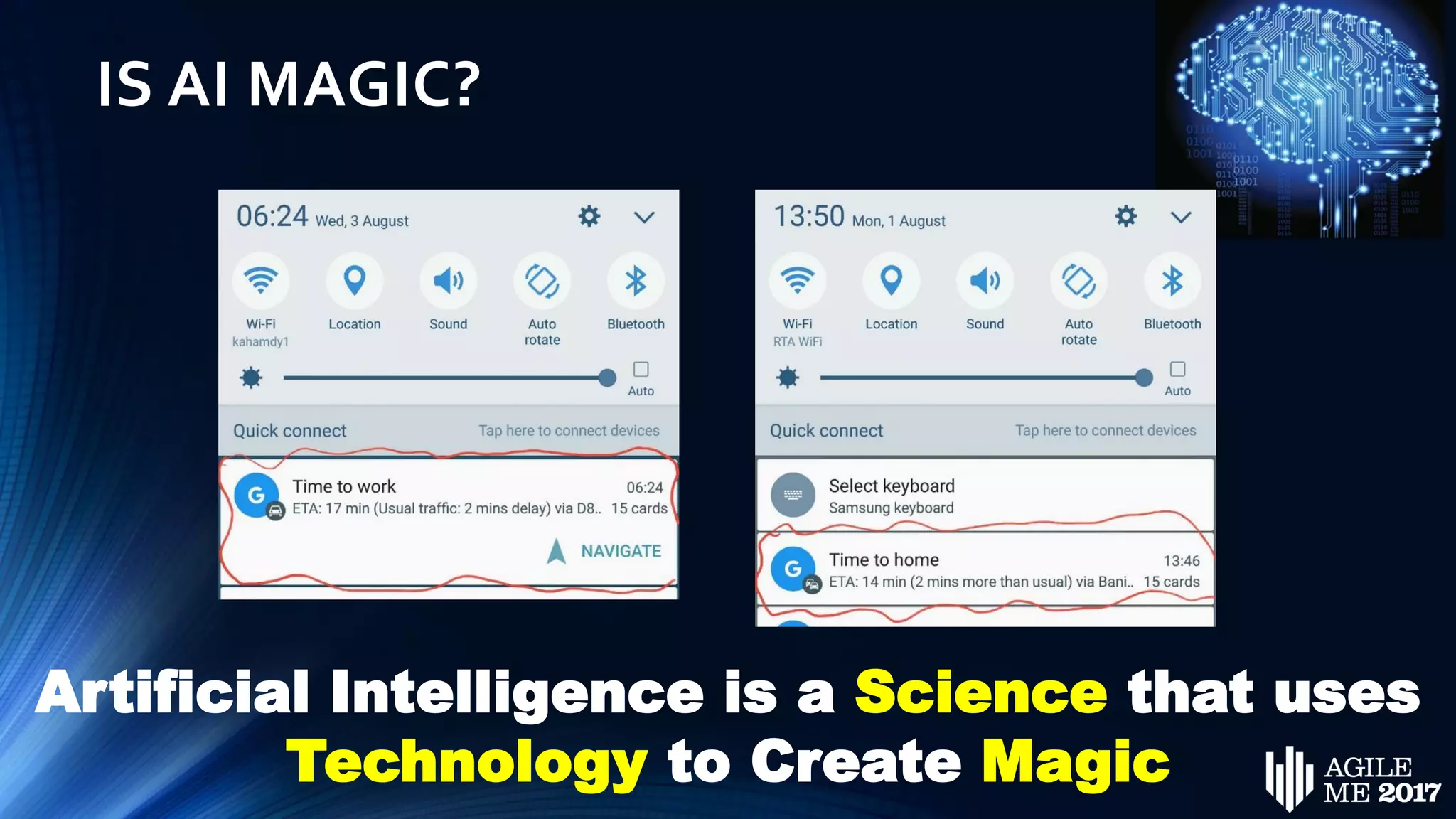
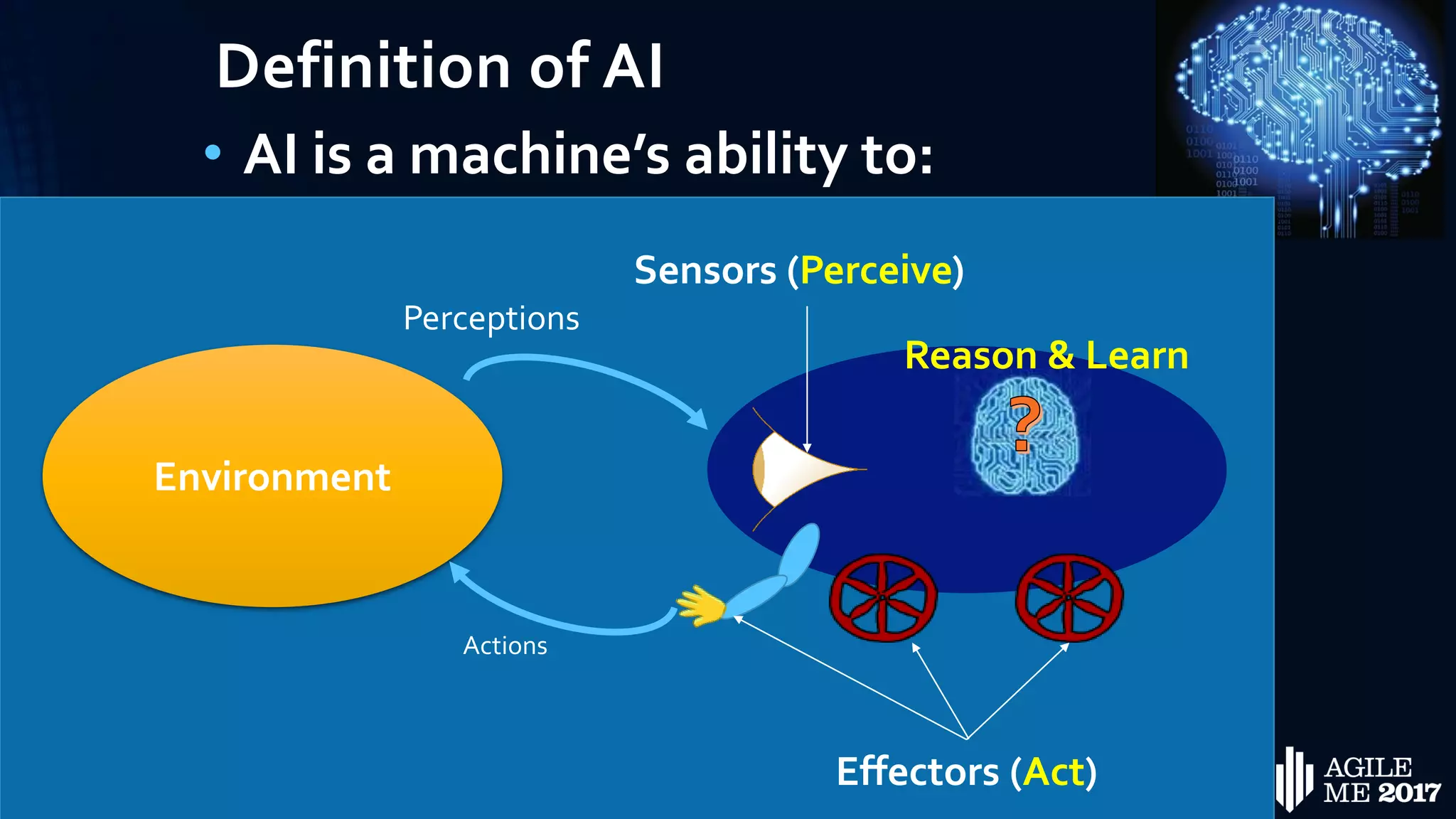
