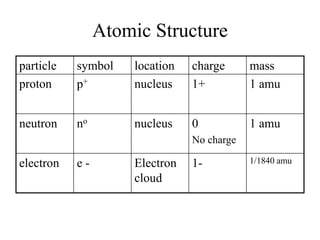
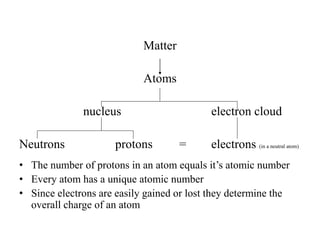
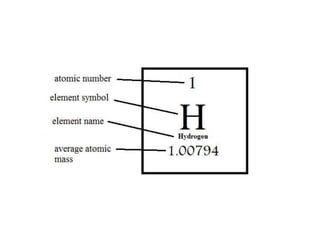
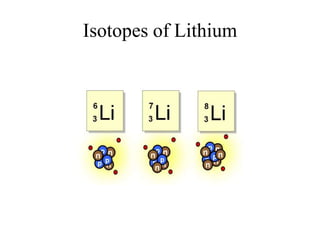
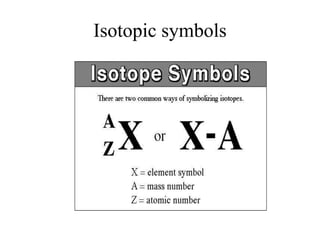
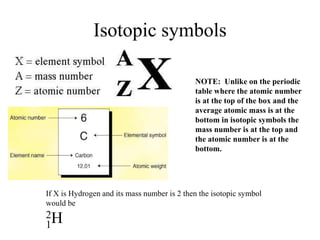
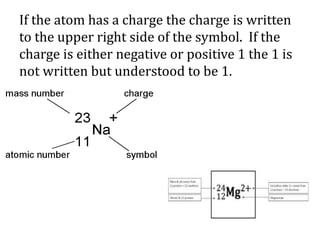
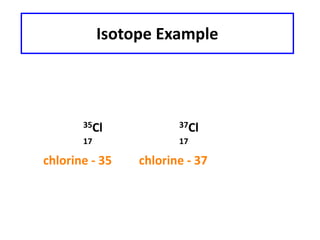
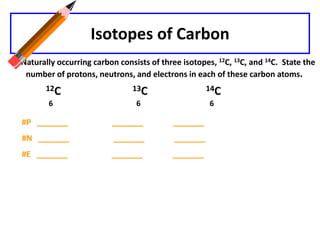
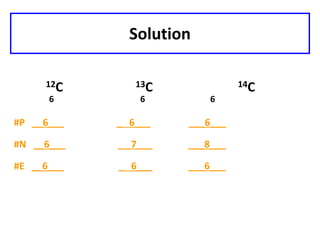
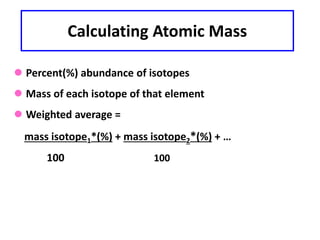
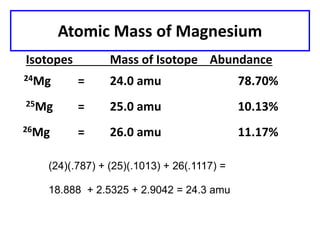
This document discusses atomic structure and isotopes. It defines the basic particles that make up an atom including protons, neutrons, and electrons. It explains that isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The document provides examples of isotopic symbols and how to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in different carbon and zinc isotopes. It also discusses how atomic mass is calculated based on the relative abundances of an element's naturally occurring isotopes.