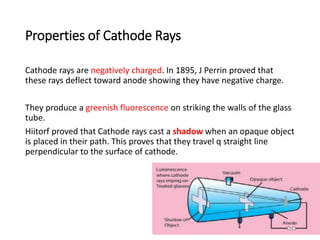
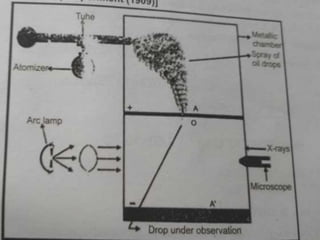
This document provides an overview of atomic structure and the discovery of subatomic particles like electrons. It discusses J.J. Thomson's cathode ray tube experiments in the late 1800s that led to the discovery of electrons and determination of their charge to mass ratio (e/m). It also describes Millikan's oil drop experiment from 1909 that precisely measured the charge of individual electrons as 1.6022×10-19 coulombs and calculated the mass of an electron as 9.1095×10-31 kg.