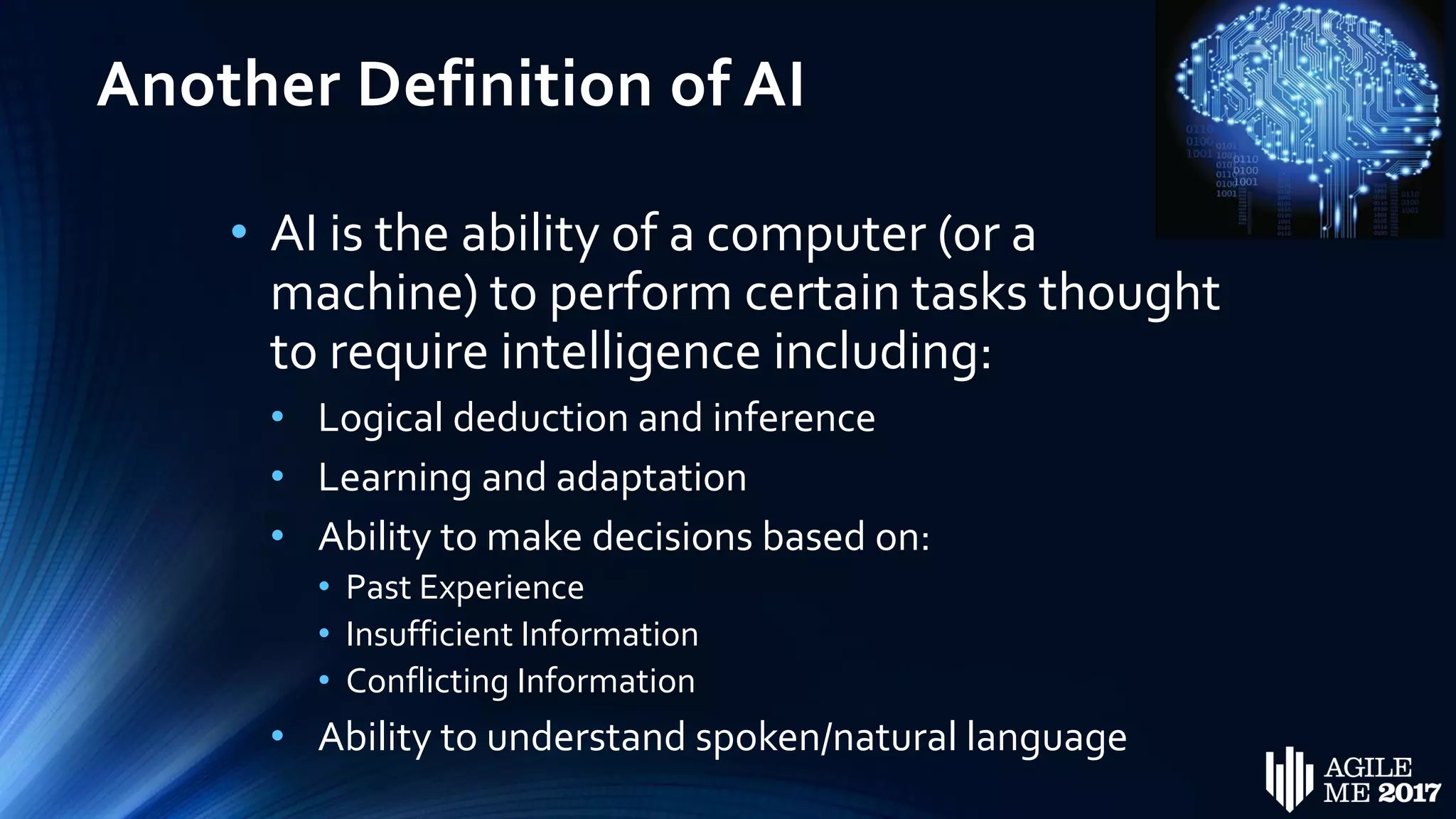
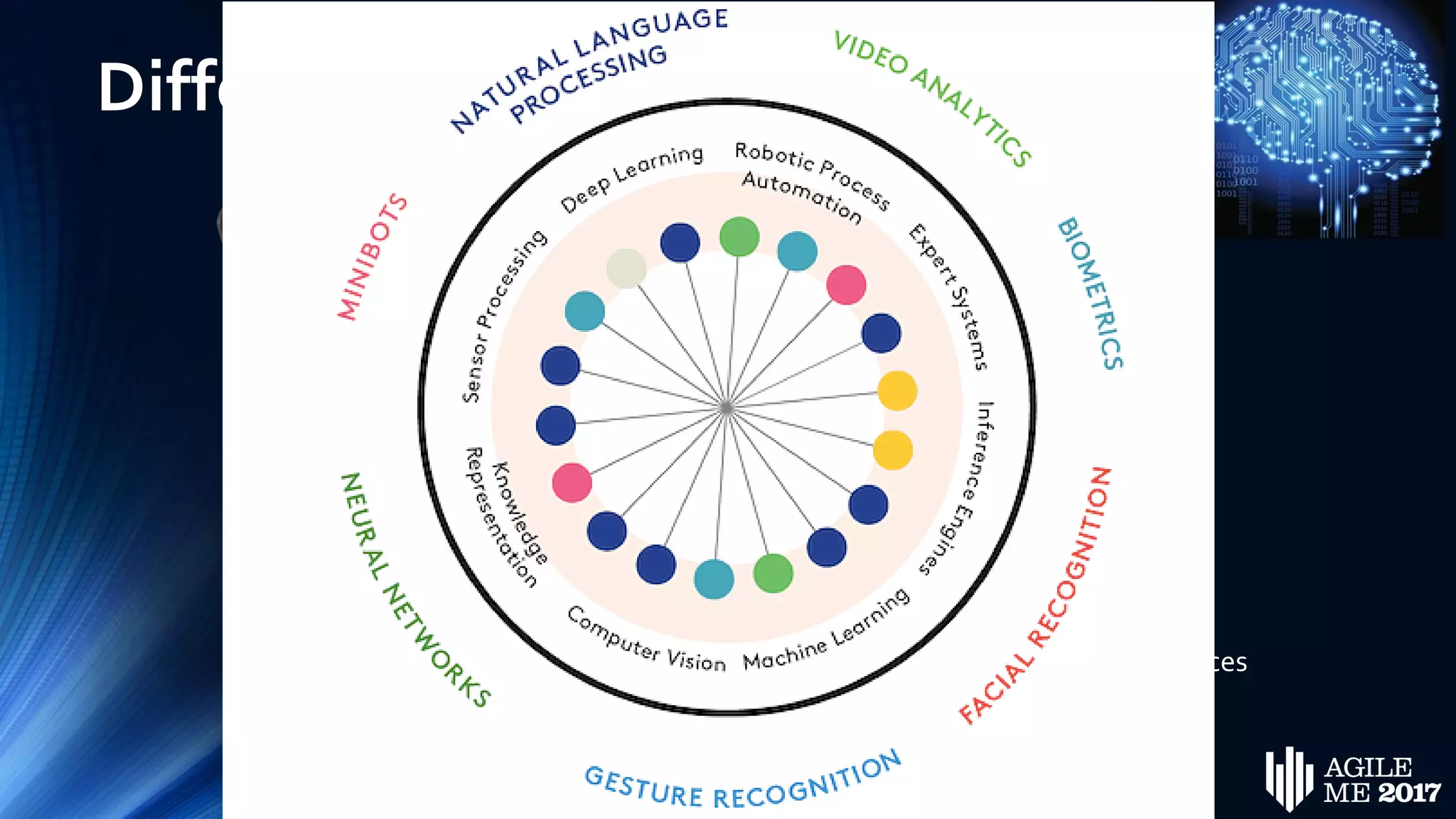
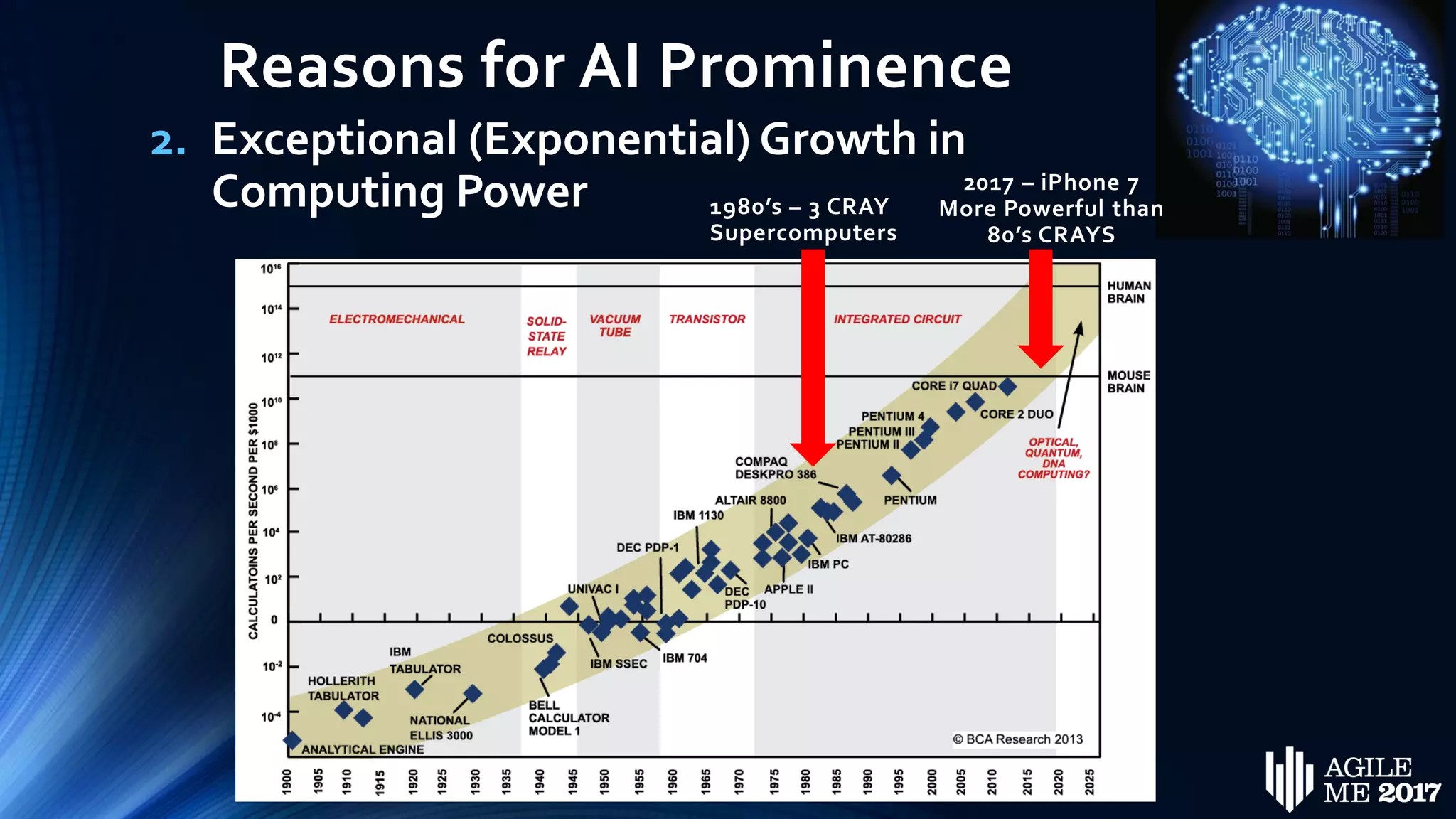
