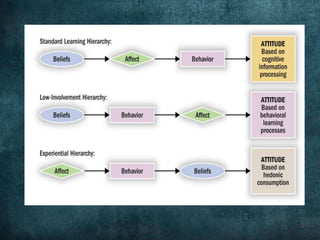
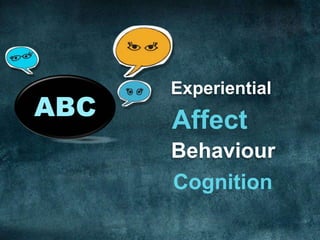
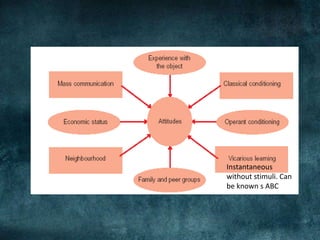
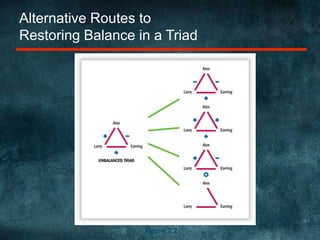
Attitudes are evaluative statements that reflect how people feel about objects, ideas, and people. There are three components of attitudes: affective (feelings), behavioral (intentions), and cognitive (beliefs). Attitudes serve important functions like helping people minimize harm and maximize happiness. Different models explain the relationships between the three components and how they are formed, including the ABC model where affect precedes cognition and behavior, and the CAB model where cognition comes first. Low involvement products often follow a CBA sequence. Marketers use techniques like cognitive dissonance theory and the foot-in-the-door technique to influence attitudes. Balance theory also examines how attitudes are structured in relationships between people and objects.