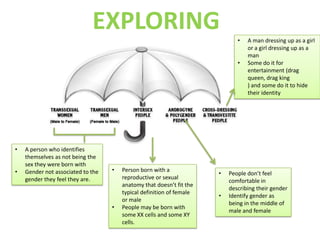
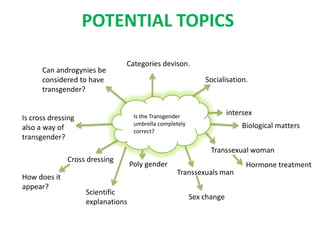
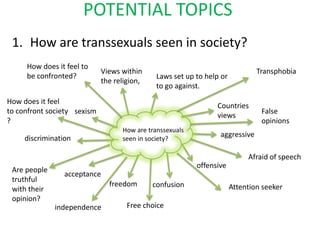
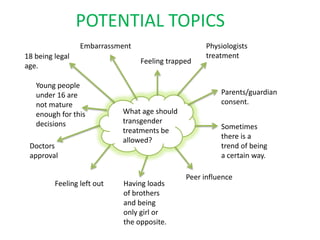
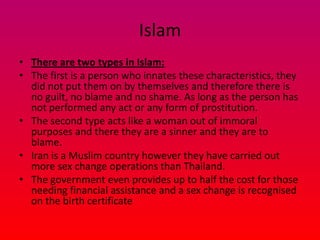
Here are the key points I found in my research on intersex people:
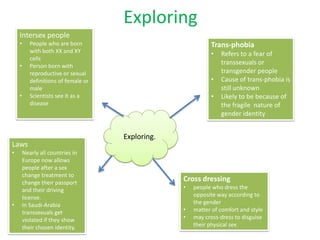
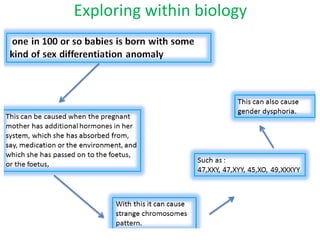
- Intersex people are born with sex characteristics (such as chromosomes, gonads, or genitals) that do not fit typical binary notions of male or female bodies. About 1-2% of the population is born intersex.
- There are many different intersex variations that can occur. Some common variations include Klinefelter syndrome (extra X chromosome), Turner syndrome (missing X chromosome), and congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH).
- In the past, doctors often recommended "corrective" genital surgery on intersex infants to make their genitals appear more typically male or female. However, this practice is now