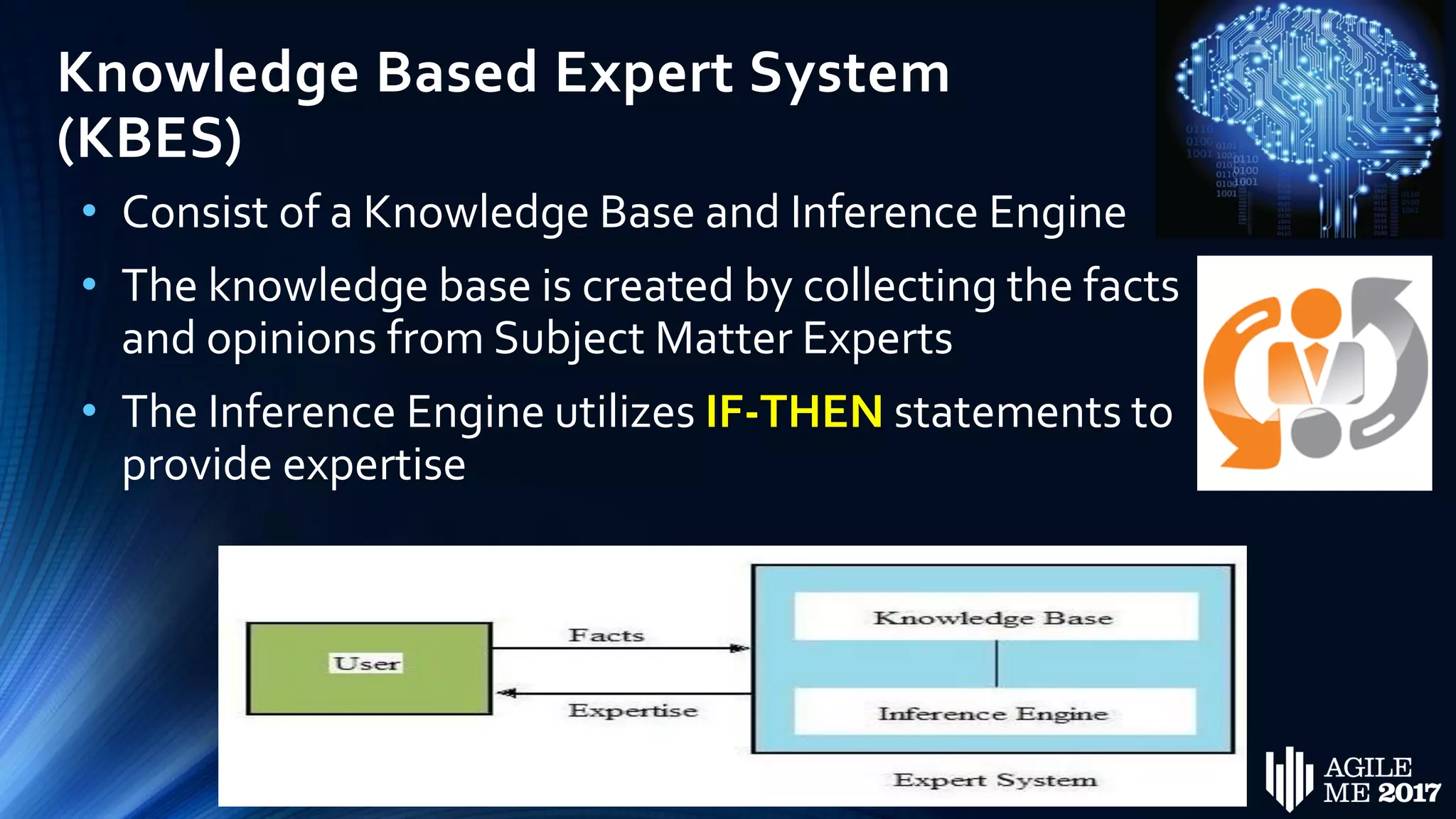
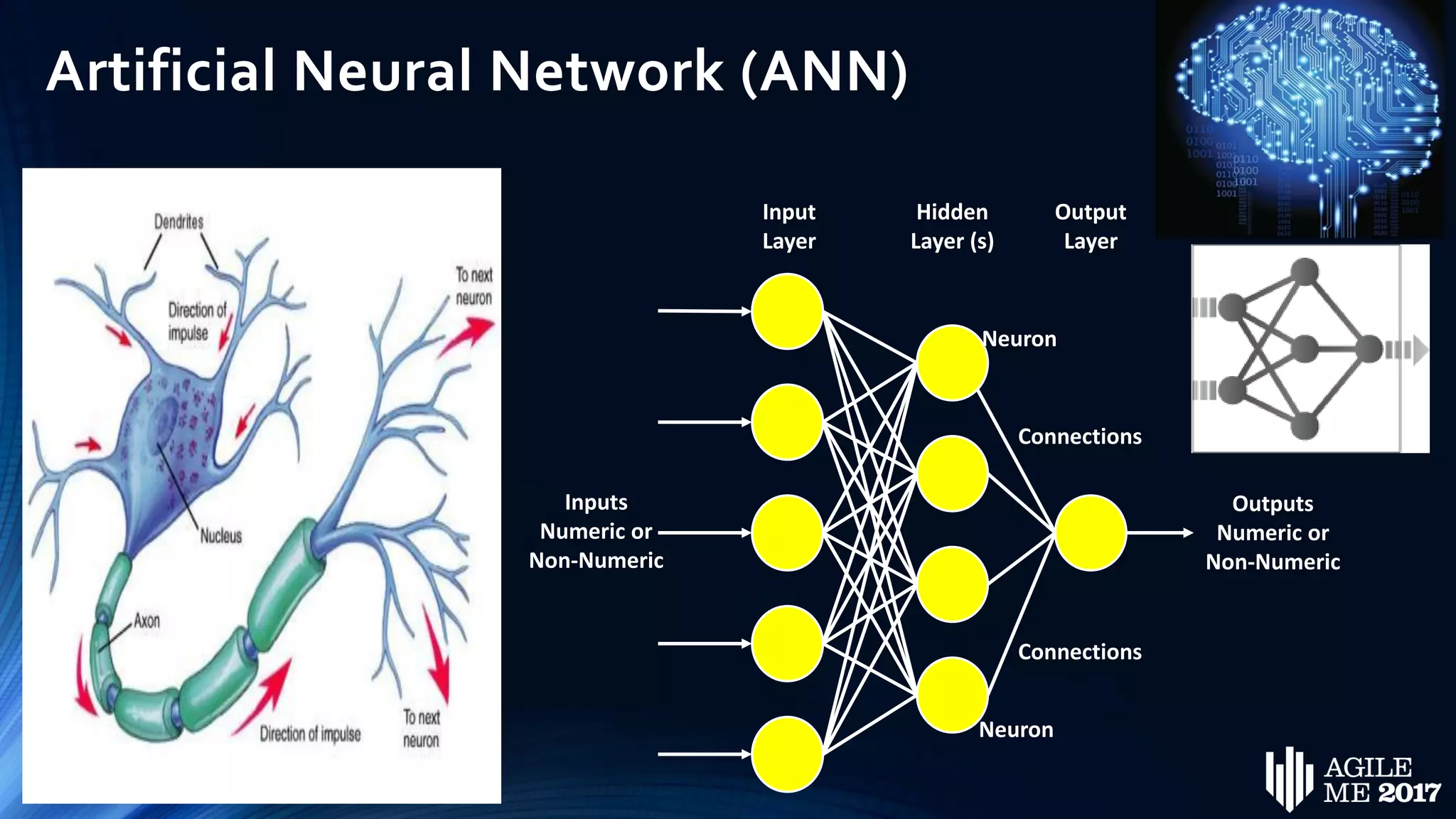
