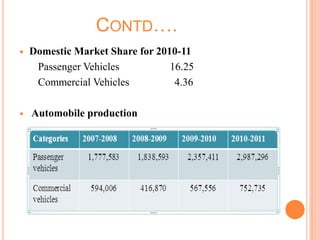
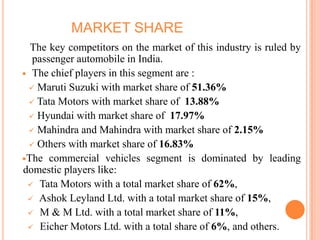
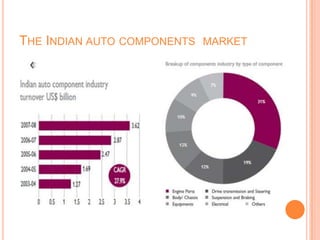
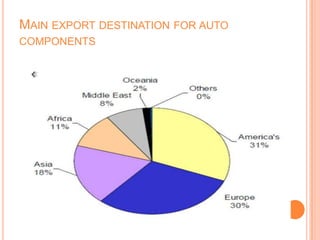
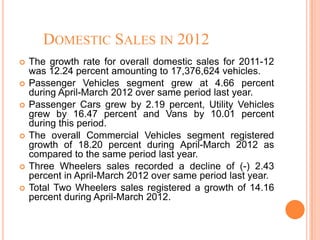
The document provides an overview of the Indian automobile industry. It discusses key topics such as production and market share, growth drivers, domestic production and exports in 2012, SWOT analysis, and future projections. The automobile industry is an important sector in India, manufacturing over 11 million vehicles annually. Major players like Maruti Suzuki and Tata Motors dominate different vehicle segments. Factors like rising incomes, financing availability, and government policies are driving growth in the industry.