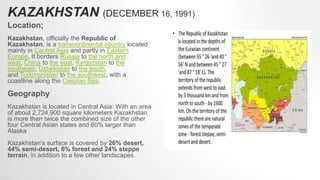
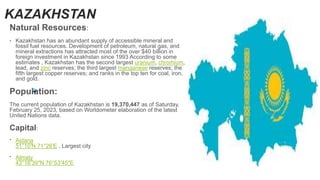
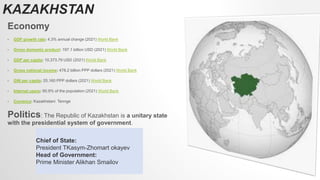
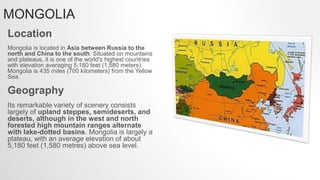
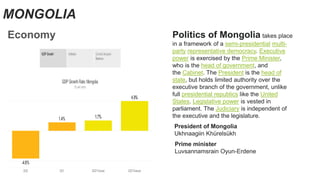
Kazakhstan was originally inhabited by nomadic tribes and became part of various empires and states over centuries. It gained independence in 1991 after being part of the Soviet Union. Kazakhstan has a population of over 19 million and a largely commodity-based economy focused on mineral and energy extraction. It has strong economic growth and borders Russia, China, and other Central Asian countries. Mongolia has a long history as the homeland of the Mongol people and was once the center of the vast Mongol Empire. It has a population of over 3 million and its economy was traditionally based on herding and agriculture but is now focused more on mining. Both countries have presidential systems of government and significant mineral resources.