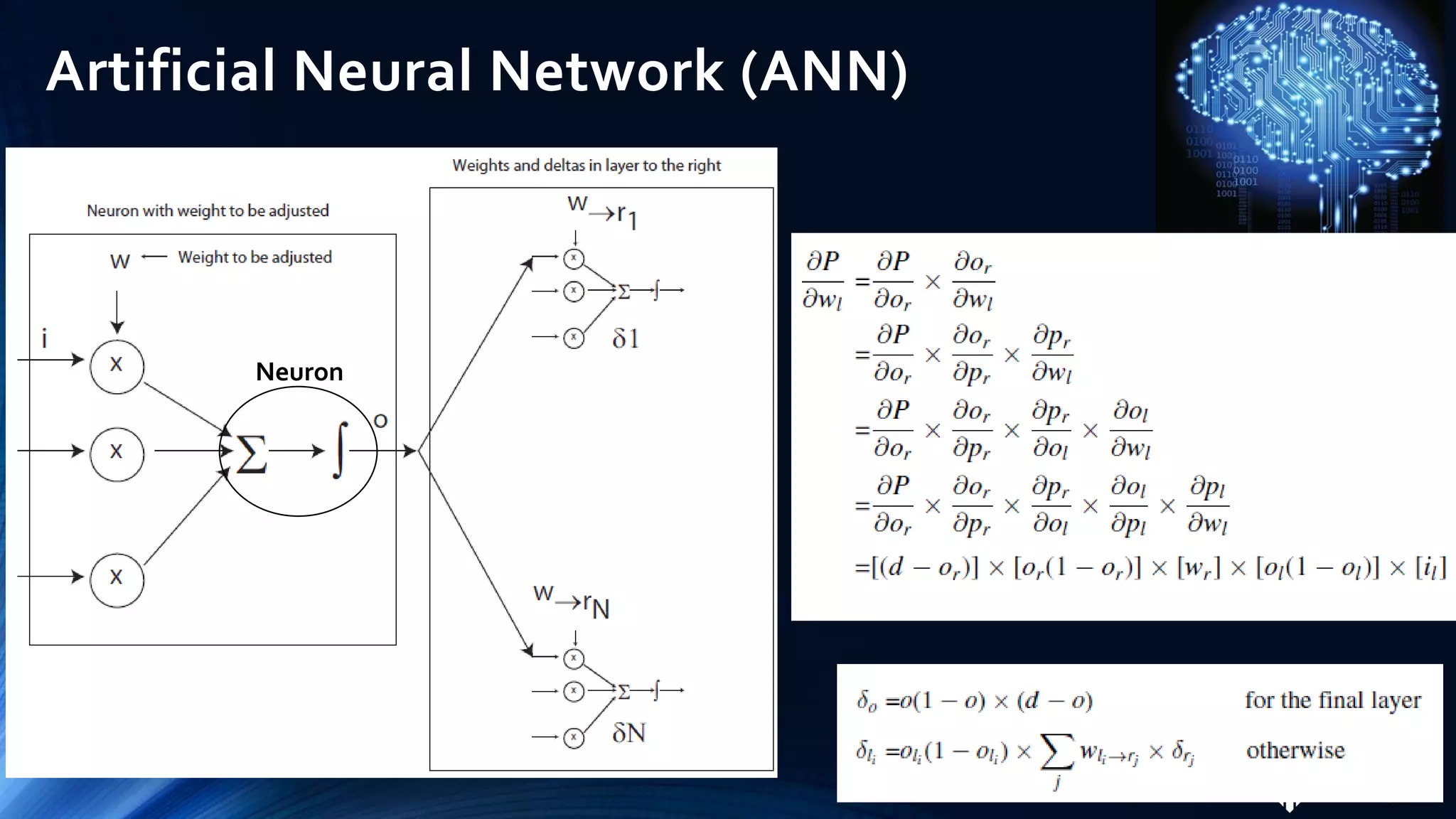
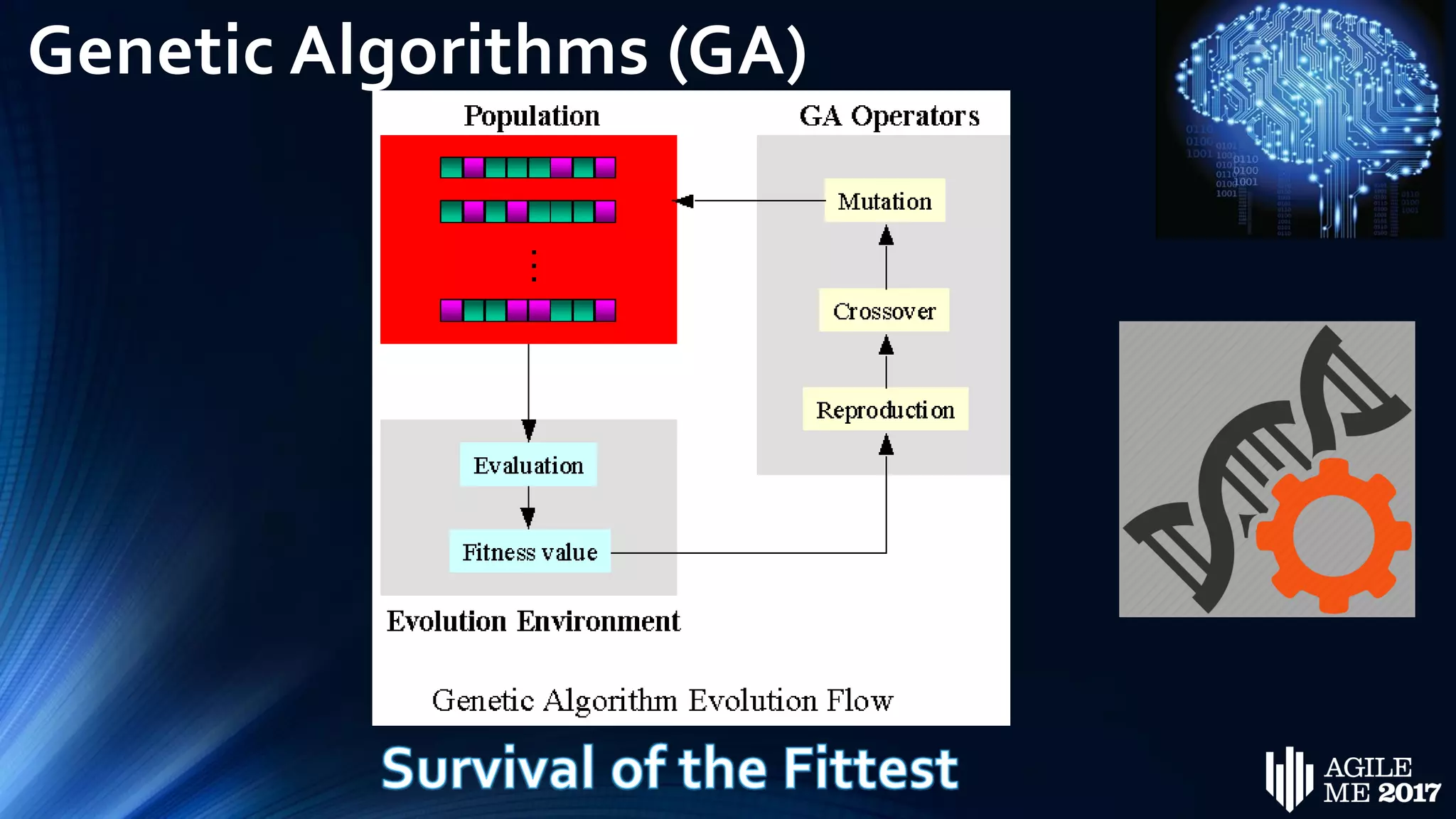
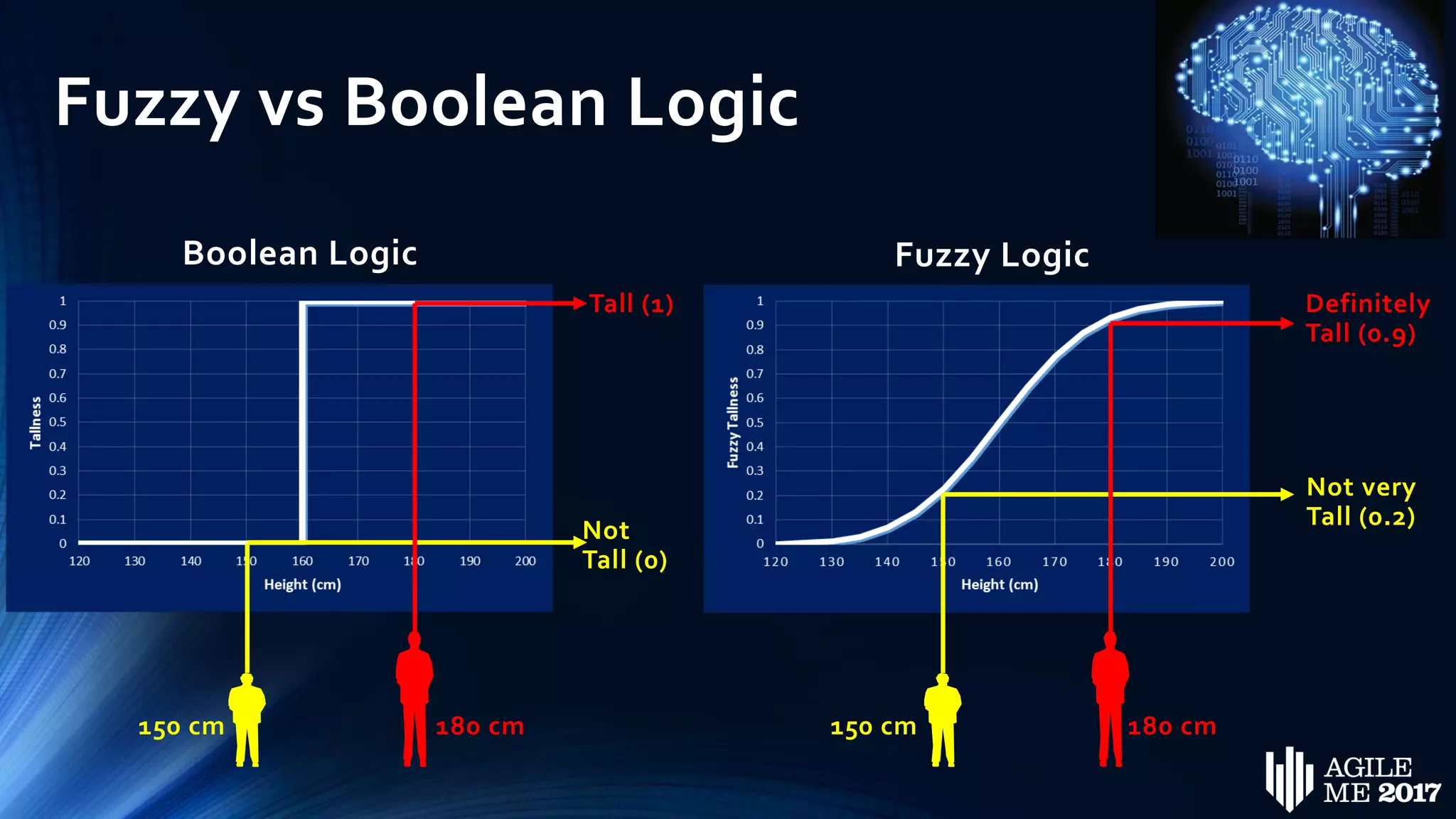
