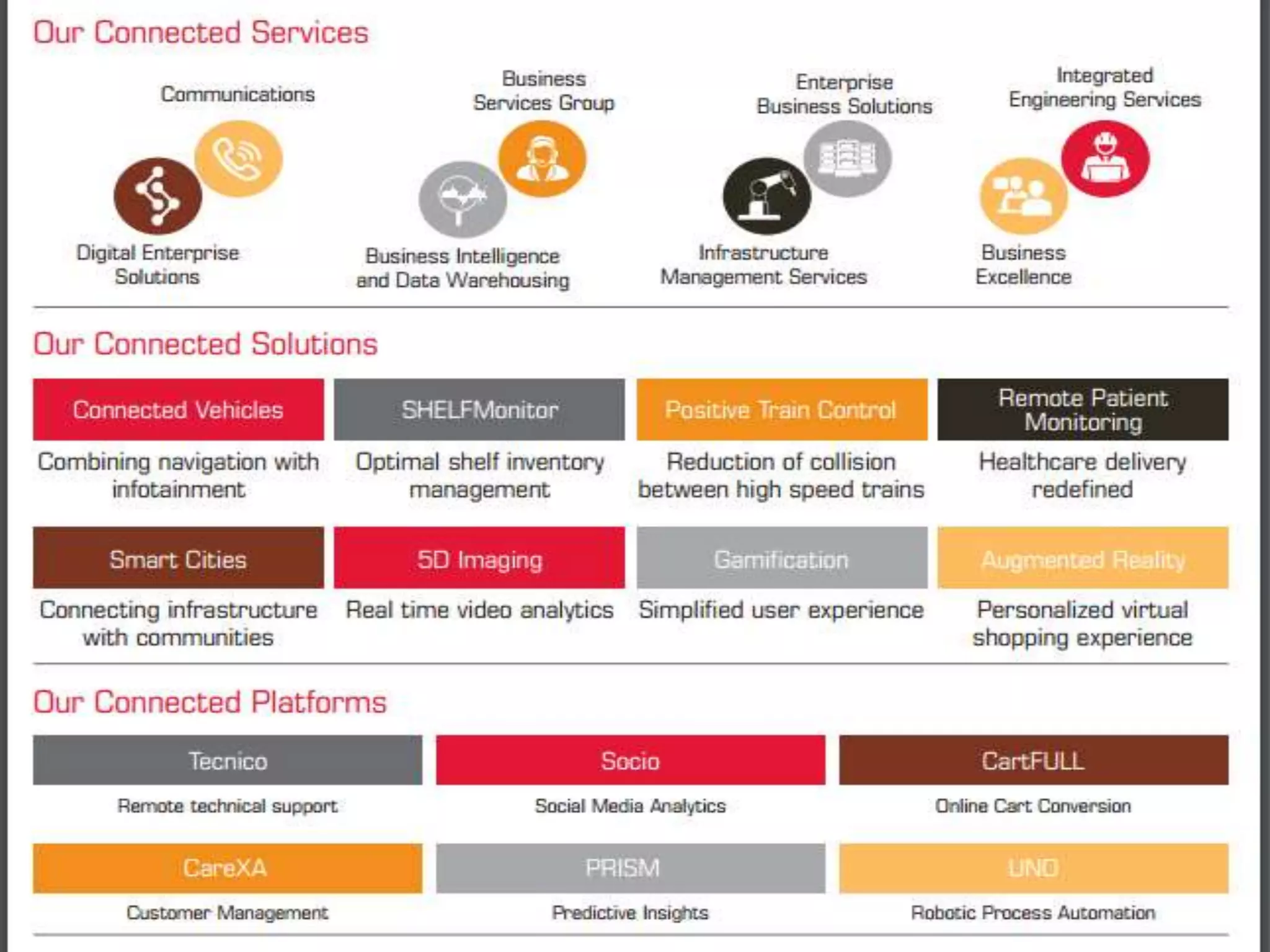
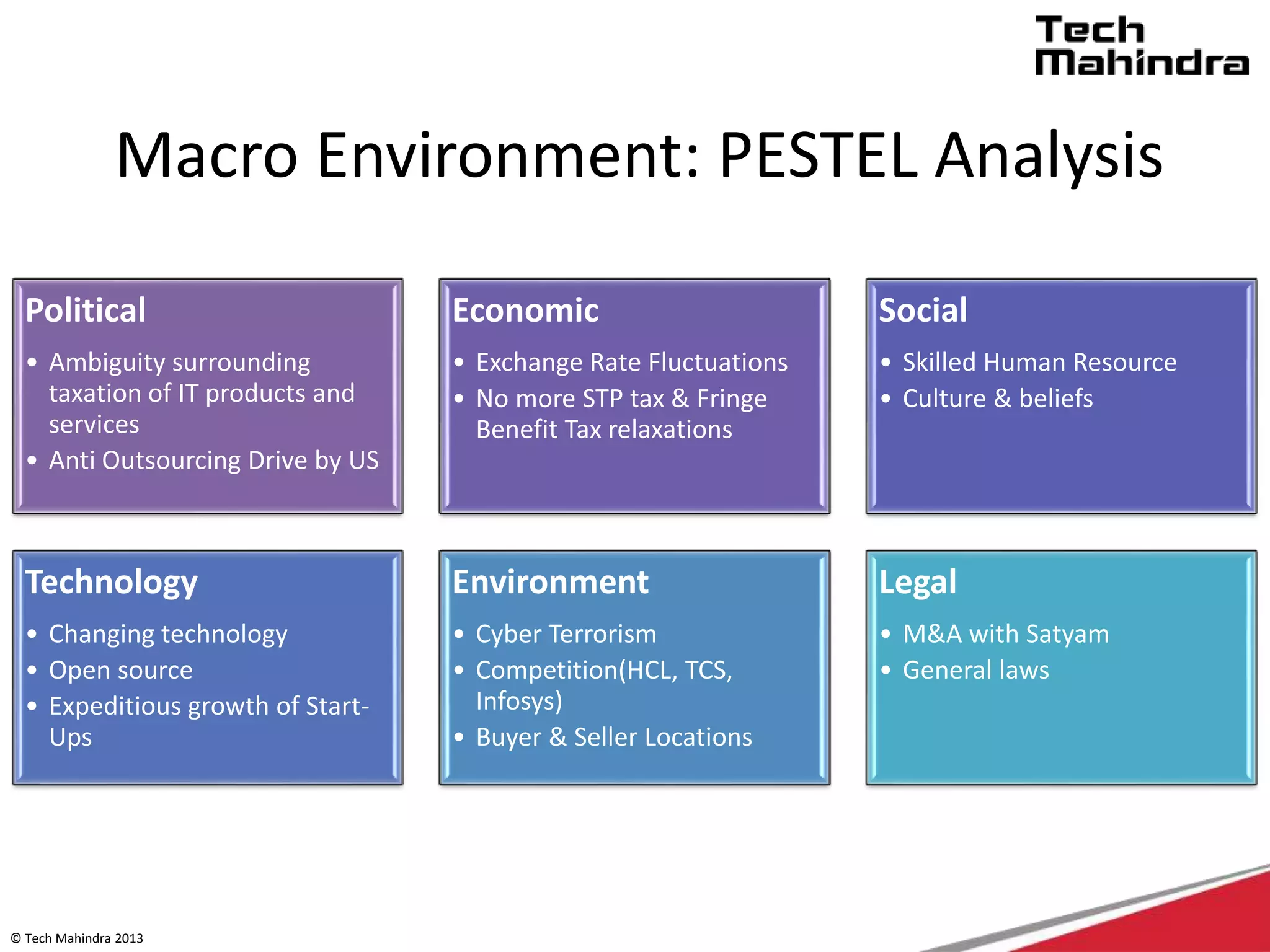
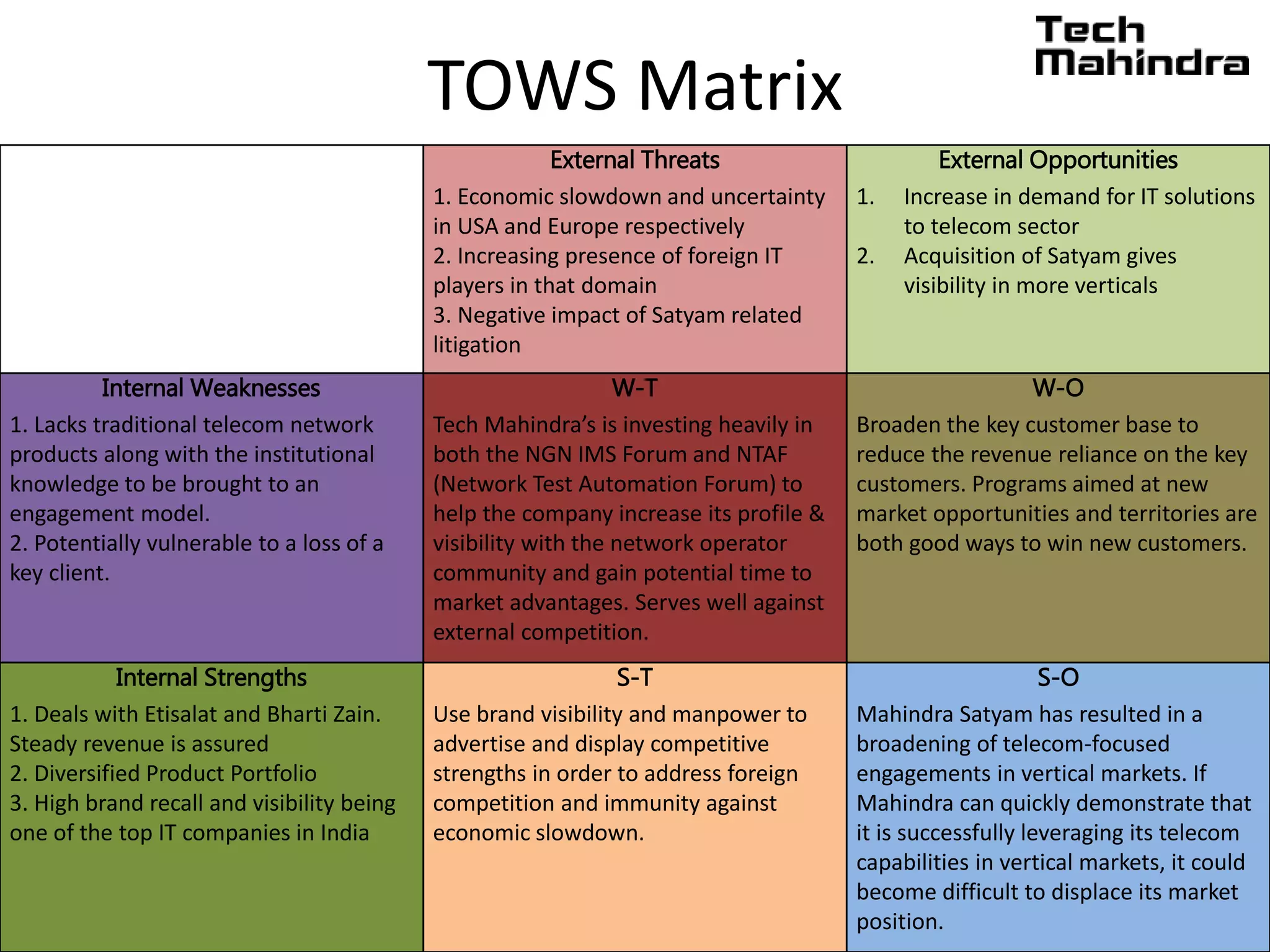
