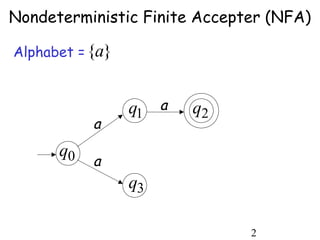
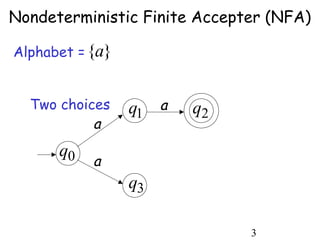
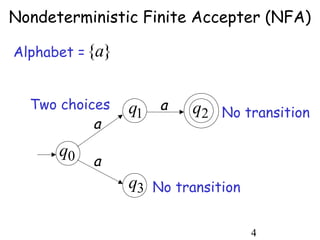
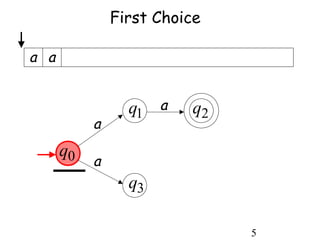
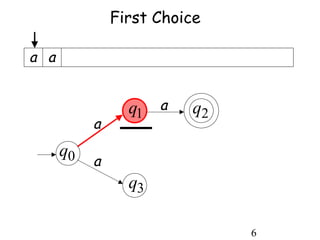
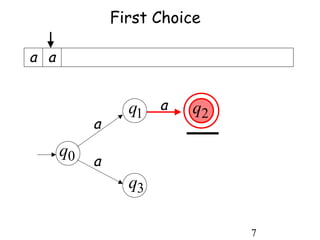
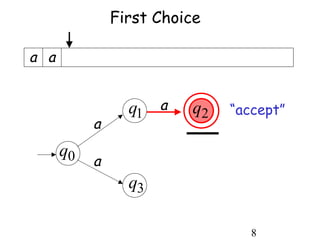
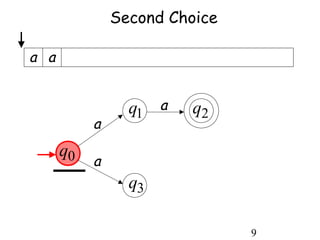
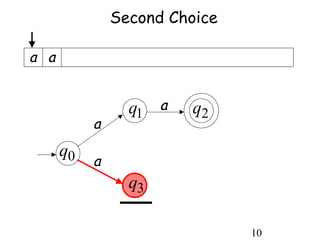
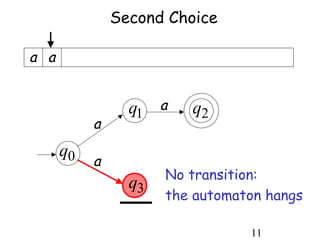
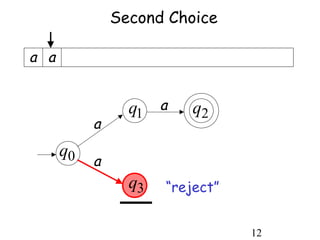
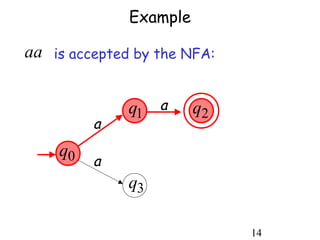
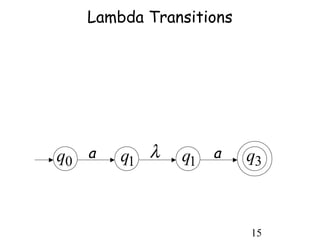
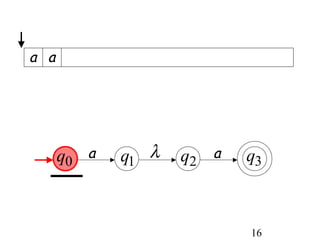
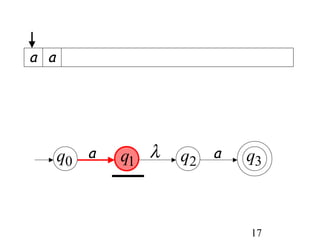
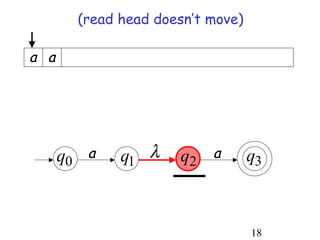
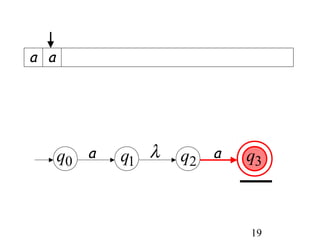
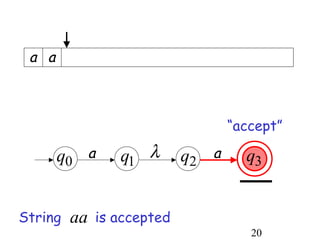
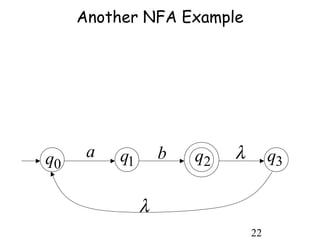