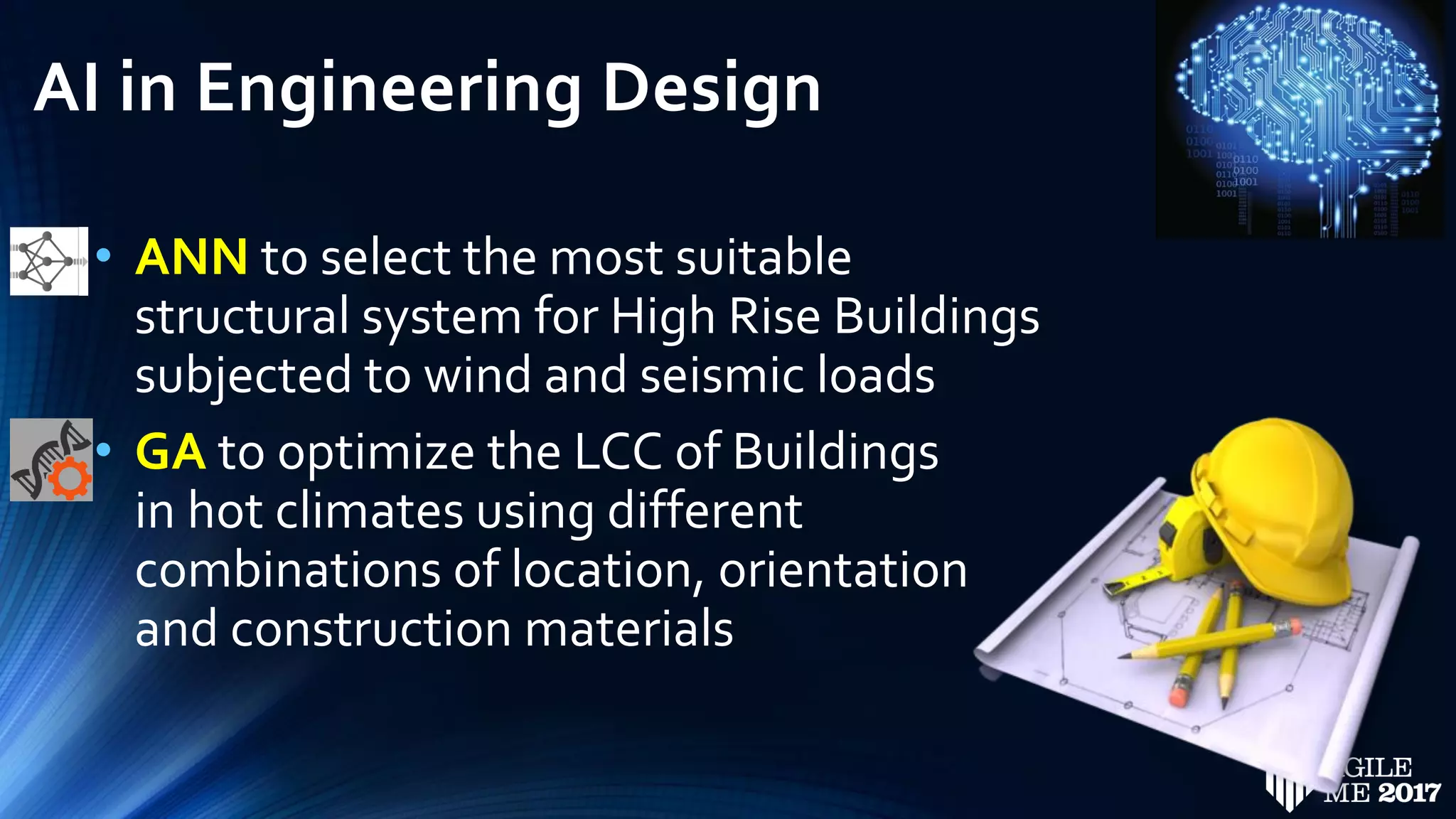
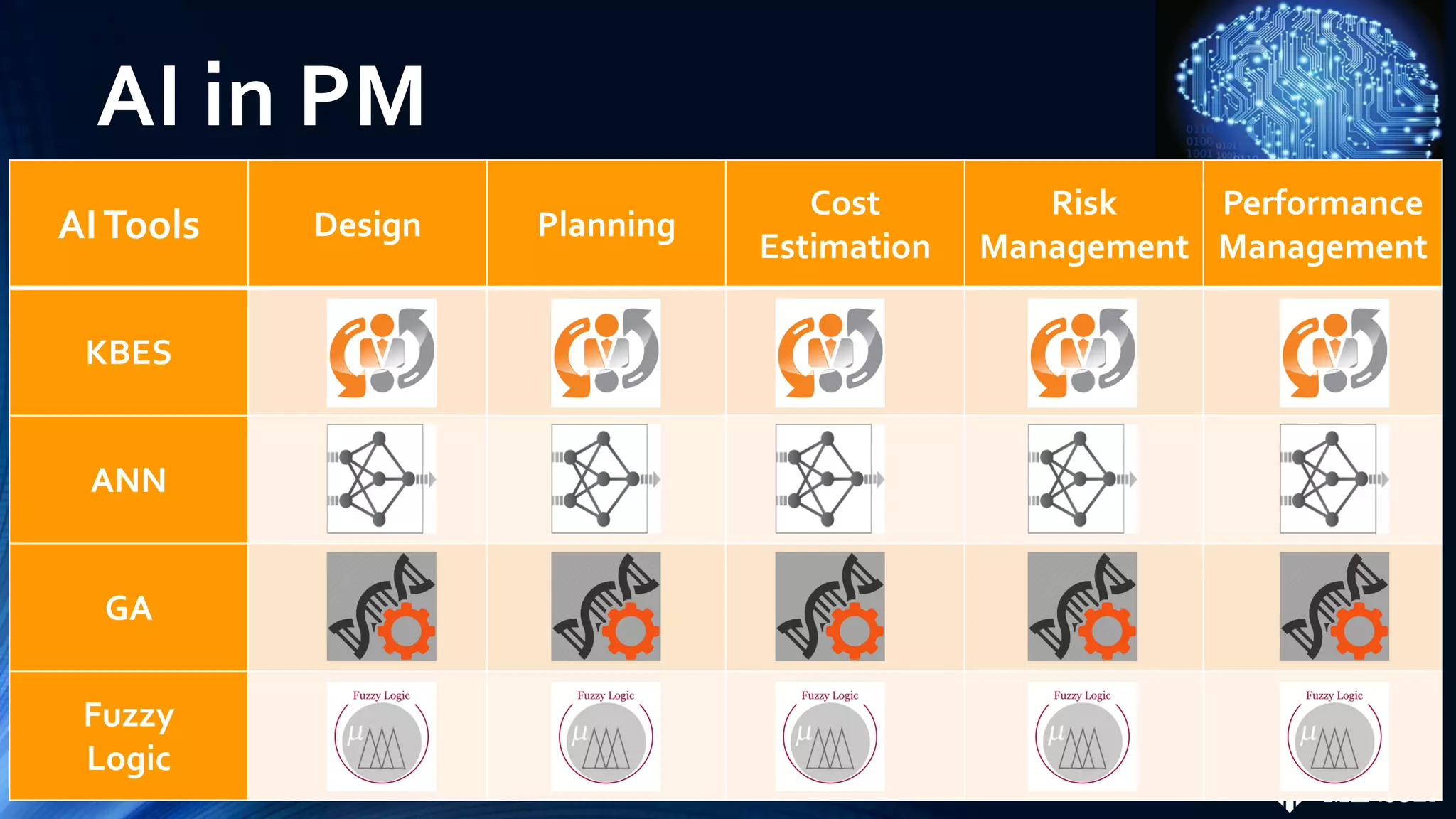
