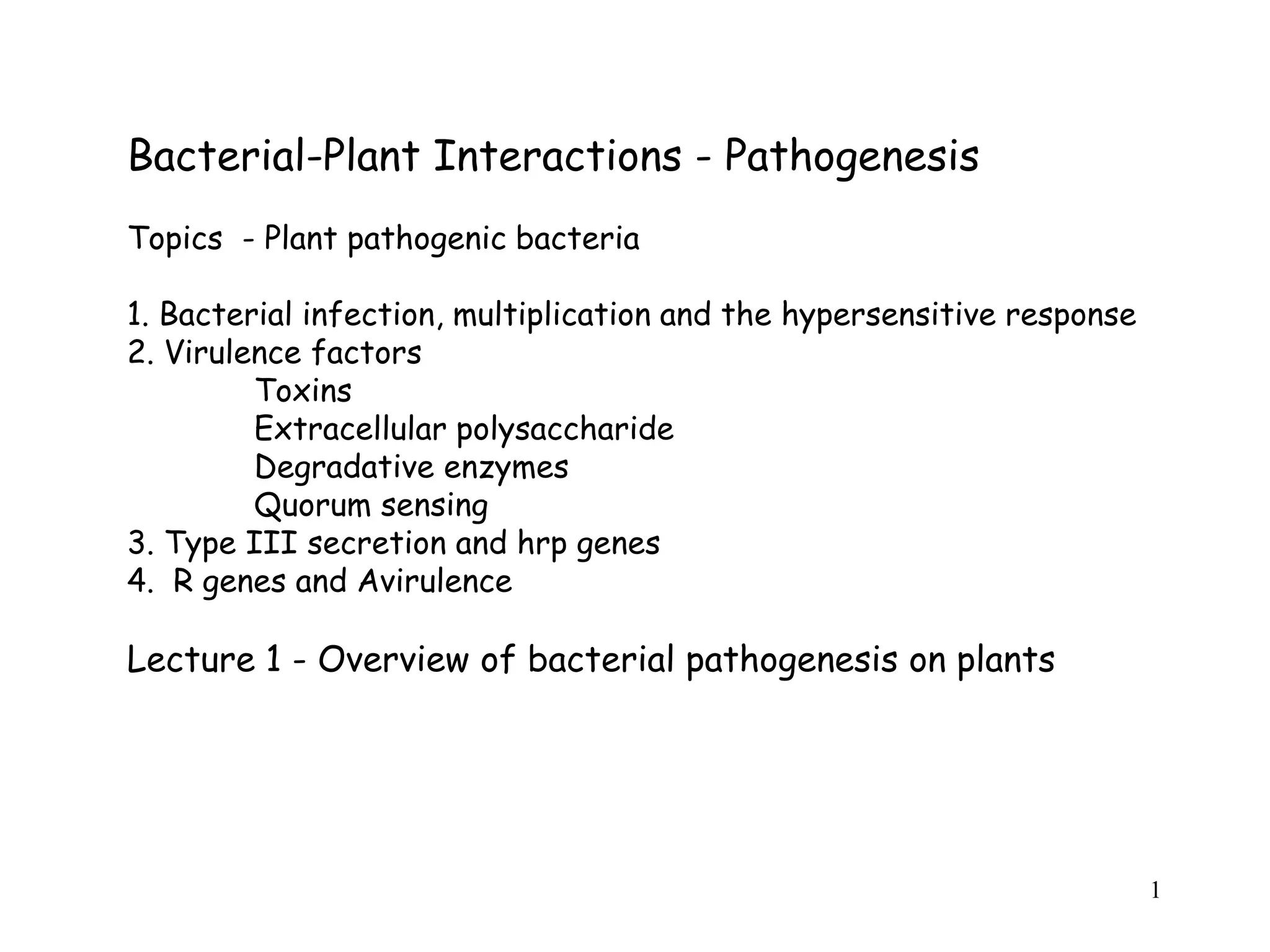
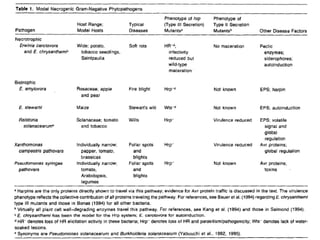
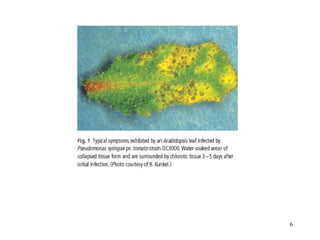
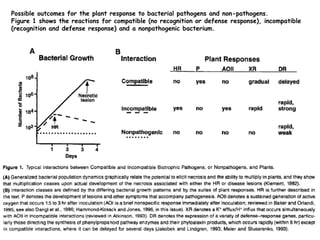
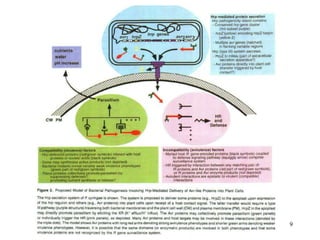
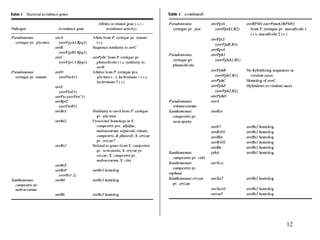
Bacterial pathogens of plants have specialized properties that allow them to infect plants. They parasitize plant cells and cause cell death. Important virulence factors include toxins, extracellular polysaccharides, and degradative enzymes. Bacterial pathogens use type III secretion systems and effector proteins to manipulate plant cells and cause disease symptoms. The interaction between bacterial effectors and plant resistance proteins determines if the interaction is compatible and leads to disease, or incompatible and triggers a hypersensitive response.