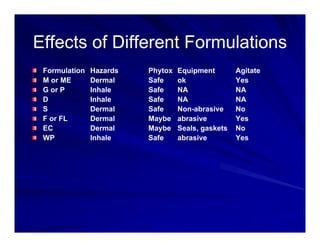
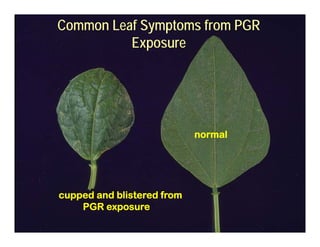
This document discusses pesticide formulations and adjuvants. It defines a formulation as how a pesticide is packaged, which contains both active and inert ingredients. The active ingredient is responsible for the pesticidal effect, while inert ingredients are added to make the formulation easier to handle or store. Common formulations include liquids, wettable powders, granules and pellets. The document also discusses the effects of different formulations and types of adjuvants that can be added to enhance pesticide performance. It provides examples of different pesticide modes of action and the visual symptoms caused by each.