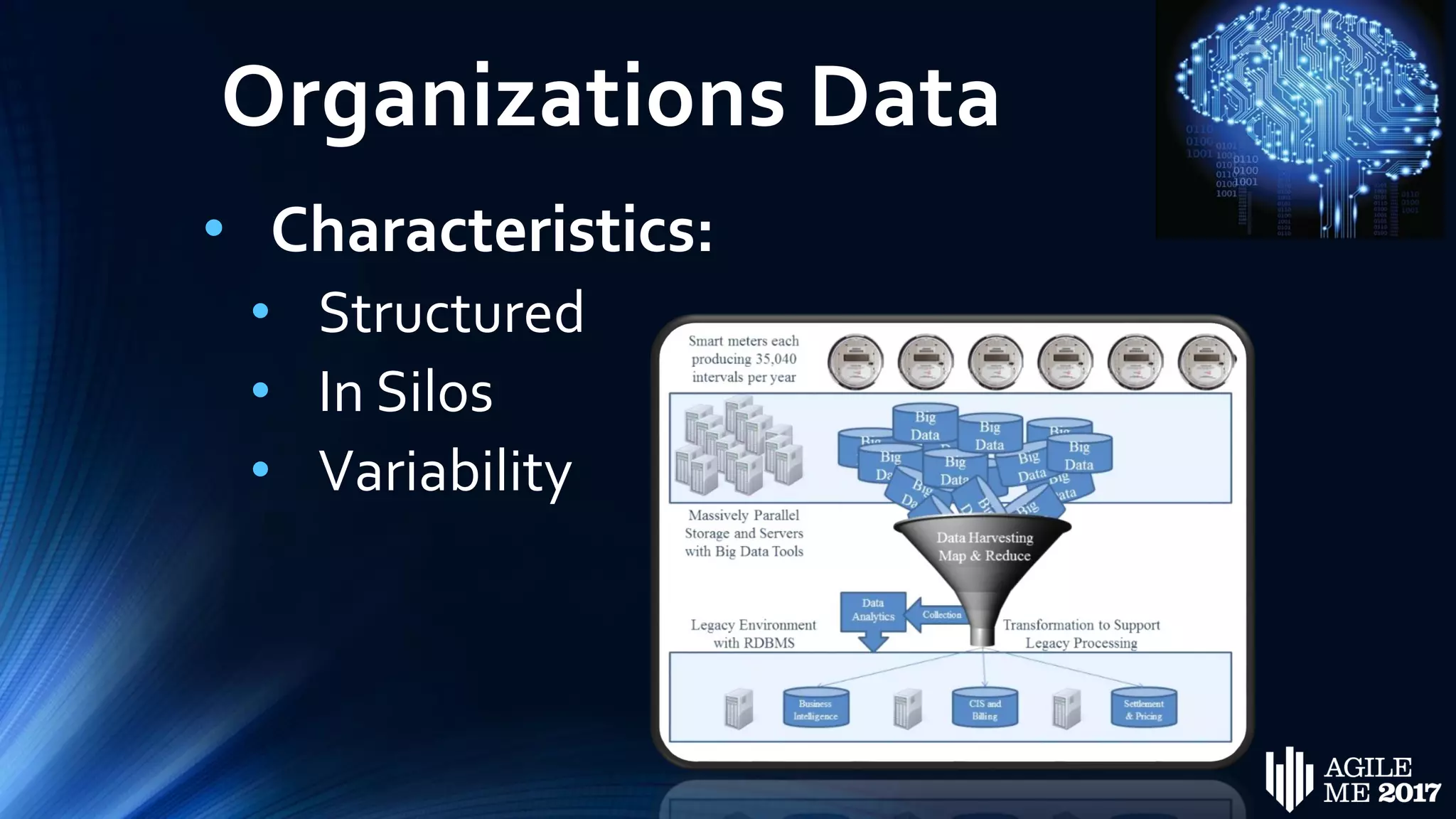
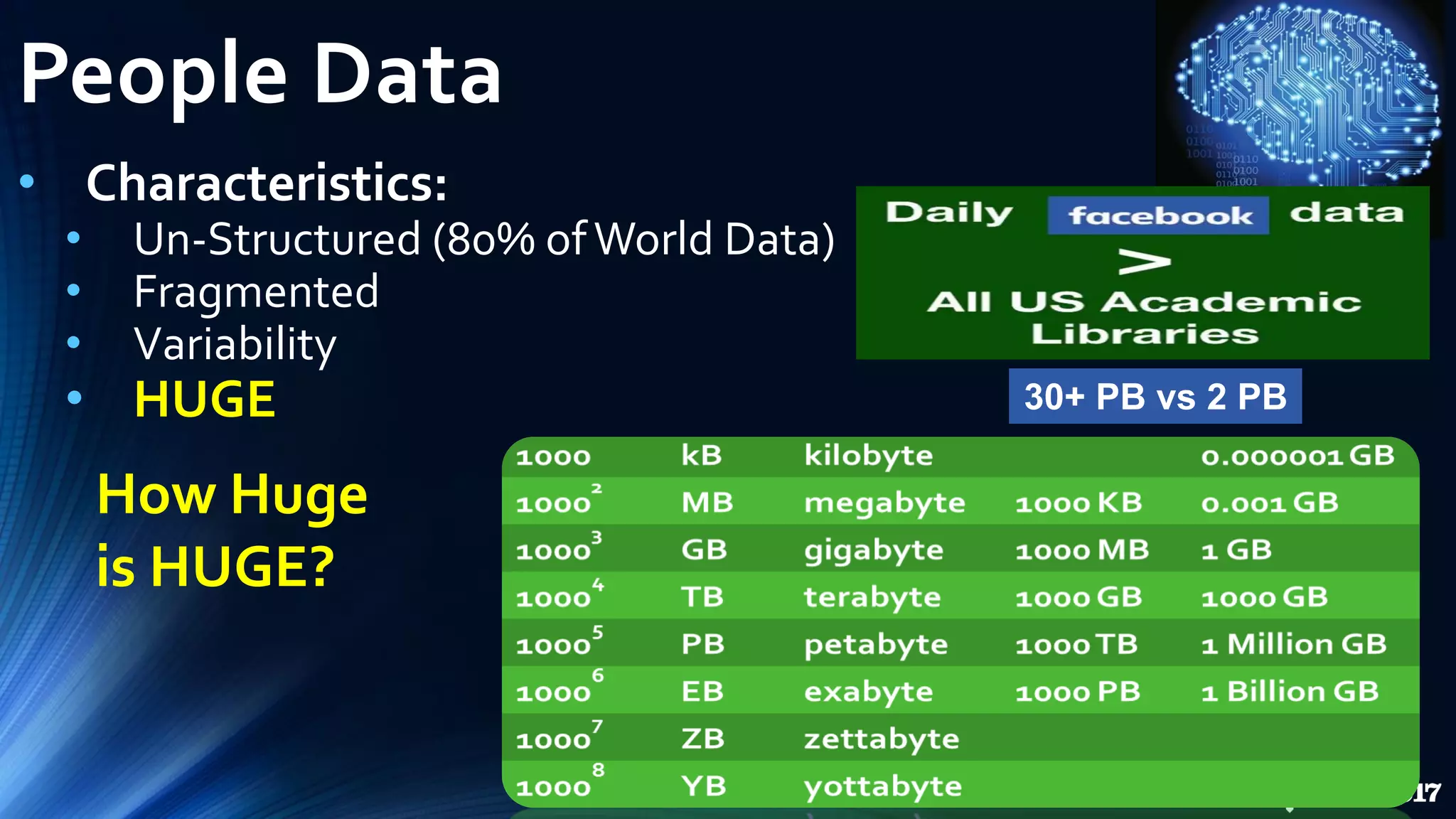