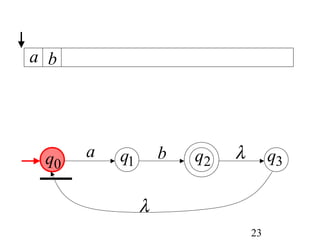
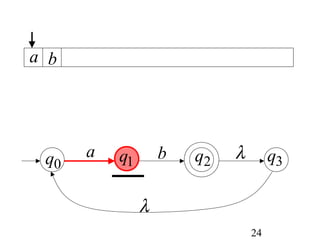
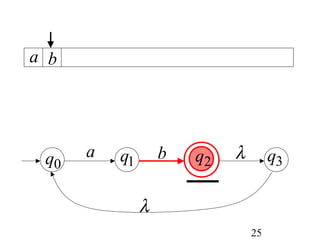
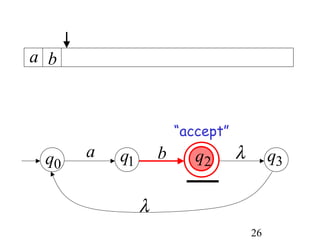
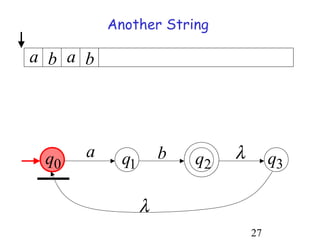
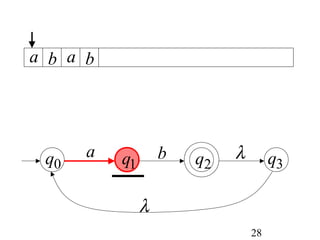
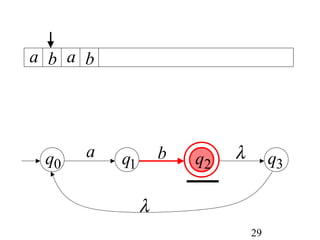
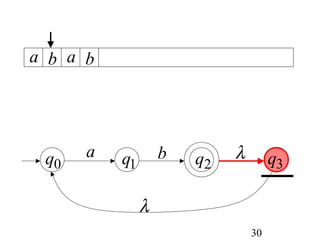
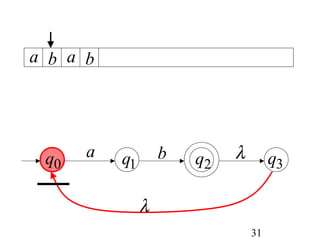
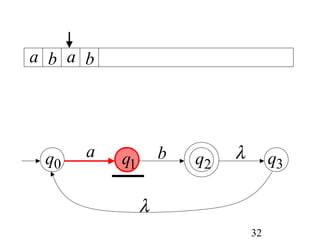
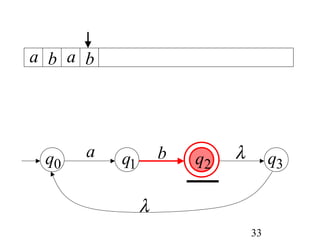
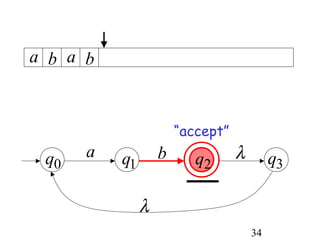
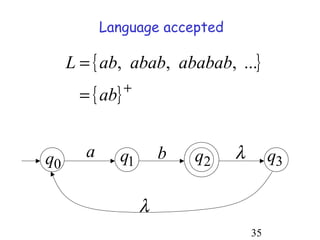
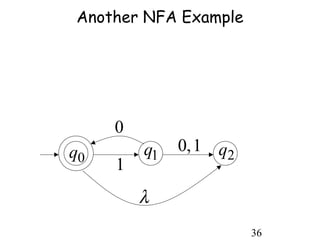
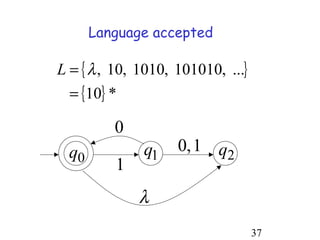
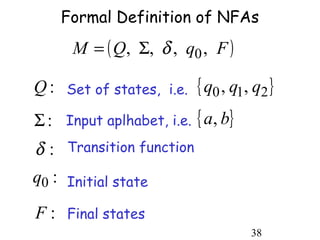
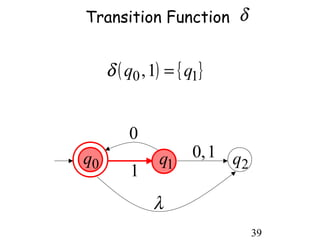
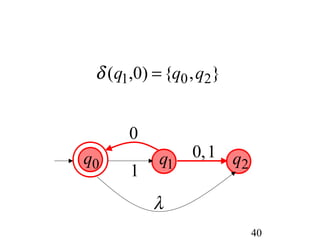
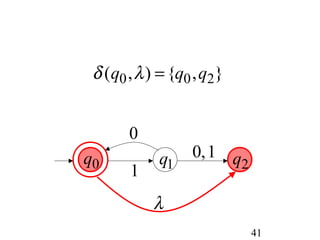
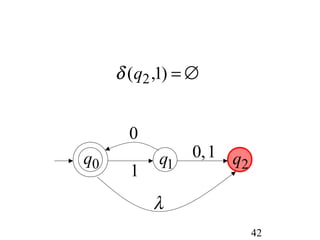
