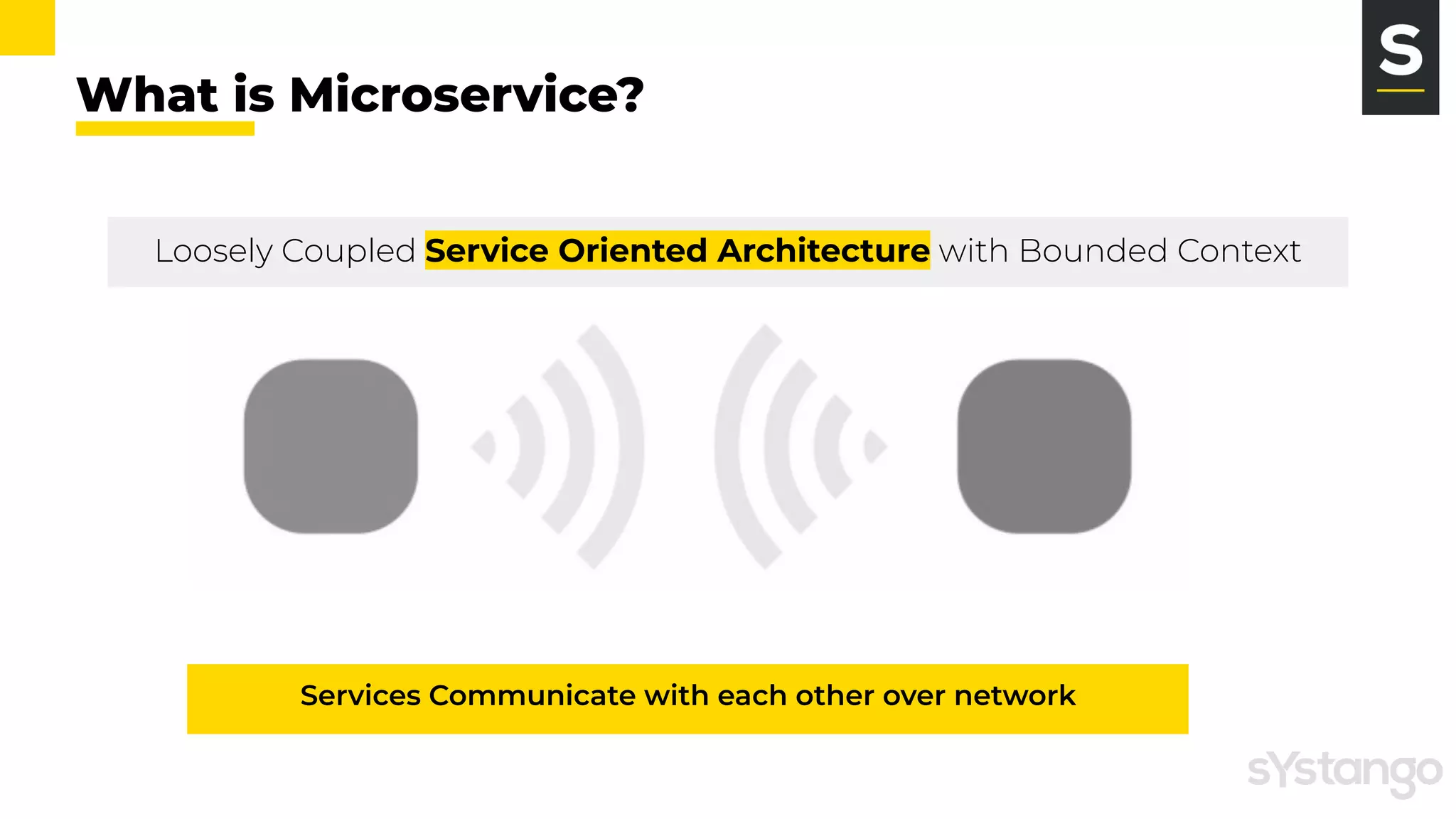
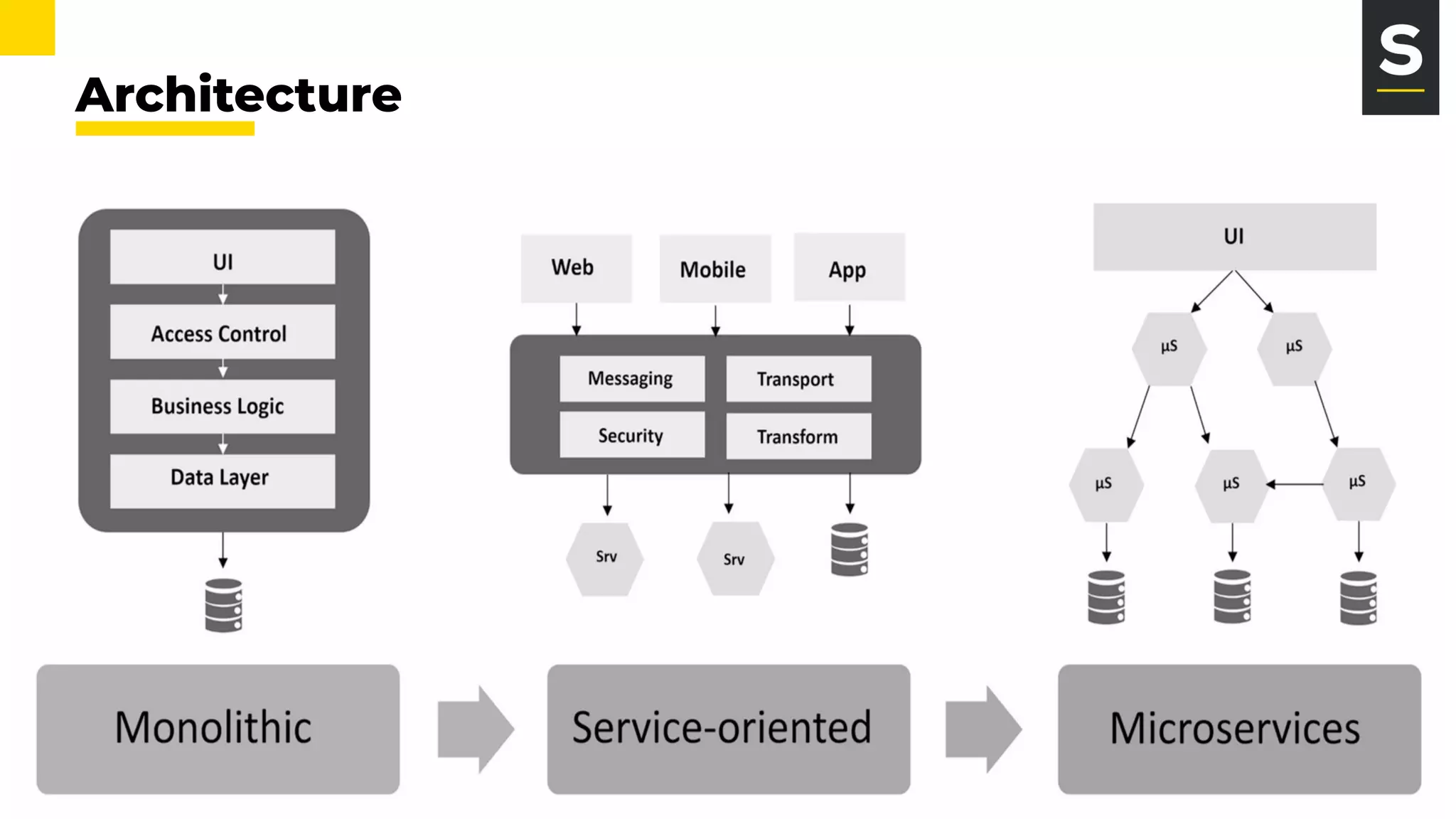
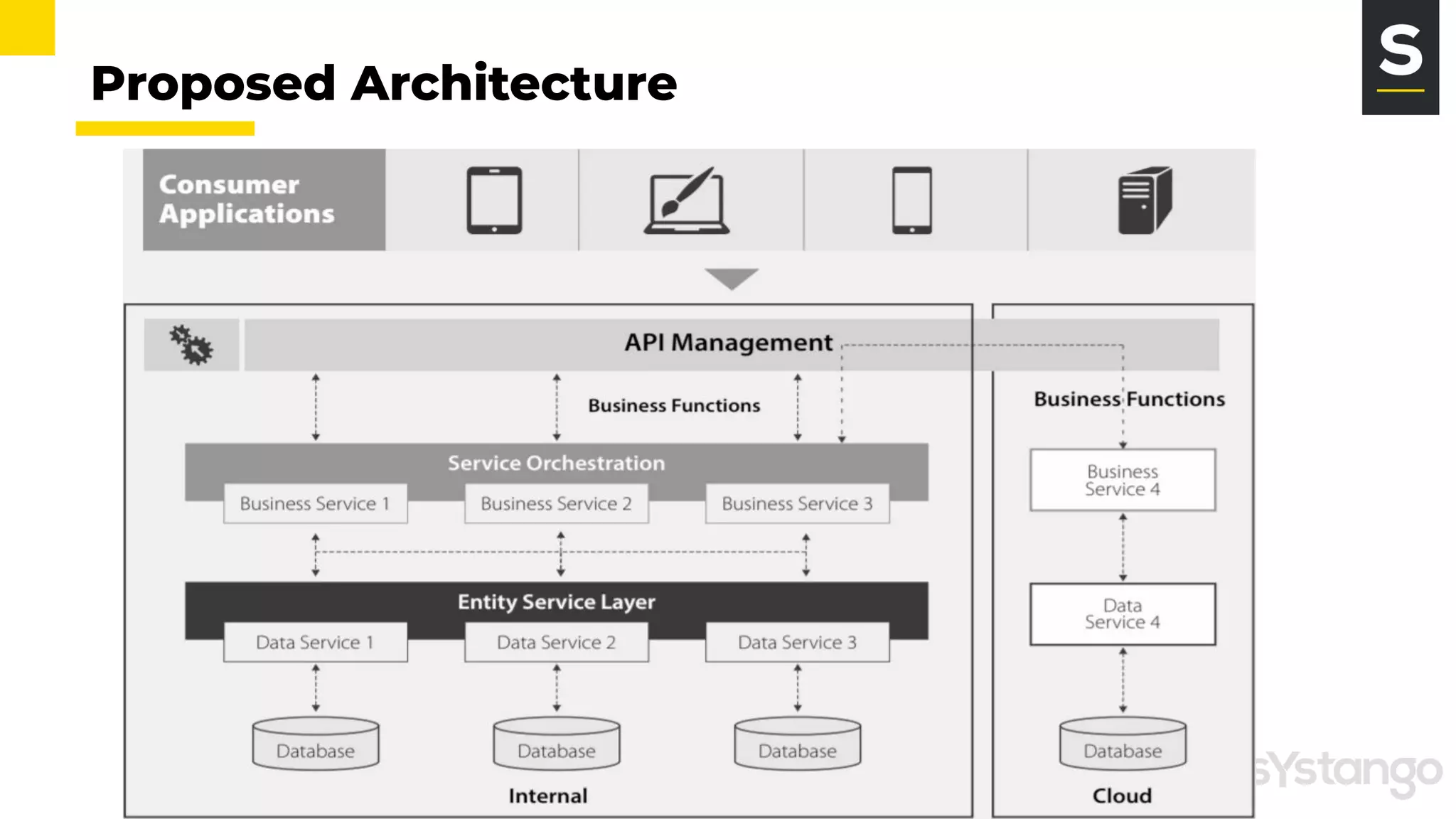
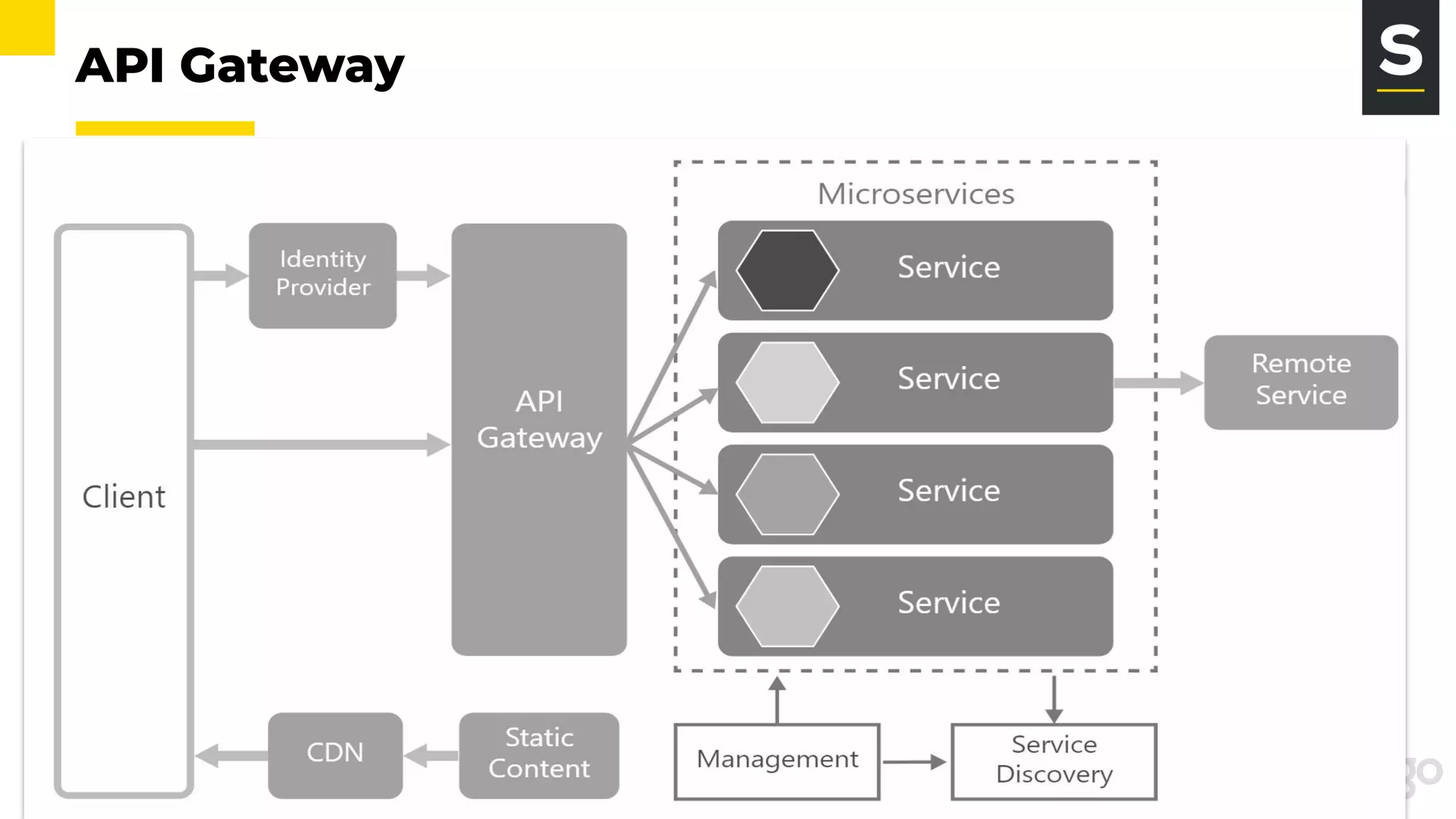
The document discusses the evolution and architecture of microservices, comparing them to the F1 pit stop for efficiency. It highlights key characteristics such as loose coupling, independent scaling, and the importance of APIs for communication, while also noting benefits and challenges associated with microservices. It emphasizes best practices including decentralized data storage and isolation of failures through an API gateway.