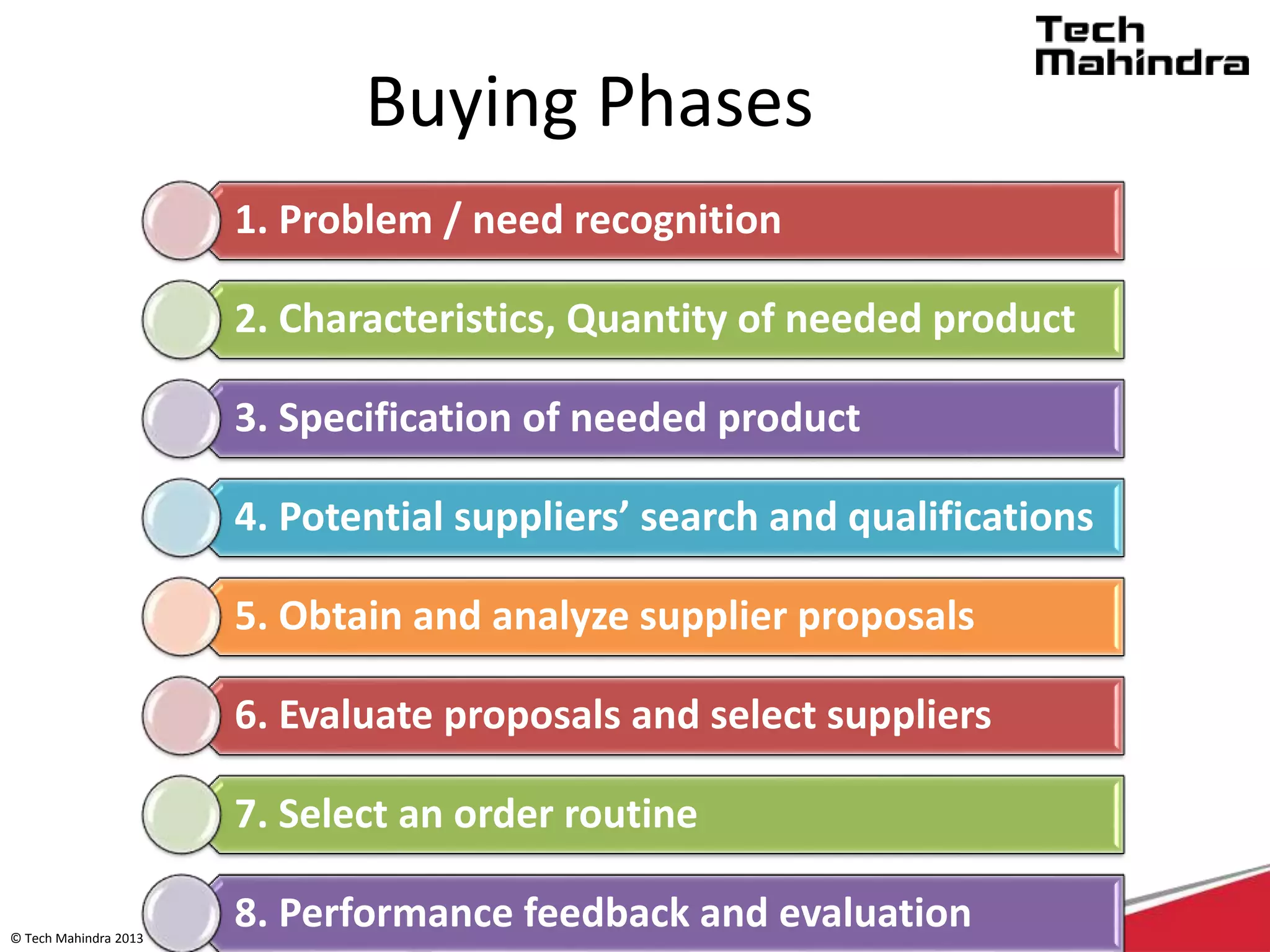
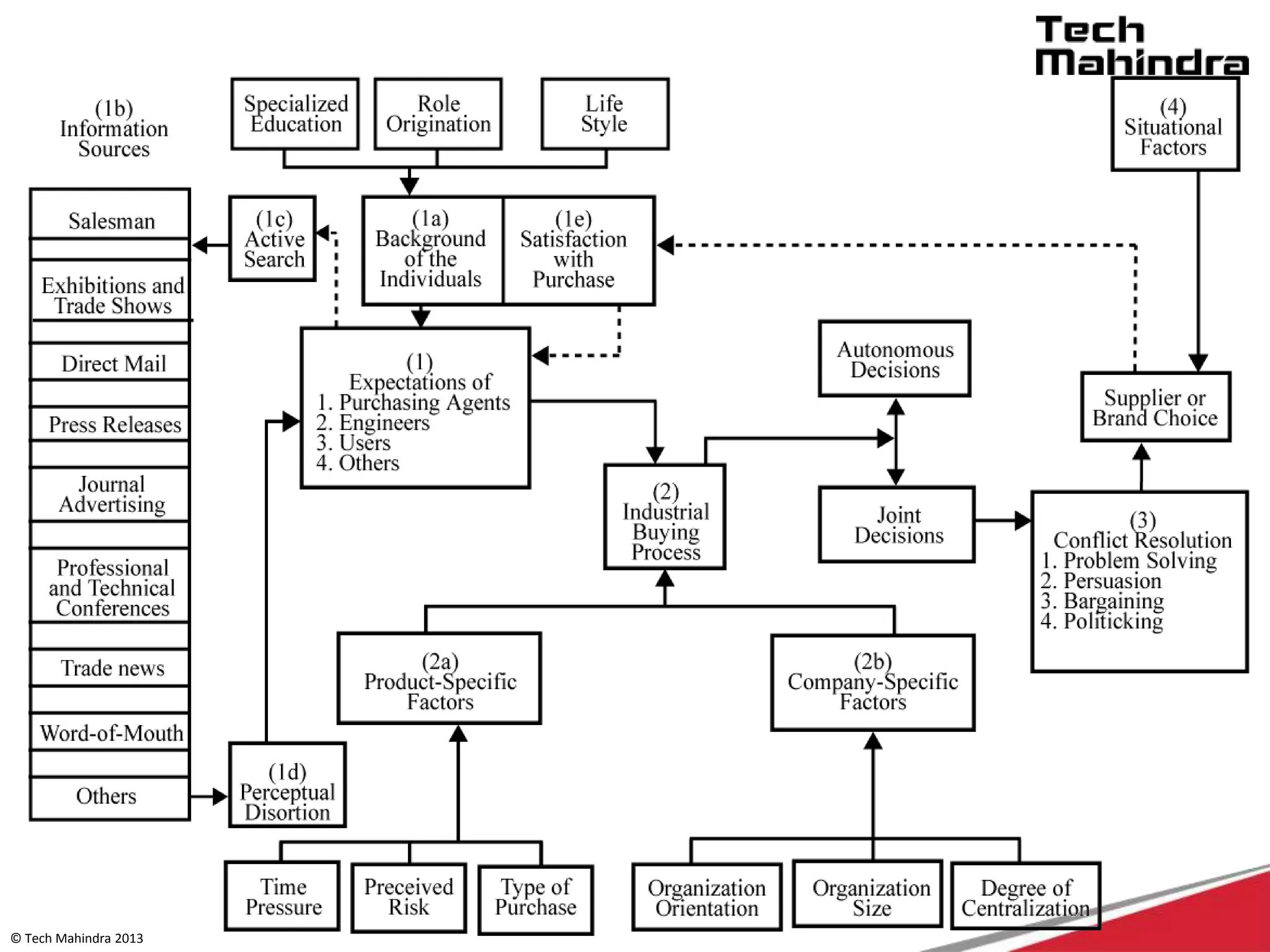
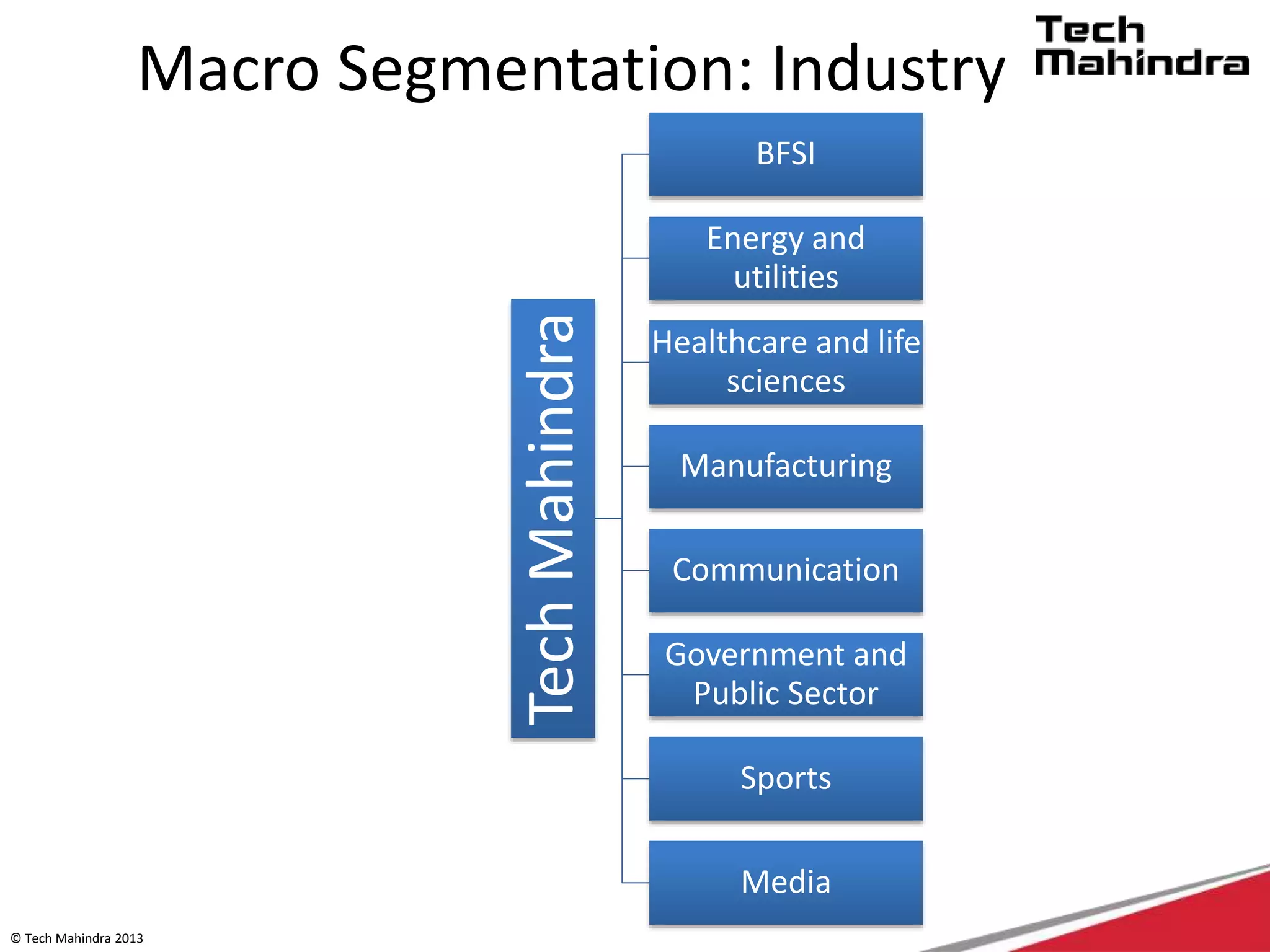
