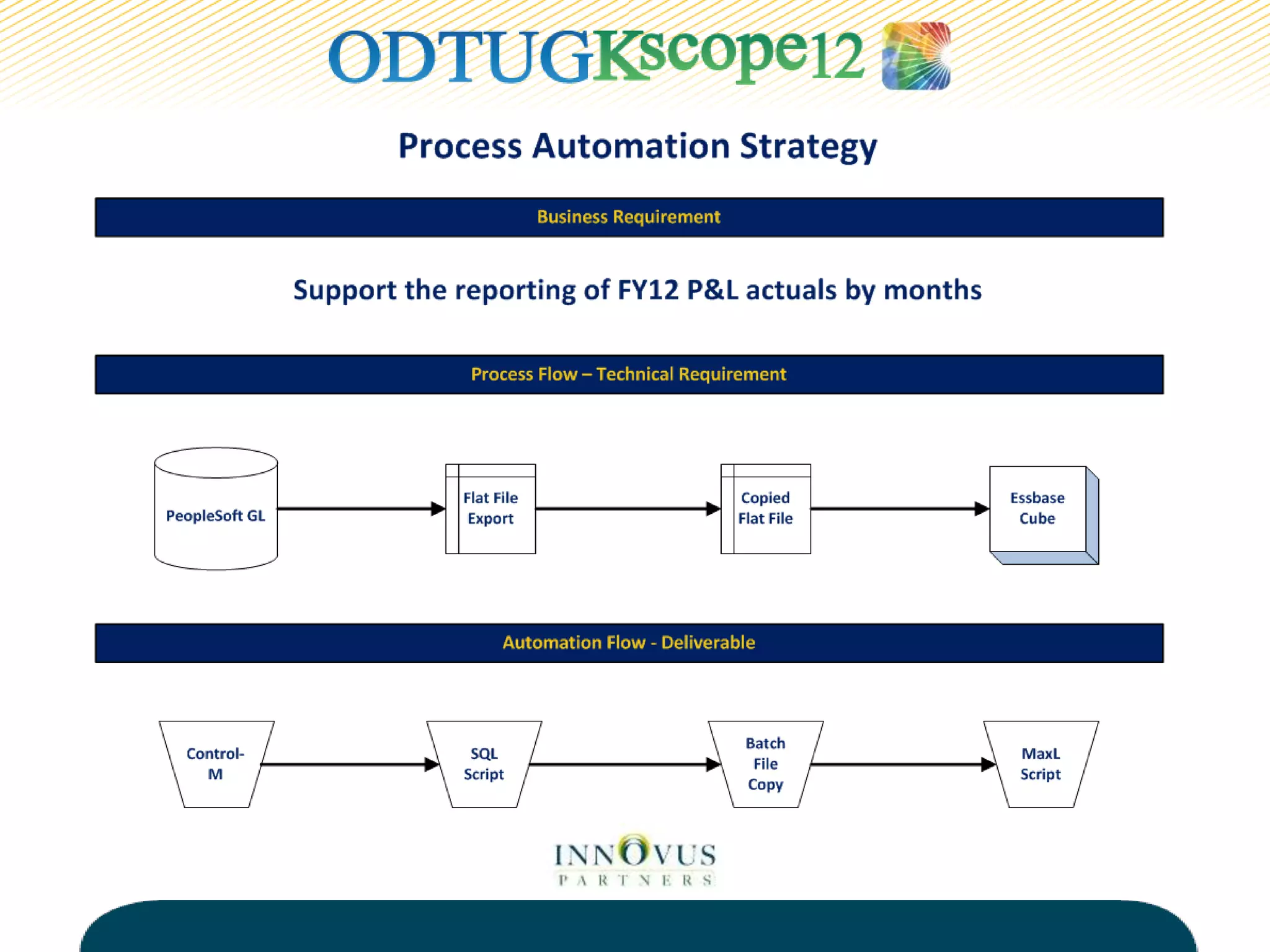
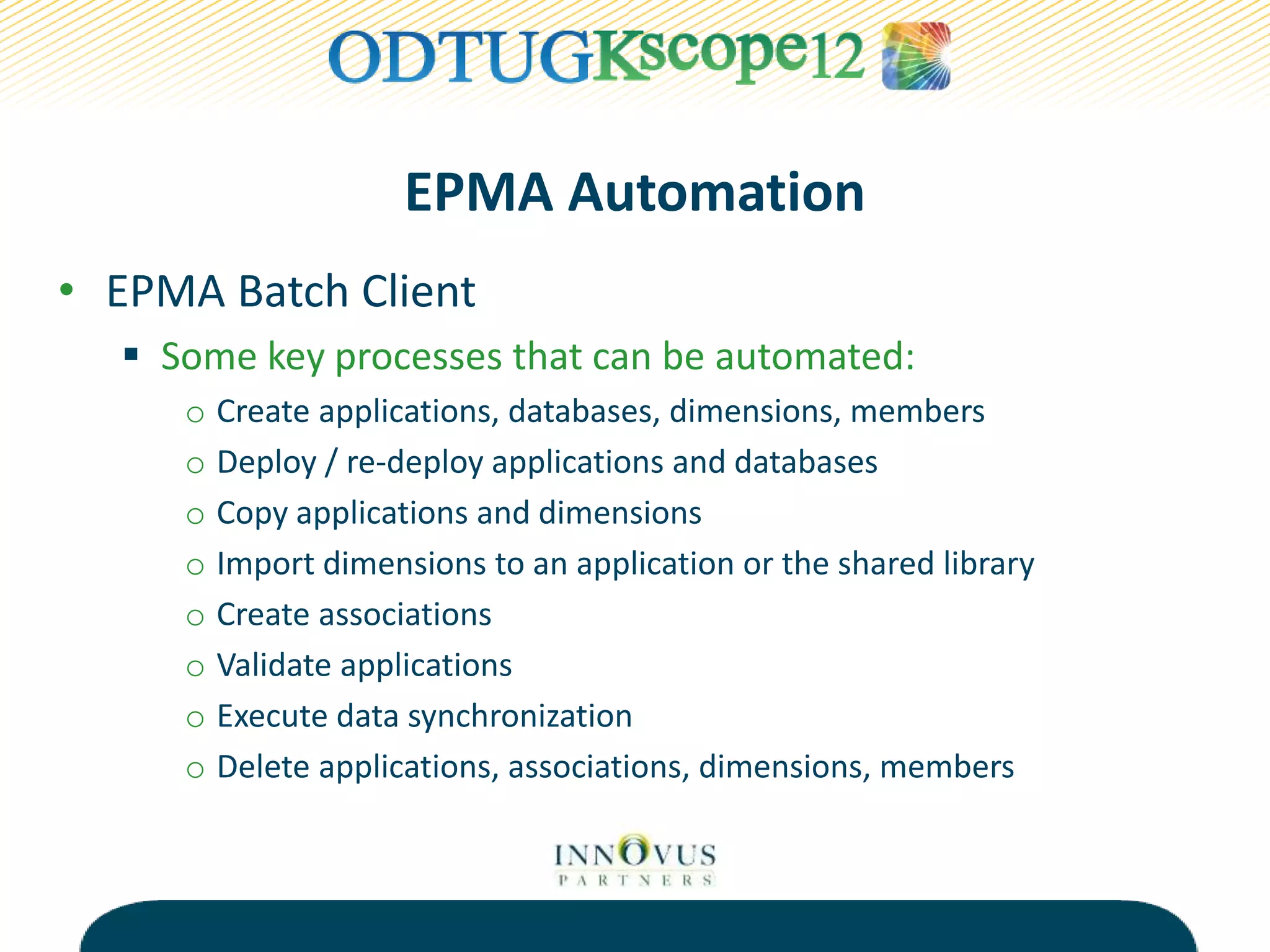
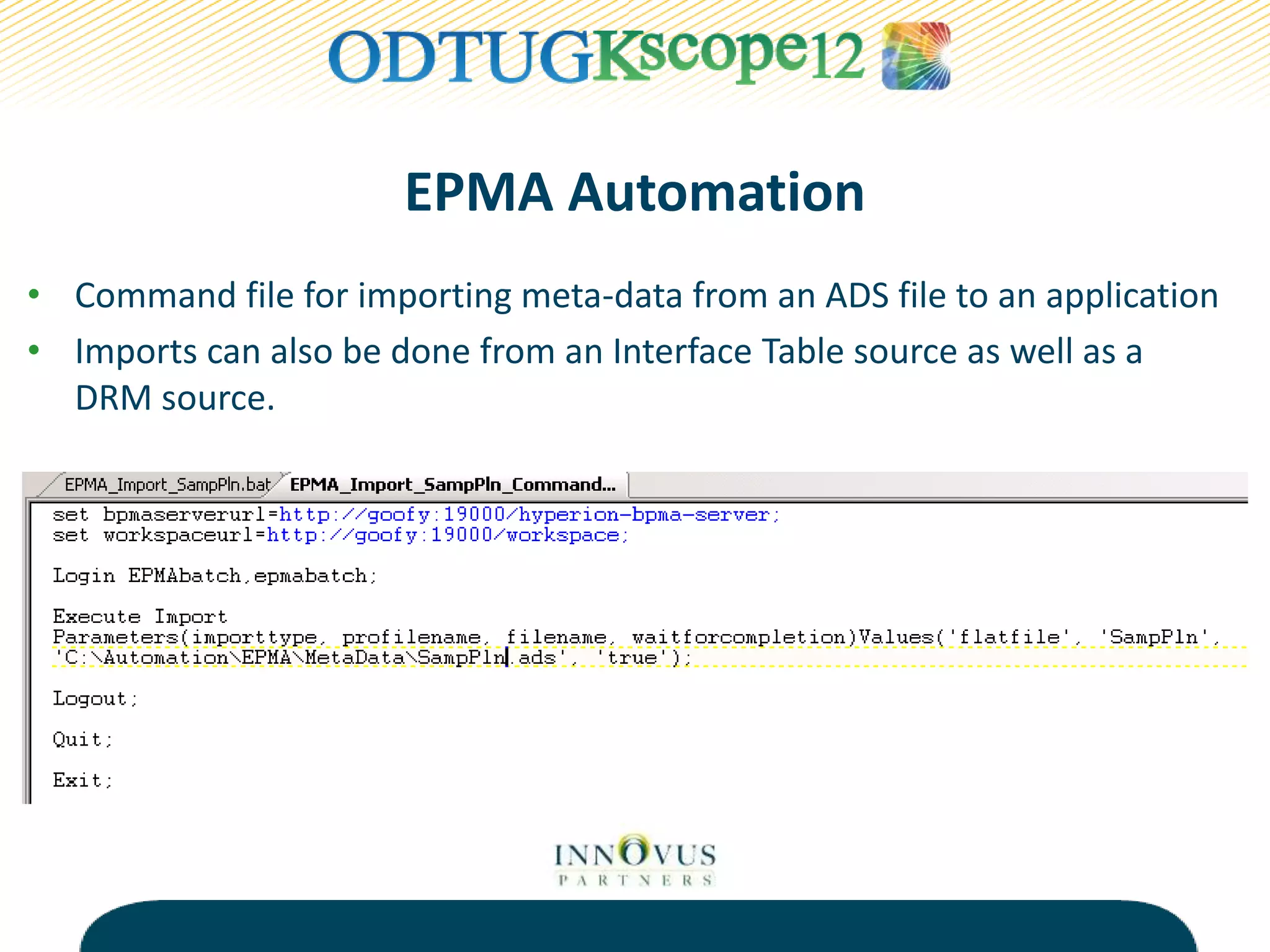
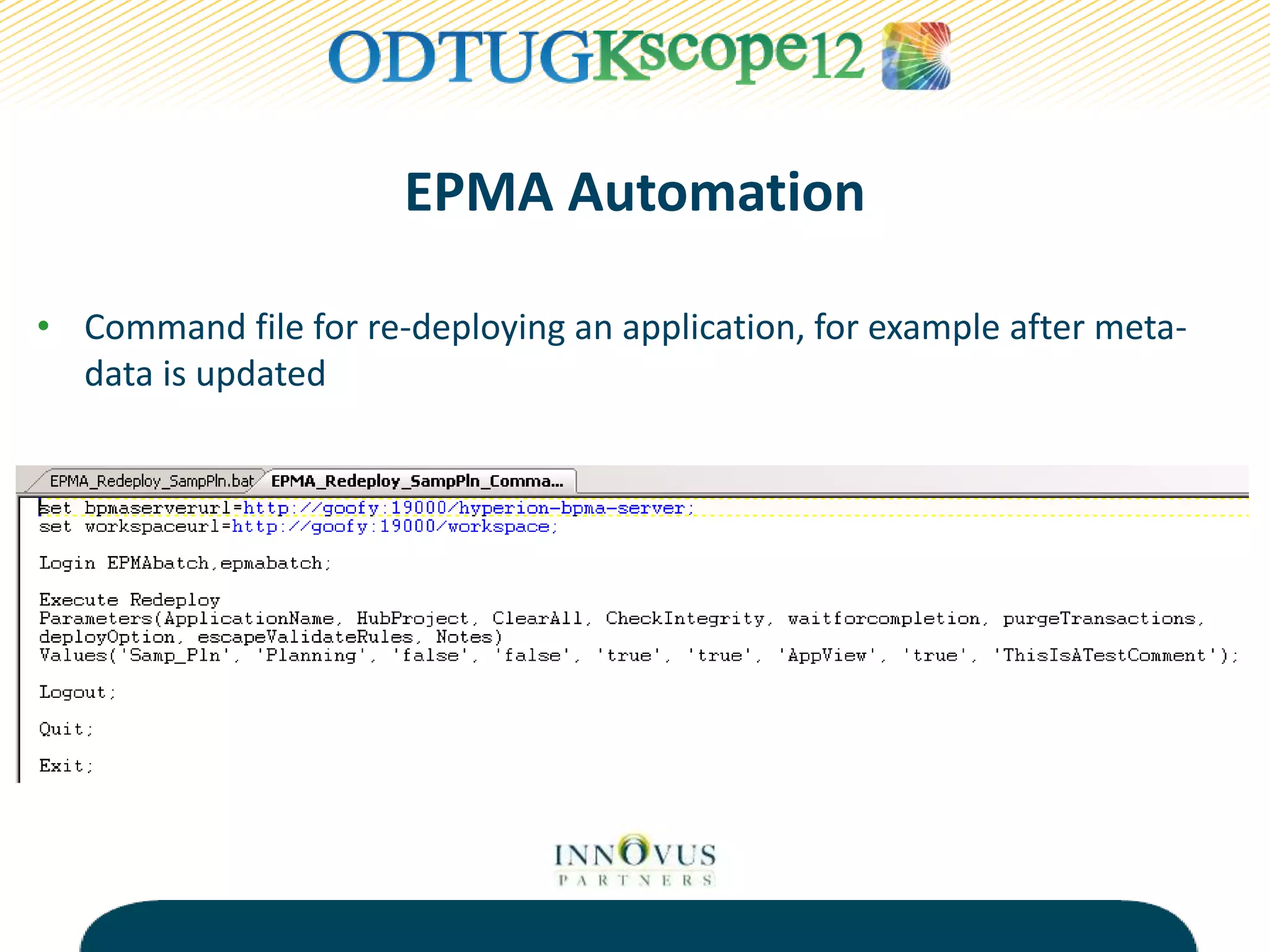
