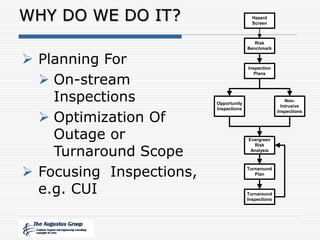
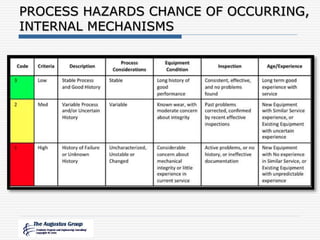
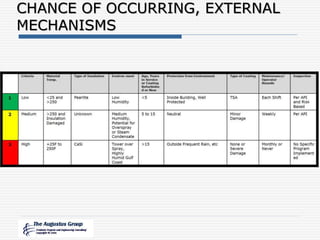
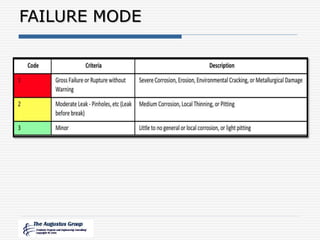
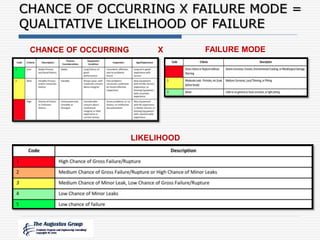
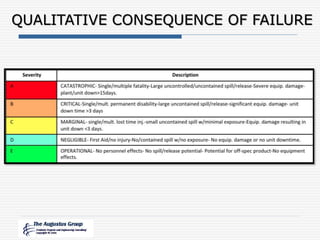
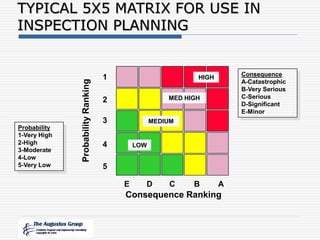
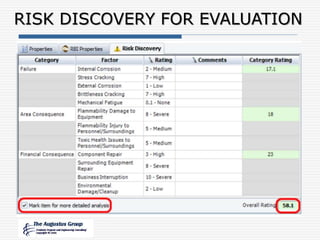
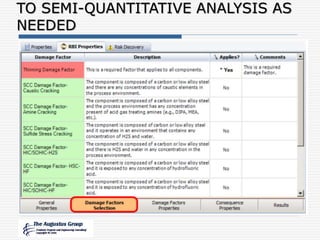
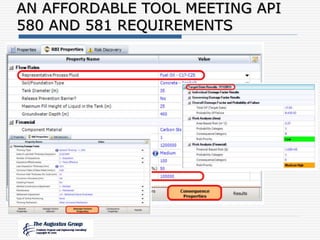
This document provides an overview of a webinar/seminar series on managing corrosion under insulation presented by The Augustus Group. The Augustus Group is an engineering consulting firm focused on materials technology, asset integrity problem solving, and risk management for refining, chemicals, and aerospace industries. The webinar will discuss causes of corrosion under insulation, methods for detection and prevention, and risk-based approaches to inspection and management of corrosion under insulation.