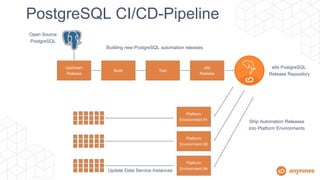
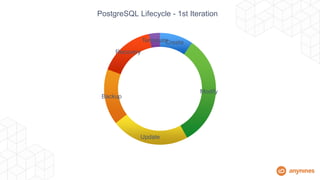
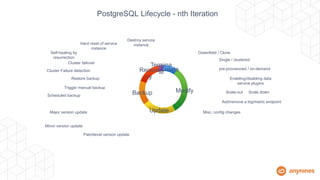
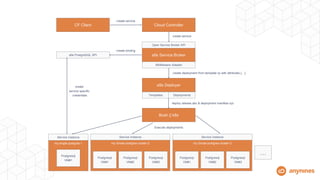
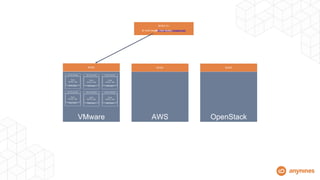
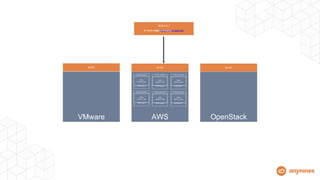
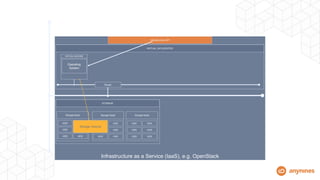
This document discusses automating the lifecycle of PostgreSQL databases. It recommends using BOSH to automate provisioning, configuration, backups, upgrades, and other lifecycle tasks across infrastructure. Key points covered include:
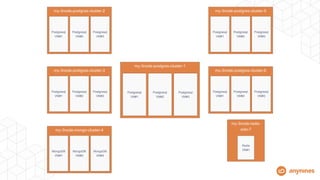
- BOSH allows automating the PostgreSQL lifecycle in a repeatable, scalable way across platforms.
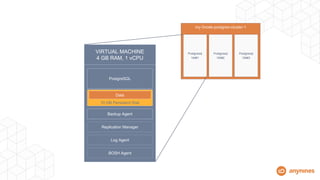
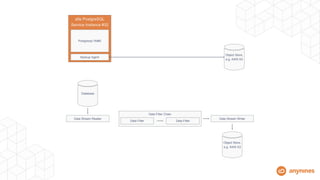
- It provisions VMs with persistent disks to decouple data from VM lifecycles.
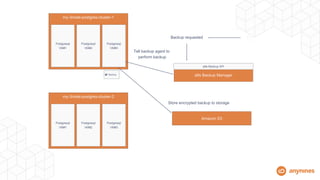
- Automation handles high availability clustering, failover, backups to object storage, and vertical/horizontal scaling.
- The approach makes dedicated PostgreSQL instances on-demand and automates their full lifecycles.