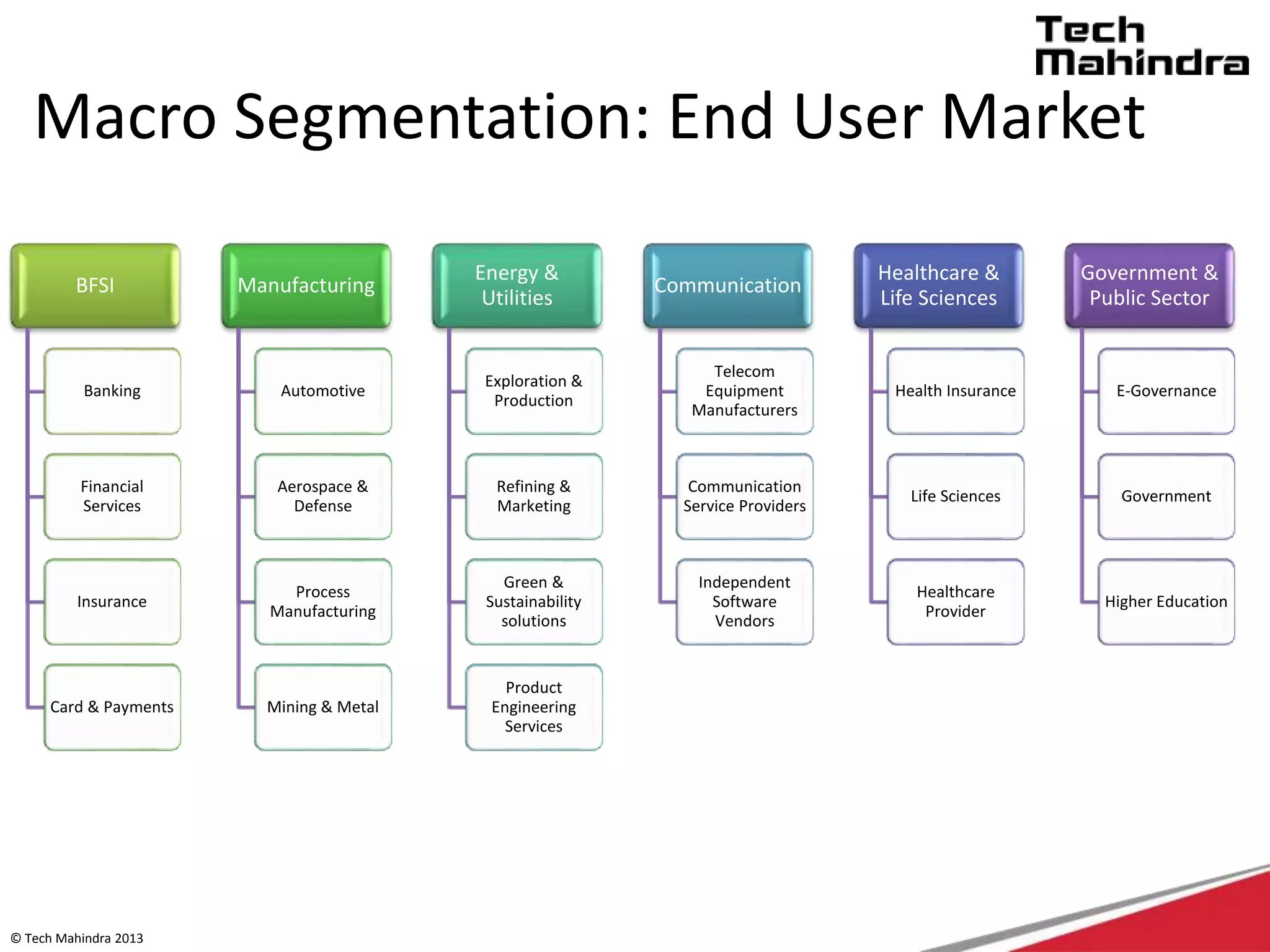
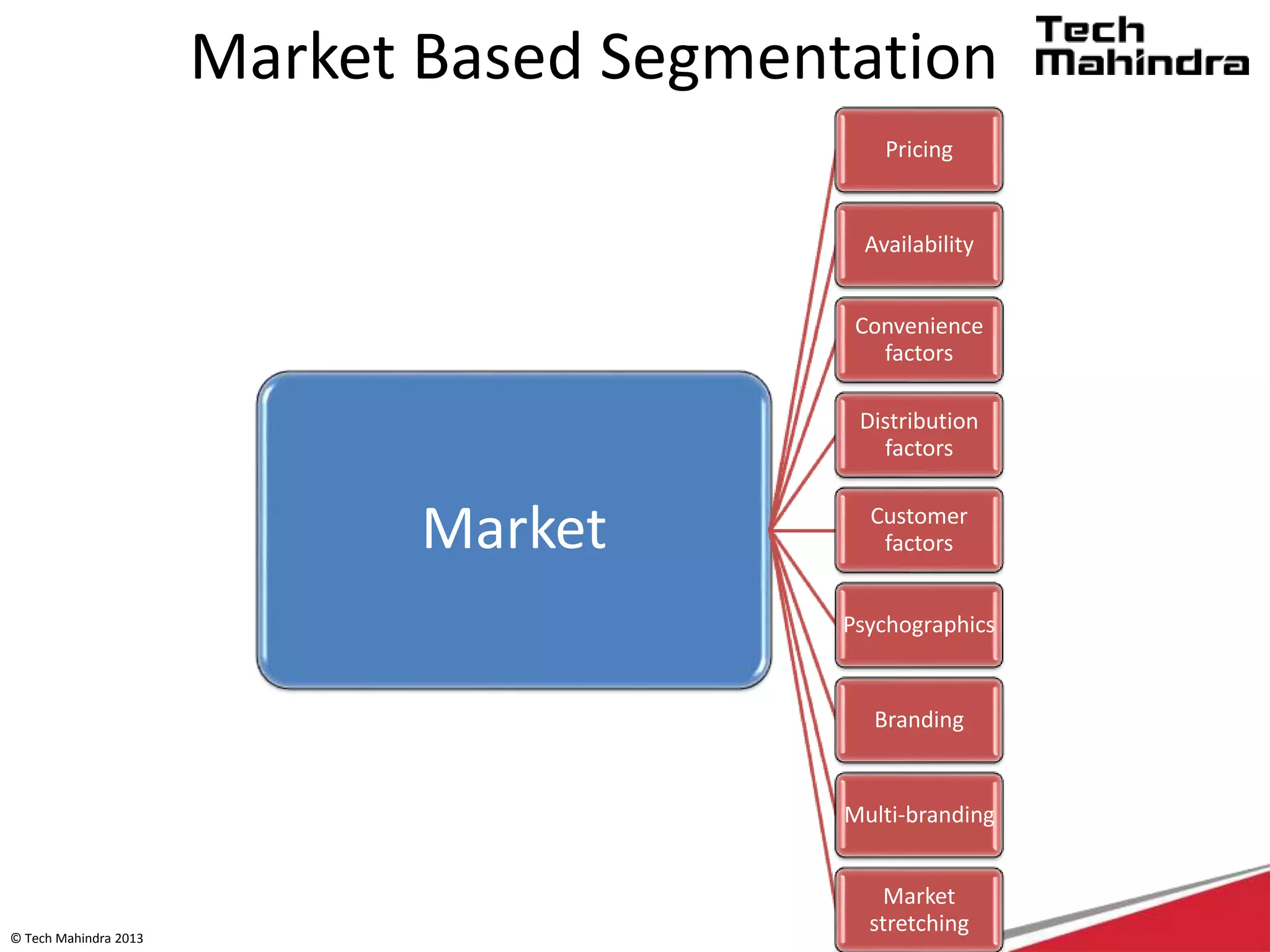
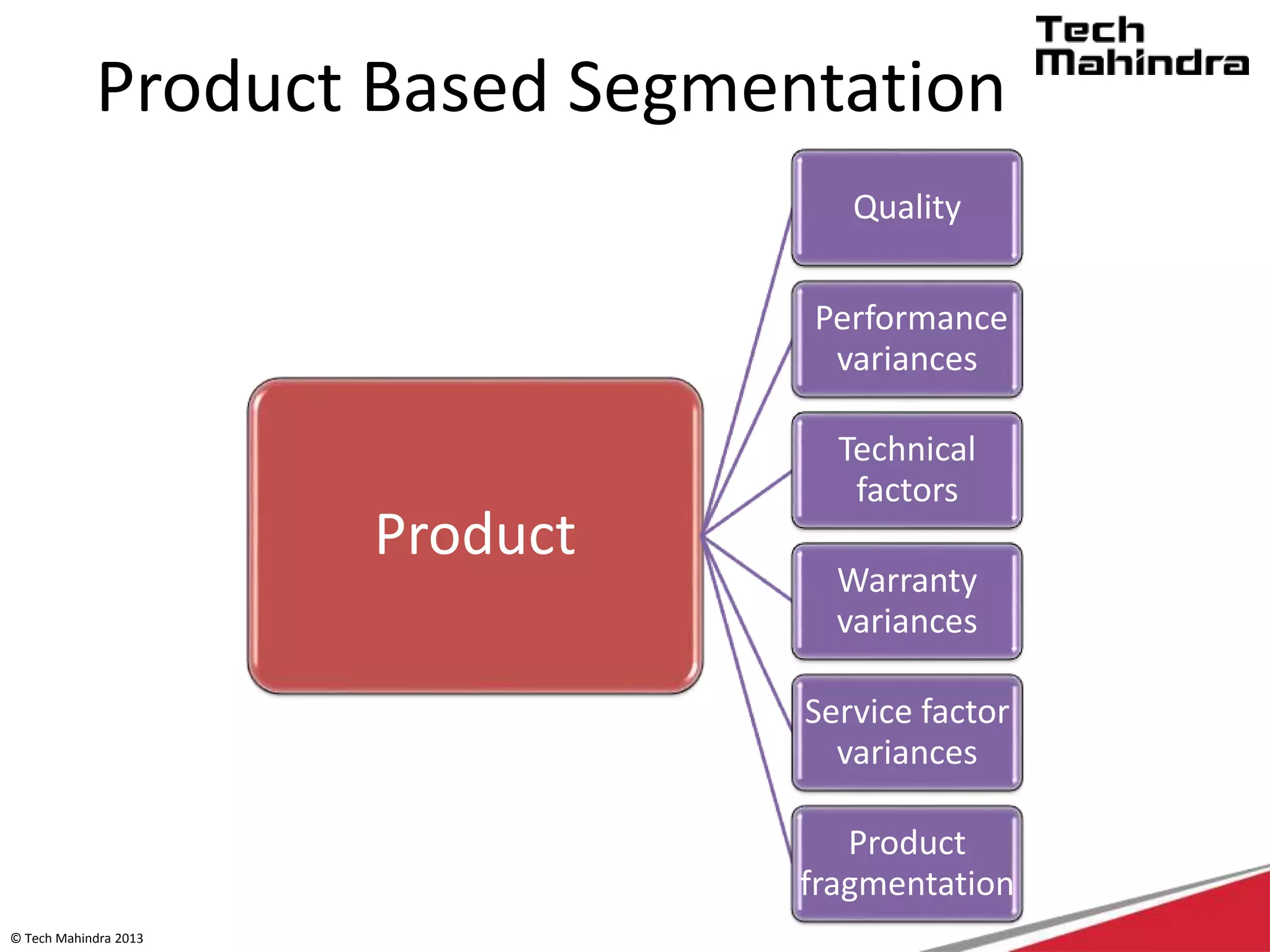
