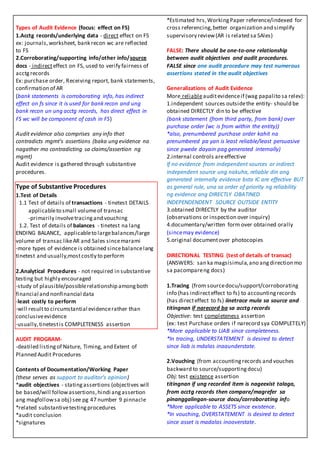
This document provides an overview of audit evidence and substantive testing procedures. It discusses:
- The nature, timing, and extent of audit procedures and how they are contained in the audit program.
- Financial statement assertions that are the subject of audit testing like existence, completeness, valuation.
- Types of substantive procedures like tests of details and analytical procedures.
- Characteristics of sufficient and appropriate audit evidence and the hierarchy of reliability.
- Direction of testing procedures like tracing and vouching.
- Types of evidence like accounting records and corroborating information.