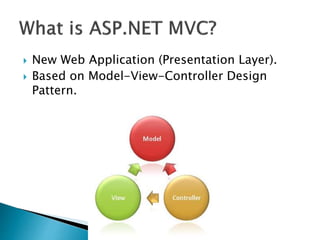
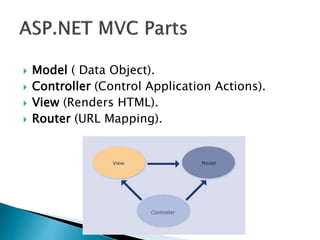
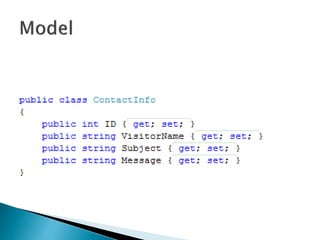
The document discusses ASP.NET MVC, which is a web application framework that follows the model-view-controller pattern. It separates an application into three main components: the model, which is the data object; the controller, which controls application actions; and the view, which renders HTML. The framework allows for complete control over HTML, smooth development of web 2.0 applications, and SEO-friendly URLs. It compares ASP.NET MVC to traditional ASP.NET web forms.