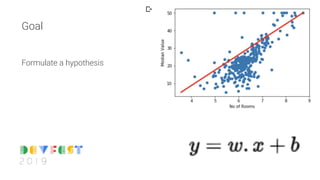
This document introduces machine learning concepts and provides a step-by-step guide to creating a machine learning model with TensorFlow. It begins with an overview of machine learning and formulating hypotheses. Then it shows how to load data, create a simple linear regression model manually, and train it with gradient descent. Next, it demonstrates how to simplify the process using TensorFlow Keras to build and train neural network models. It concludes by discussing feature engineering techniques like bucketizing features to improve model performance.



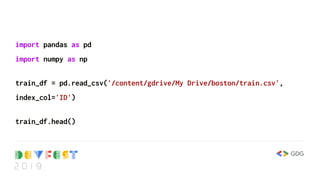
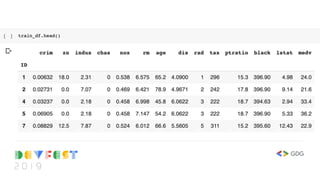
![train_df[['rm', 'medv']].head()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-7-320.jpg)

![y = train_df['medv'].values
train_df['constant'] = 1
columns = ['constant', 'rm', 'zn', 'indus']
x = train_df[columns].values
w = np.zeros((x.shape[1], 1))
y_pred = np.dot(x, w)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-9-320.jpg)

![error = y - y_pred
print(error.shape)
squared_error = np.power(error, 2)
root_mean_squared_error = sqrt(squared_error.sum()) / y_pred.shape[0]
print(root_mean_squared_error)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-11-320.jpg)

![costs = []
w_0_s = []
w_1_s = []
learning_rate = 1e-3
steps = 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-13-320.jpg)
![for a in range(steps):
w_0 = w[0][0]
w_1 = w[1][0]
# make prediction
y_pred = np.dot(x, w)
error = y - y_pred
error_squared = np.power(error, 2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-14-320.jpg)
![# cost function is Least Mean Squares
LMS = error_squared.sum() / (2 * y.shape[0])
costs.append(LMS)
w_0_s.append(w_0)
w_1_s.append(w_1)
# update
w_0 = w_0 + learning_rate/y.shape[0] * error.sum()
w_1 = w_1 + learning_rate/y.shape[0] * (error * x[1]).sum()
w[0][0] = w_0
w[1][0] = w_1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-15-320.jpg)
![cost_df = pd.DataFrame({'cost': pd.Series(costs), 'w_0':
pd.Series(w_0_s), 'w_1': pd.Series(w_1_s)})
cost_df['cost'].plot()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-16-320.jpg)

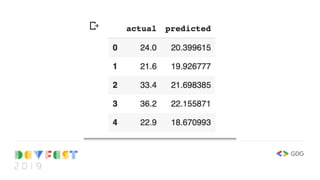
![_w = [w_0, w_1]
_w = np.asarray(_w)
_x = train_df[['constant', 'rm']].values
y_pred = np.dot(_x, _w)
_p = pd.DataFrame(dict(actual=train_df['medv'].values,
predicted=y_pred.reshape(-1)))
_p.head()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-18-320.jpg)

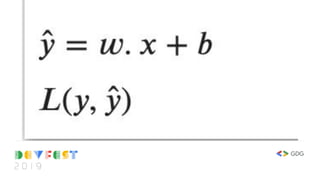
![class Model(object):
def __init__(self):
self.W = None
self.b = None
def __call__(self, x):
if self.W == None:
self.W = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal(shape=(1, x.shape[1])))
if self.b == None:
self.b = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal(shape=(x.shape[0], 1)))
return tf.matmul(x, self.W, transpose_b=True) + self.b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-22-320.jpg)
![model = Model()
output = model(tf.constant([3.0, 3.1, 1.9, 2.0, 2.5, 2.9],
shape=(3,2)))
print(output)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-23-320.jpg)


![def train(model, x, y, alpha):
x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x, np.float32)
y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y, np.float32)
with tf.GradientTape() as t:
t.watch(x)
current_loss = loss(model(x), y)
#print(current_loss)
dW, db = t.gradient(current_loss, [model.W, model.b])
#print(dW, db)
model.W.assign_sub(alpha * dW)
model.b.assign_sub(alpha * db)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-26-320.jpg)
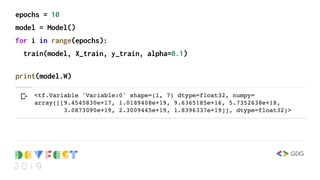
![train_df = df.sample(frac=0.8,random_state=0)
test_df = df.drop(train_df.index)
columns = ['nox', 'rm', 'chas', 'dis', 'ptratio', 'lstat', 'rad']
X_train = train_df[columns].values
X_test = test_df[columns].values
y_train = train_df[['medv']].values
y_test = test_df[['medv']].values](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-27-320.jpg)

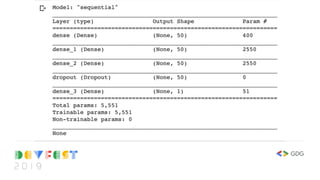
![import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(50, input_shape=(7,), activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dense(50, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dense(50, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
print(model.summary())](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-30-320.jpg)
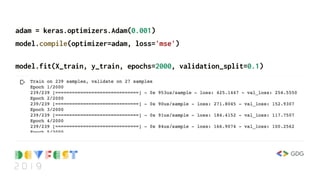

![# we need a new way of getting data into the model
def df_to_dataset(df, columns, shuffle=True, batch_size=64):
df = df.copy()
labels = df.pop('medv')
features_df = df[columns]
ds = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices( (dict(features_df), labels) )
if shuffle:
ds = ds.shuffle(buffer_size=len(df))
ds = ds.batch(batch_size)
return ds](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-34-320.jpg)
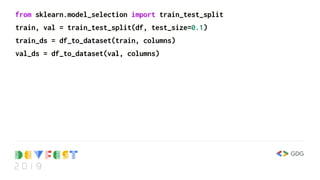
![feature_columns = []
# numeric columns
for _col in columns:
feature_columns.append(tf.feature_column.numeric_column(_col))
# bucketize number of rooms
rm_buckets =
tf.feature_column.bucketized_column(tf.feature_column.numeric_column('rm
'), boundaries=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-36-320.jpg)
![rad_buckets =
tf.feature_column.bucketized_column(tf.feature_column.numeric_column('rad
'), boundaries=[1, 5, 10])
nox_buckets =
tf.feature_column.bucketized_column(tf.feature_column.numeric_column('nox
'), boundaries=[0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9])
feature_columns.append(rm_buckets)
feature_columns.append(rad_buckets)
feature_columns.append(nox_buckets)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-37-320.jpg)
![featuresLayer = keras.layers.DenseFeatures(feature_columns)
model = keras.Sequential([
featuresLayer,
keras.layers.Dense(50, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dense(50, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
keras.layers.Dense(1)
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mse')
model.fit(train_ds, epochs=50, validation_data=val_ds)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devfest2019-lagos-babystepstomlwithtf2-211209213914/85/Baby-Steps-to-Machine-Learning-at-DevFest-Lagos-2019-38-320.jpg)