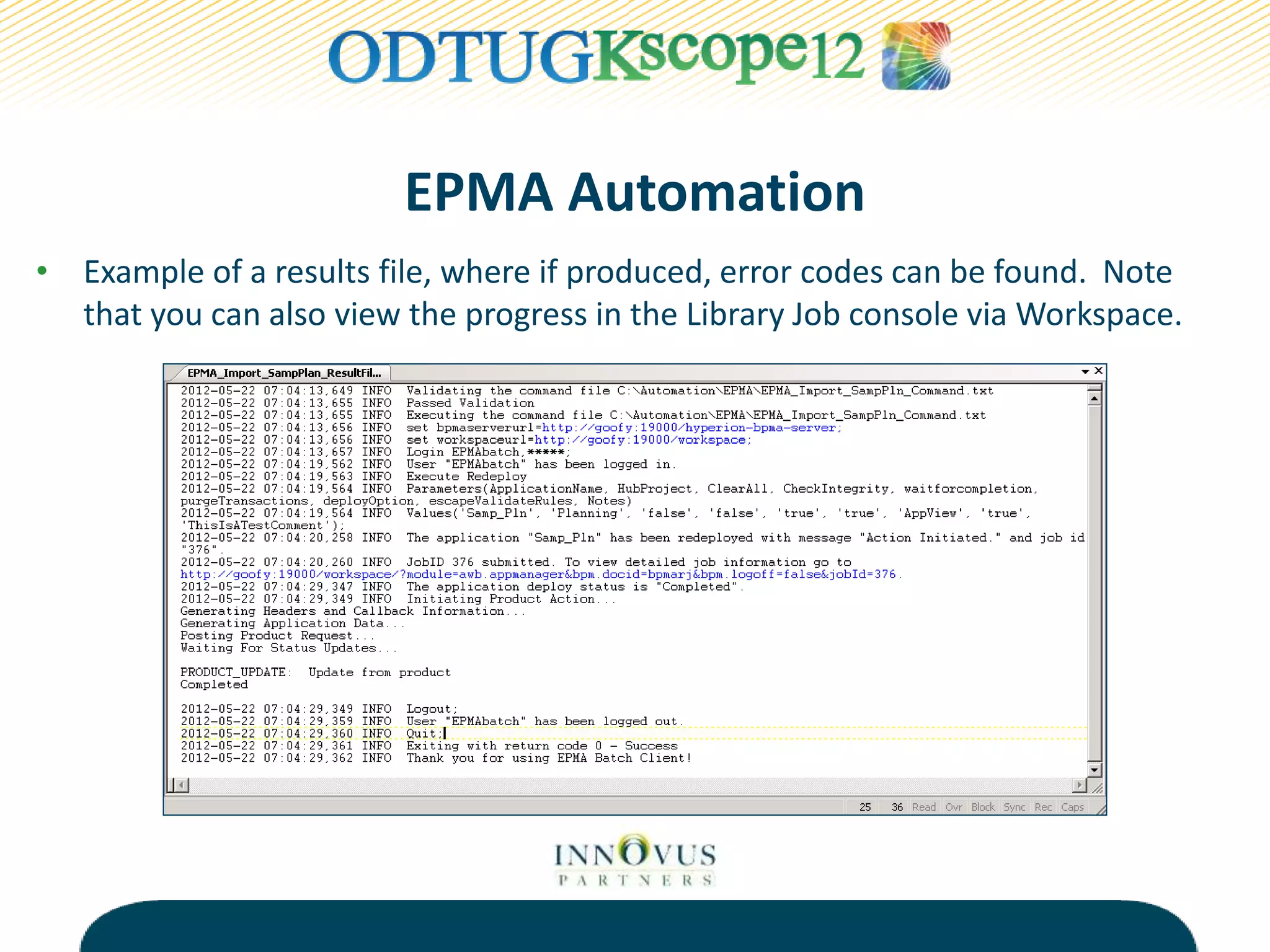
The presentation discusses various tools and methods for automating processes in Oracle Hyperion Enterprise Performance Management (EPMA), including the EPMA Batch Client for automating tasks like application deployment and data loading, the Life Cycle Management utility for migrating and backing up EPM artifacts, and MaxL scripts for exporting outlines and performing calculations in Essbase. The goal of process automation is to streamline processes, add reliability, and free up resources by eliminating manual tasks. Examples are provided of how various organizations have benefited from implementing process automation.