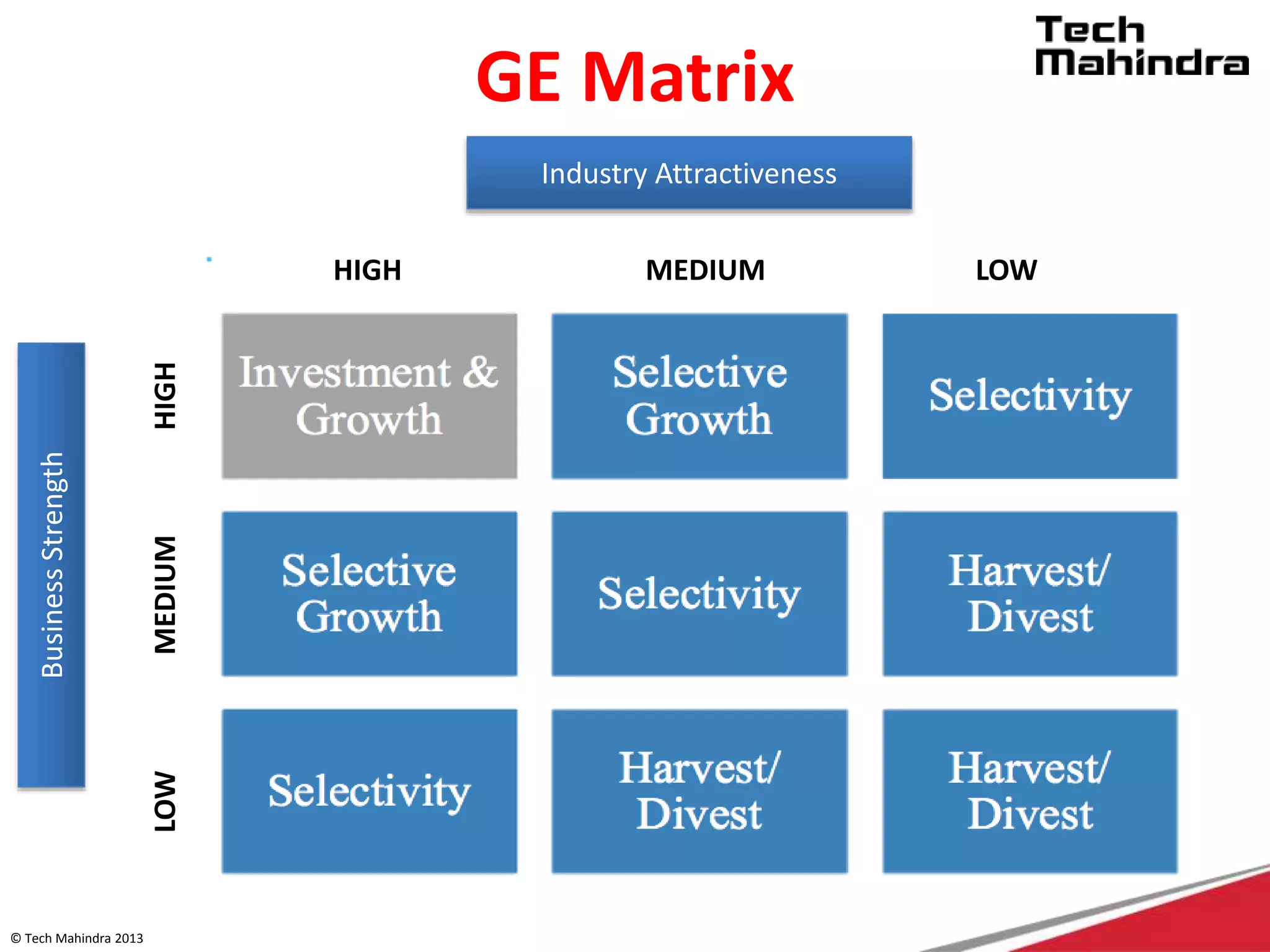
The document discusses Tech Mahindra's business environment and strategies. It analyzes factors in Tech Mahindra's macro environment like political, economic, social, technological, environmental and legal factors. It also discusses the company's customers and vendors. Further, it outlines Tech Mahindra's segmentation, targeting and positioning approach involving segmentation based on industry, end users, products and other variables. Finally, it discusses the company's diversification strategies and some examples of new initiatives.