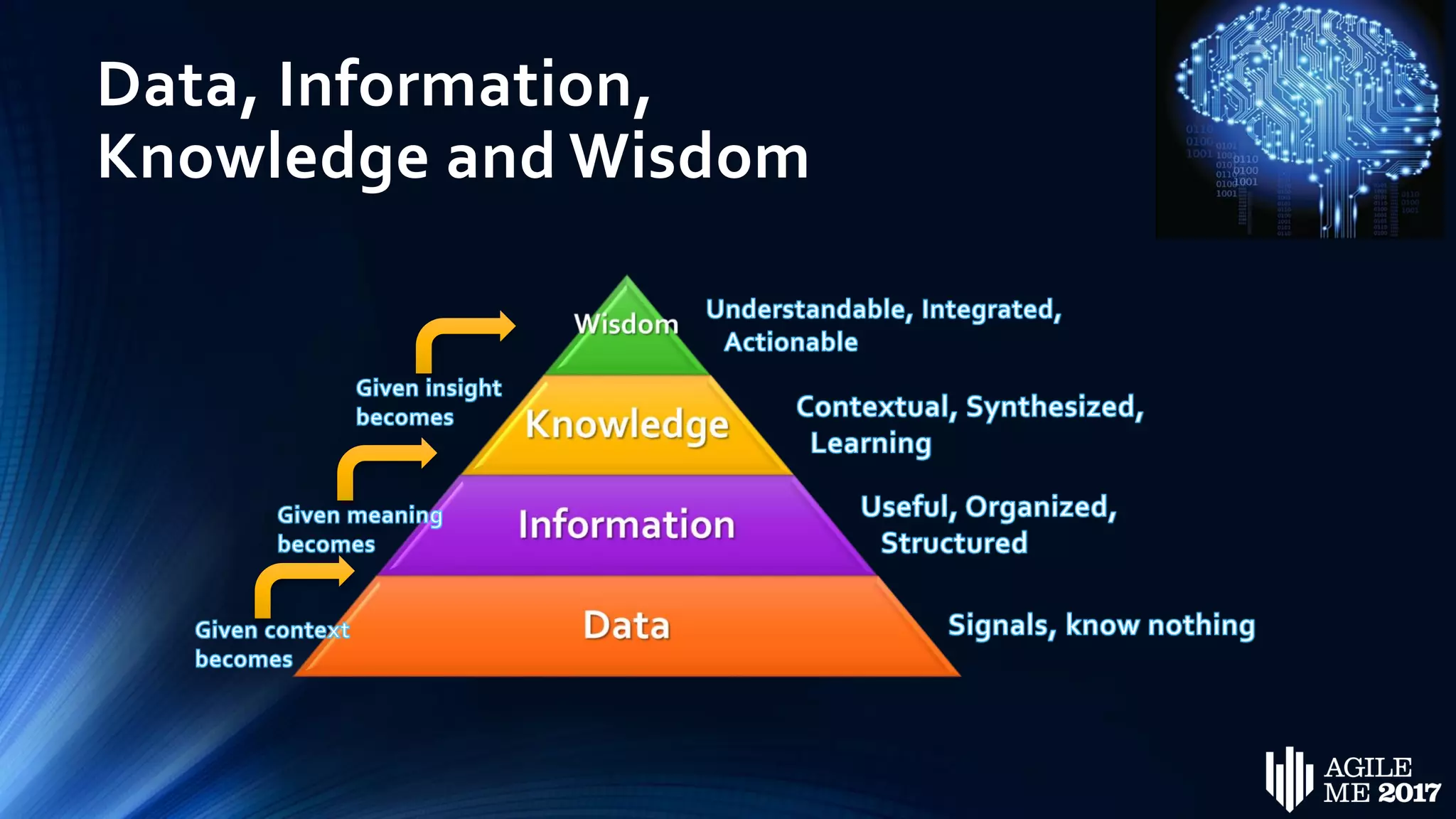
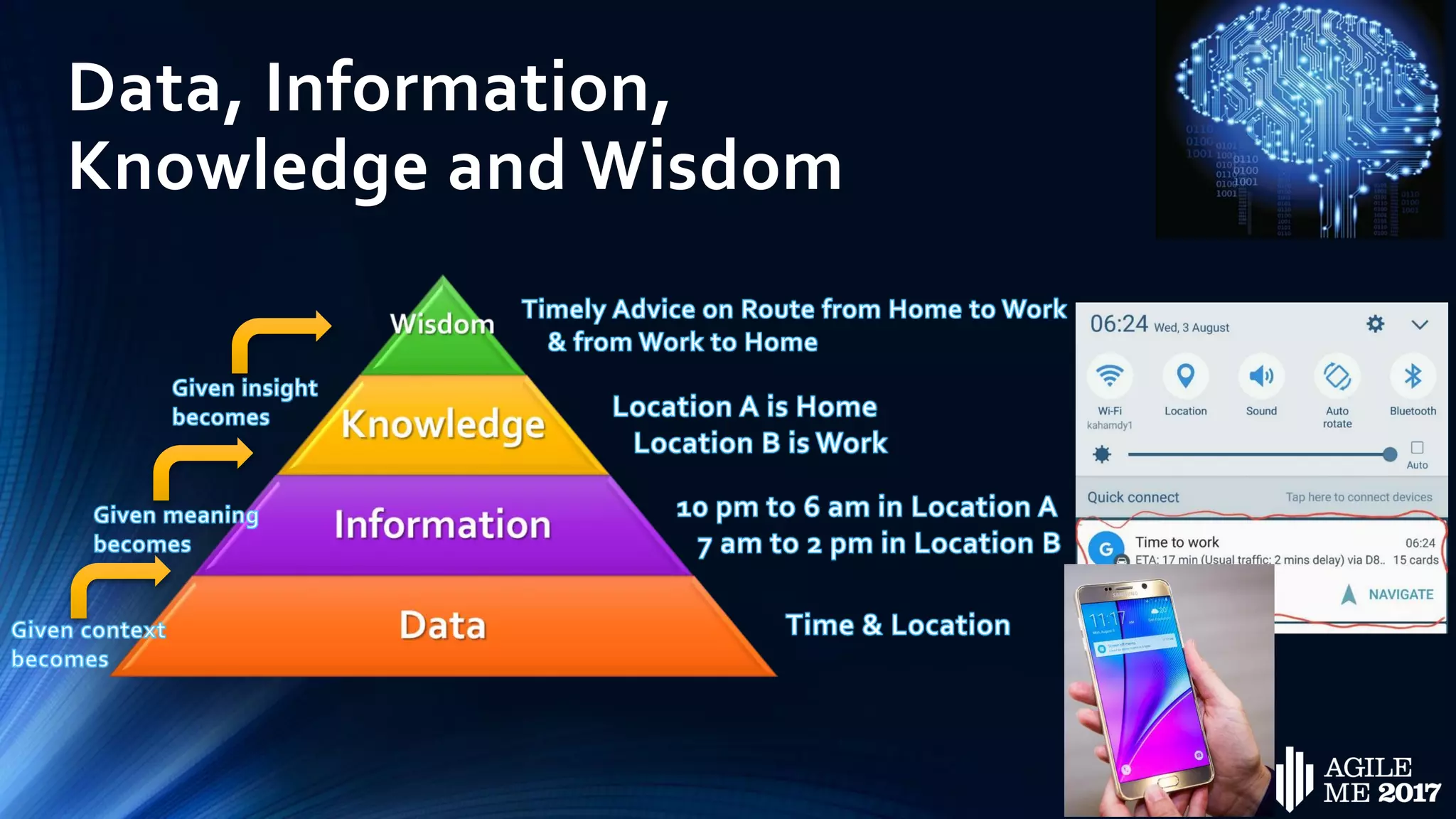
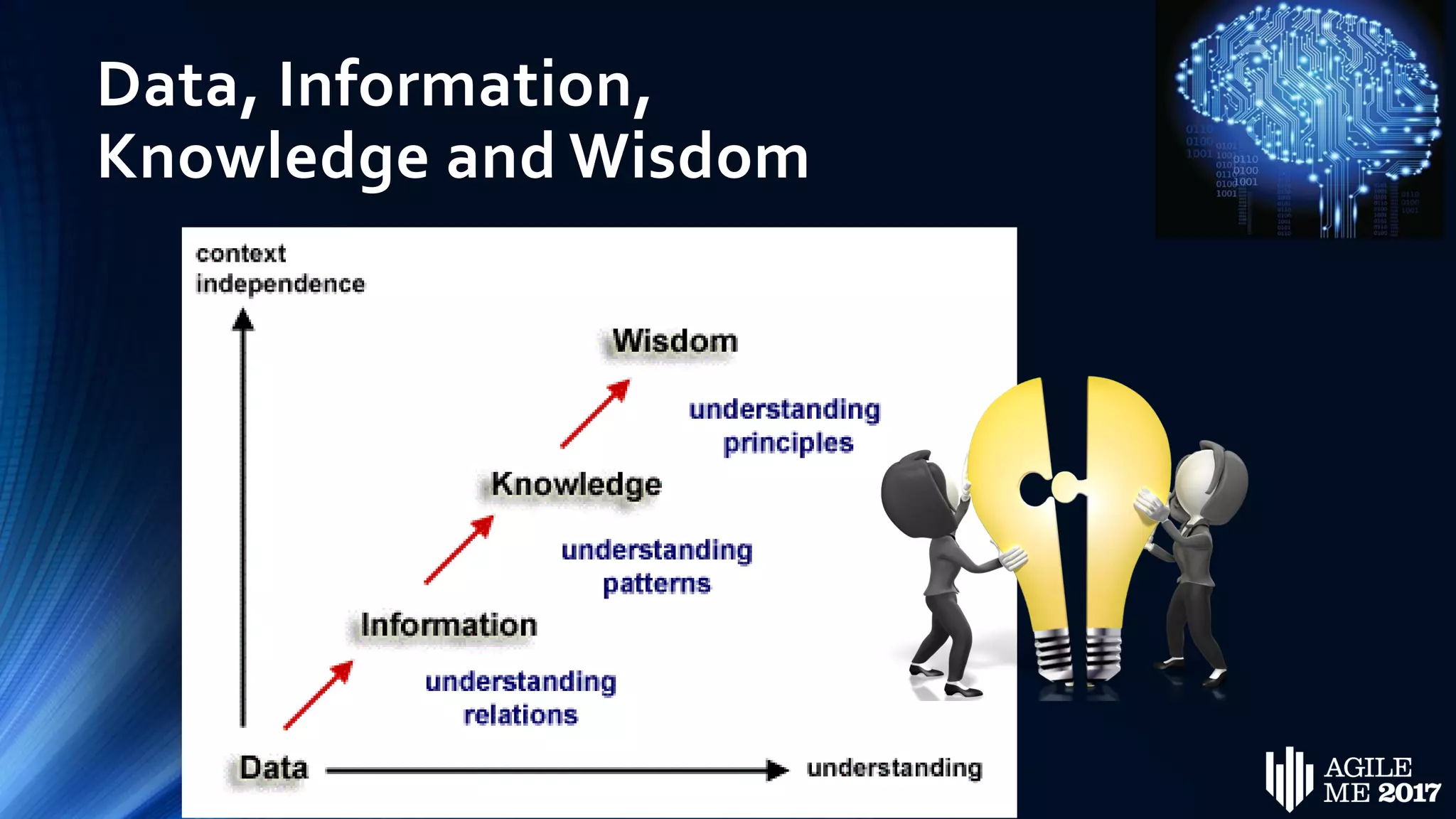
