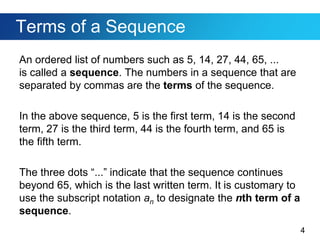
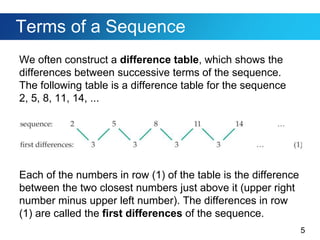
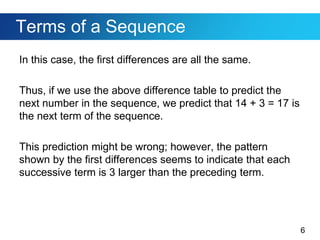
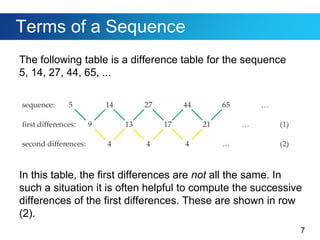
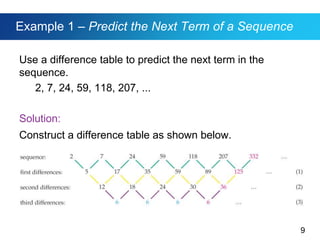
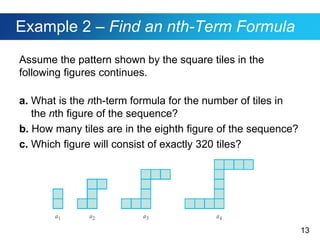
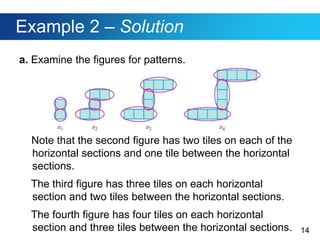
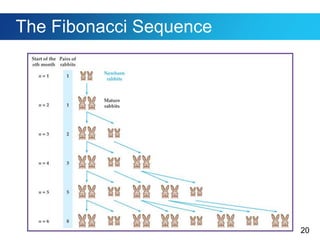
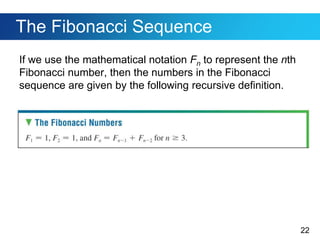
This document discusses sequences and provides examples of finding patterns in sequences to predict future terms or develop formulas. It begins by defining what a sequence is and the terms used to describe them, like first term and nth term. Difference tables are introduced as a way to analyze patterns between terms. Examples show how to use difference tables to predict future terms and find formulas. The document then introduces the famous Fibonacci sequence and provides its recursive definition to calculate future terms.