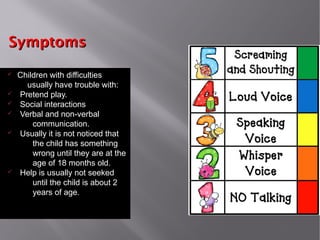
This document discusses autism, including what it is, early signs, how it affects children, related disorders, symptoms, social interaction difficulties, behaviors, signs and tests, treatments including medicine, therapy, and diet considerations. Autism is a developmental disorder appearing in the first 3 years that affects social and communication skills development in the brain. Early signs can include lack of speech, repetitive body movements, impaired social skills, and lack of eye contact. Boys are affected more than girls. Treatments aim to help with specific needs and may include applied behavior analysis therapy, medications, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. Diet changes removing gluten have shown benefits for some children with autism as well.