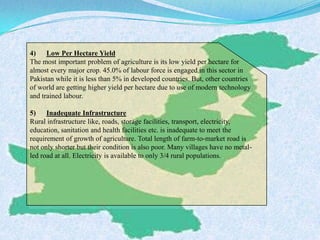
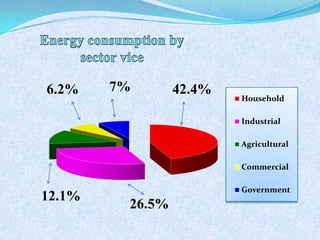
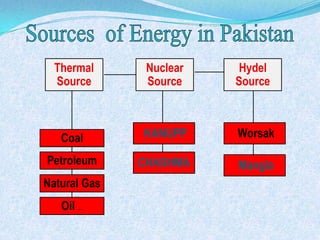
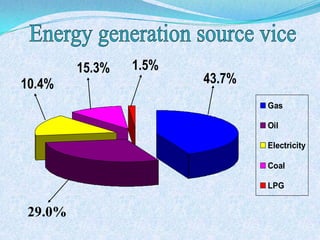
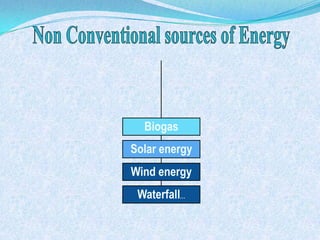
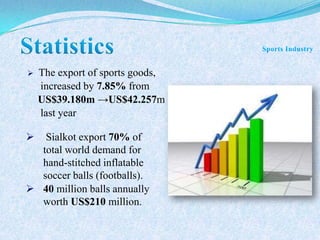
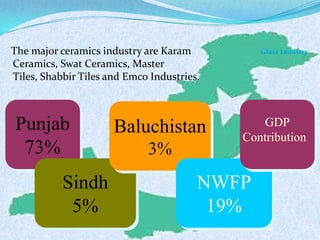
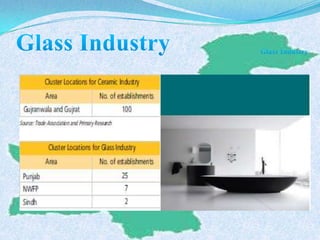
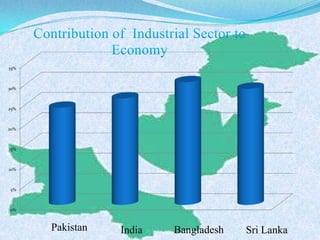
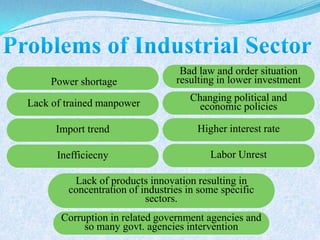
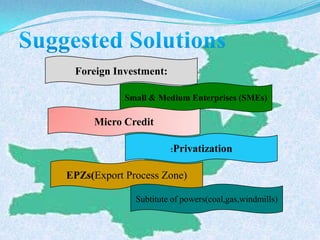
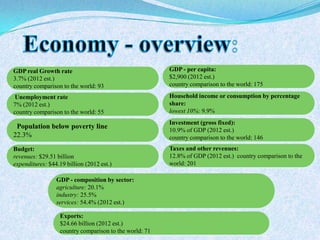
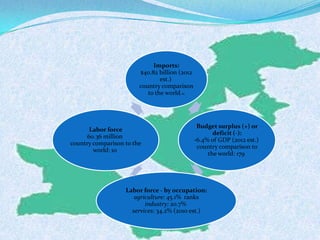
The document discusses Pakistan's agricultural sector and the challenges it faces in becoming an Asian Tiger economy. Some of the major problems in the agricultural sector include limited cultivable land, water logging and salinity issues, low crop yields, outdated farming methods, lack of infrastructure and research, and uneconomic land holdings. To address these issues, the document suggests measures such as providing farmers access to credit, improved seeds and machinery, investing in irrigation infrastructure, and expanding agricultural research. Overall, developing the agricultural sector through modernization and overcoming resource constraints is key to strengthening Pakistan's economy.