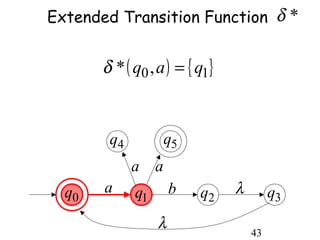
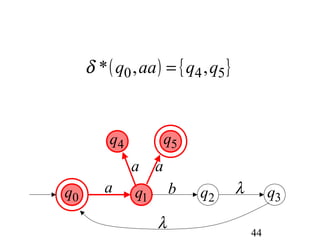
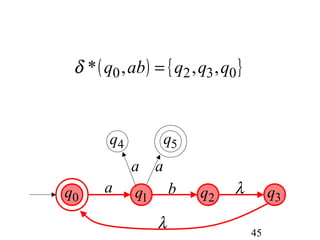
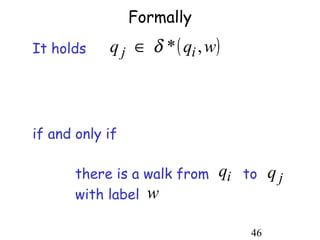
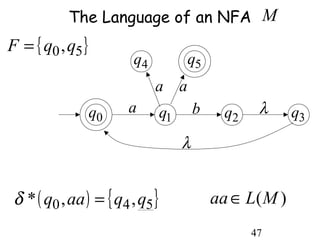
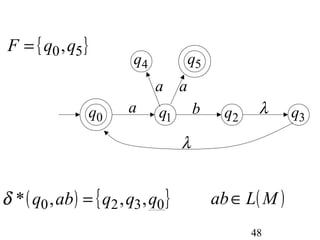
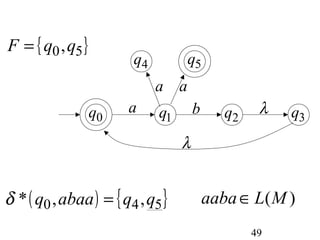
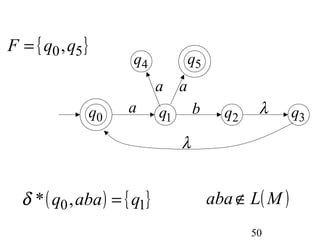
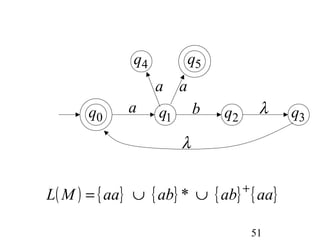
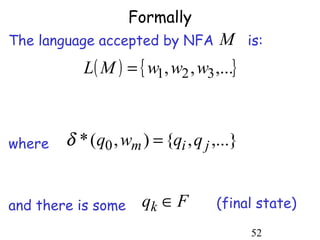
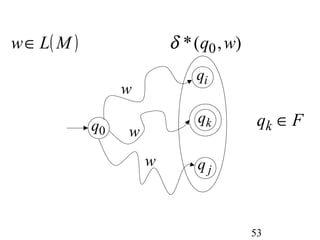
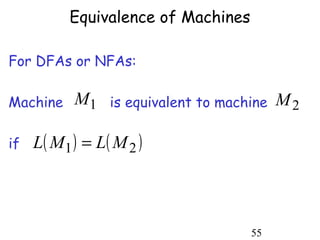
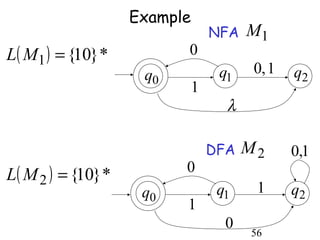
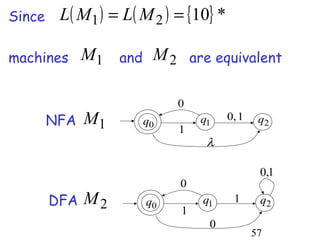
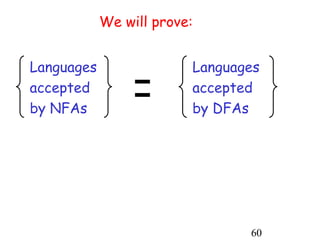
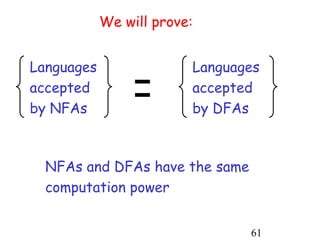
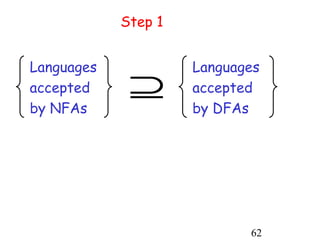
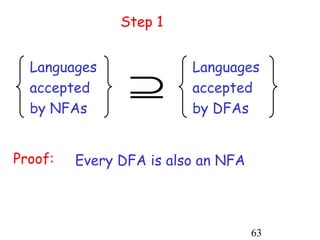
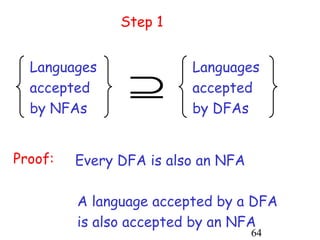
