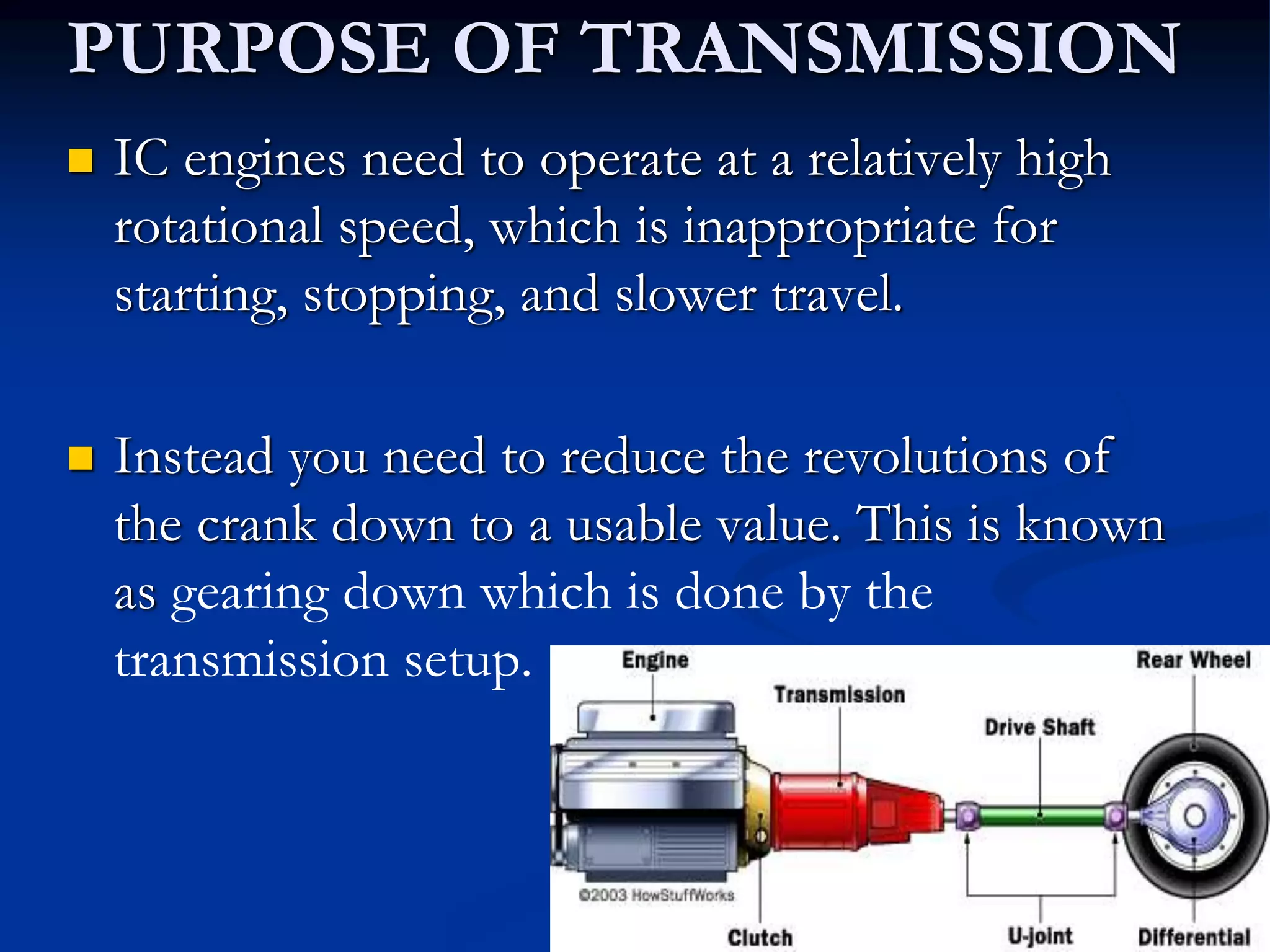
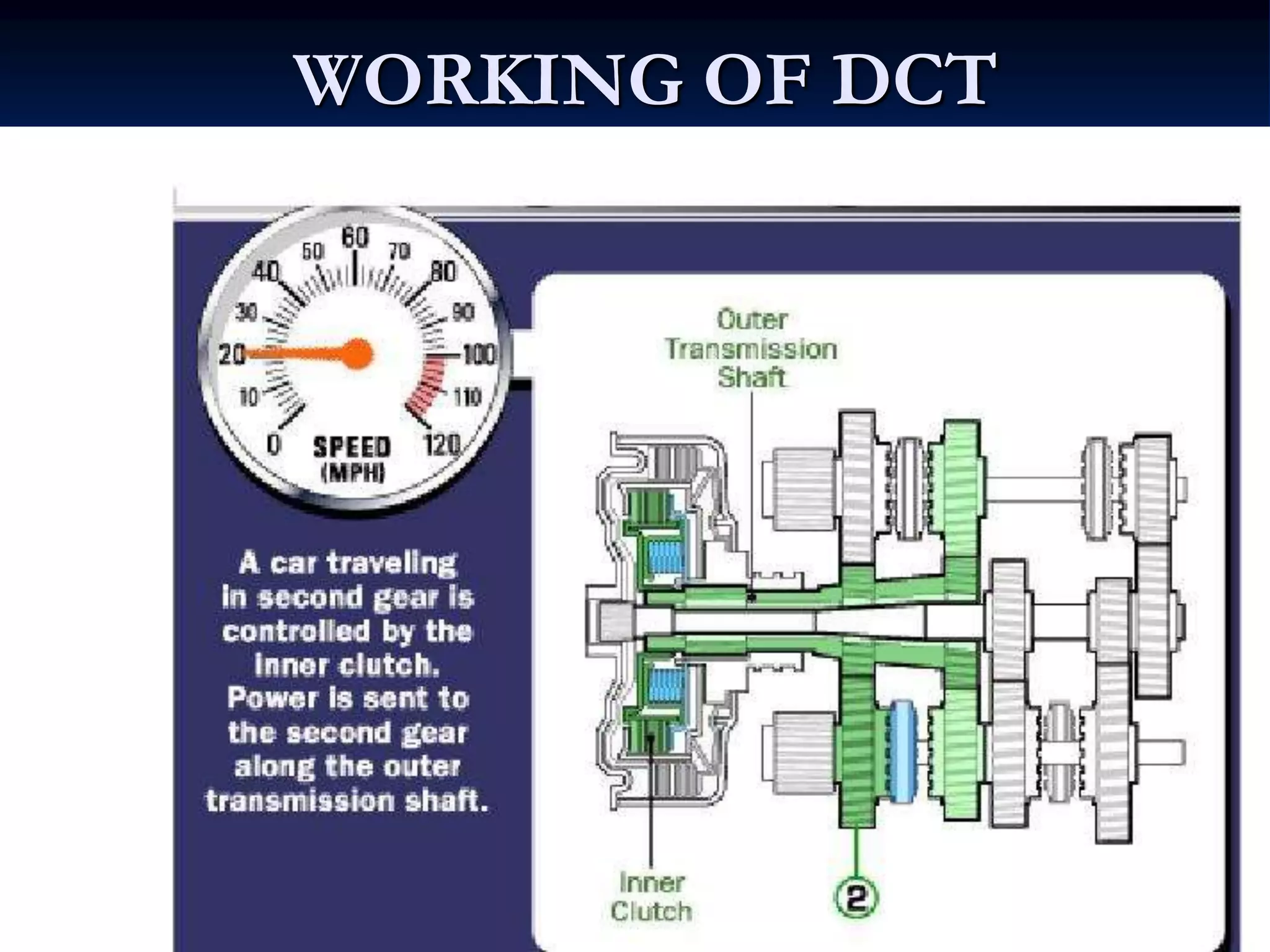
Dual clutch transmissions contain two separate manual gearboxes and clutches contained within one housing. This allows one clutch to control the odd gears while the other controls the even gears, enabling fast and smooth gear changes without any loss of power during shifts. DCTs provide better fuel economy, faster shift times, and smoother gear changes compared to single clutch transmissions. However, they are more expensive to manufacture and require specialized maintenance. DCTs are increasingly being used in high-performance cars and some public transport vehicles.