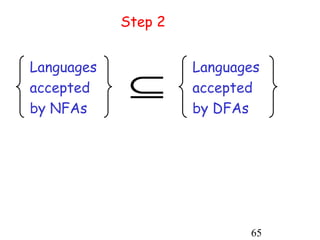
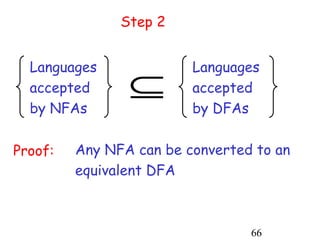
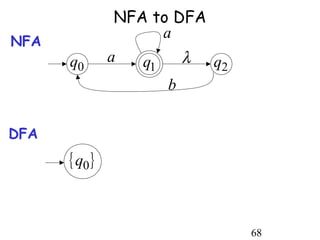
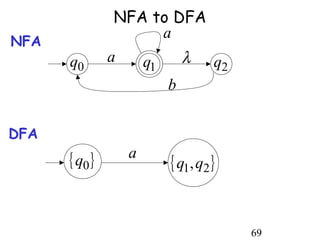
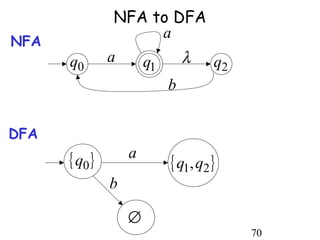
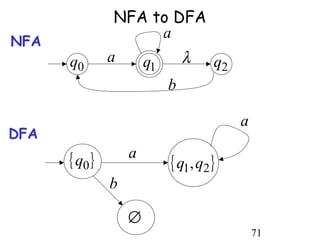
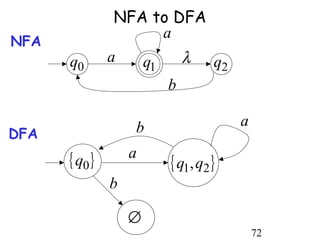
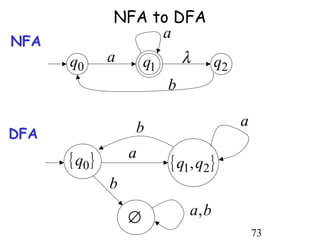
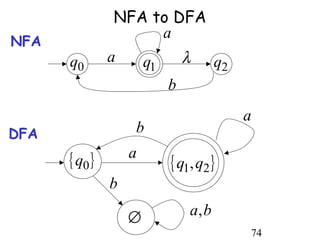
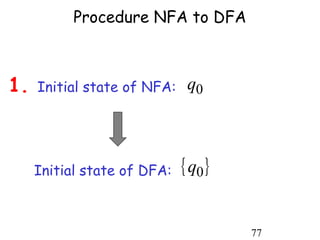
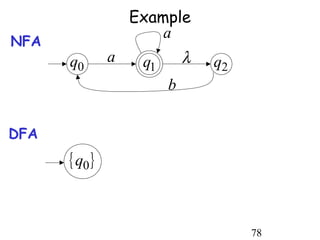
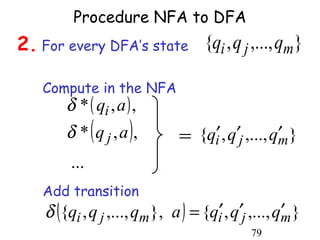
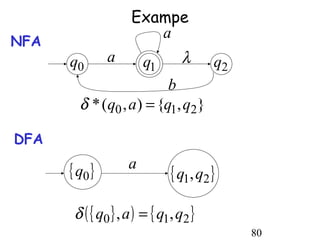
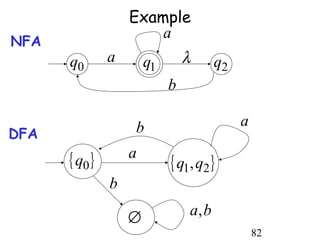
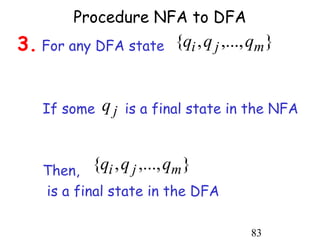
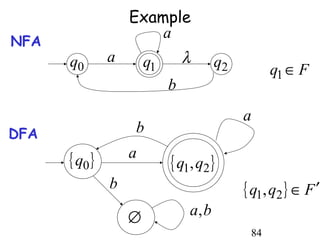
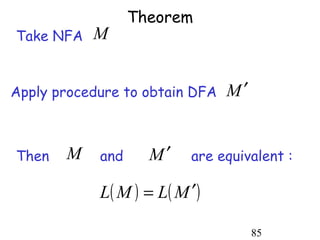
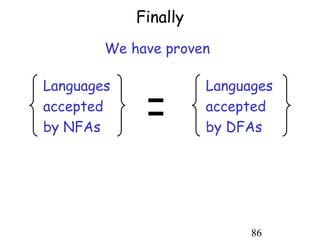
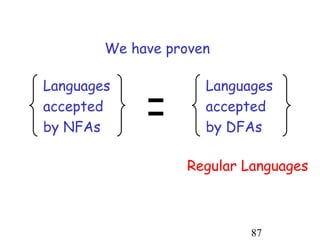
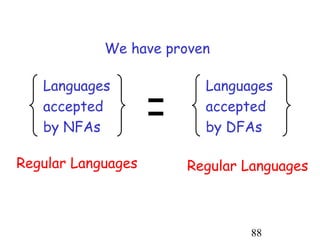
This document describes non-deterministic finite automata (NFAs). It begins by presenting examples of NFAs with different transition diagrams and explanations. It then provides a formal definition of NFAs, including their components like states, alphabet, transition function, initial state, and final states. The document explains how the transition function works and how to determine the language accepted by an NFA using the extended transition function. It proves that NFAs and deterministic finite automata (DFAs) are equivalent by showing that the languages accepted by each are equal subsets of each other. Finally, it demonstrates how to convert an NFA to an equivalent DFA by constructing the DFA states as power sets of the NFA states and defining