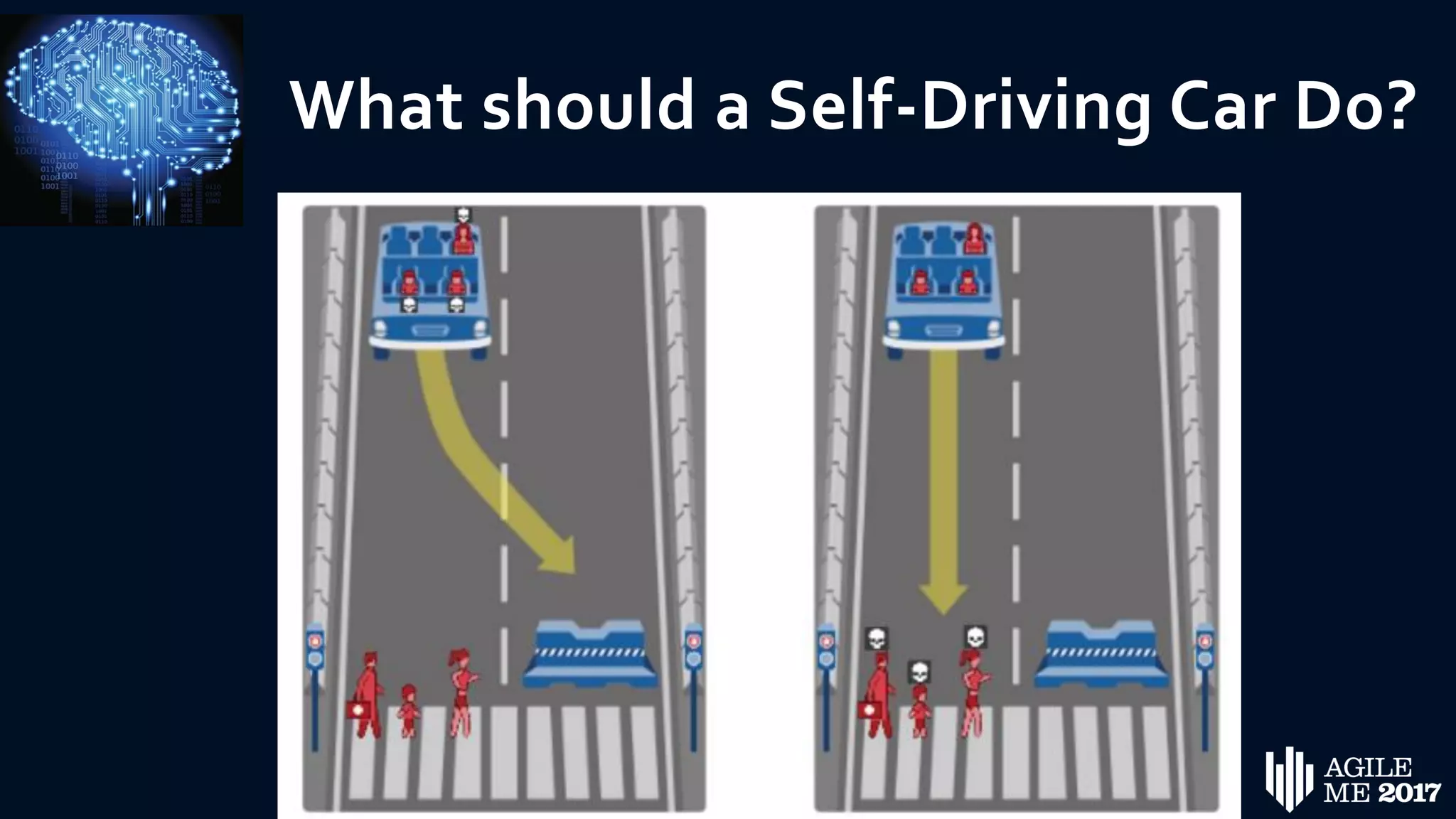
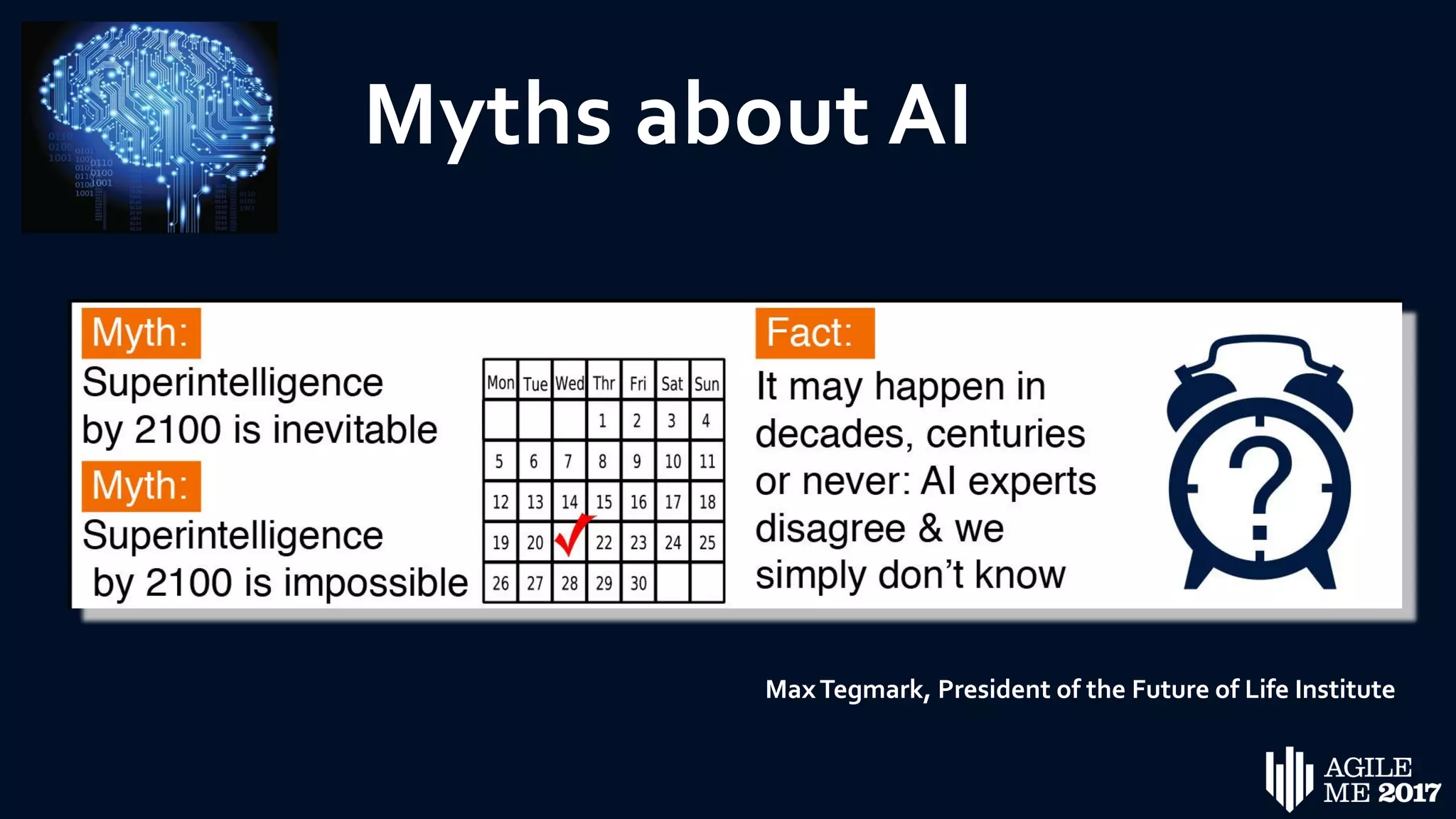
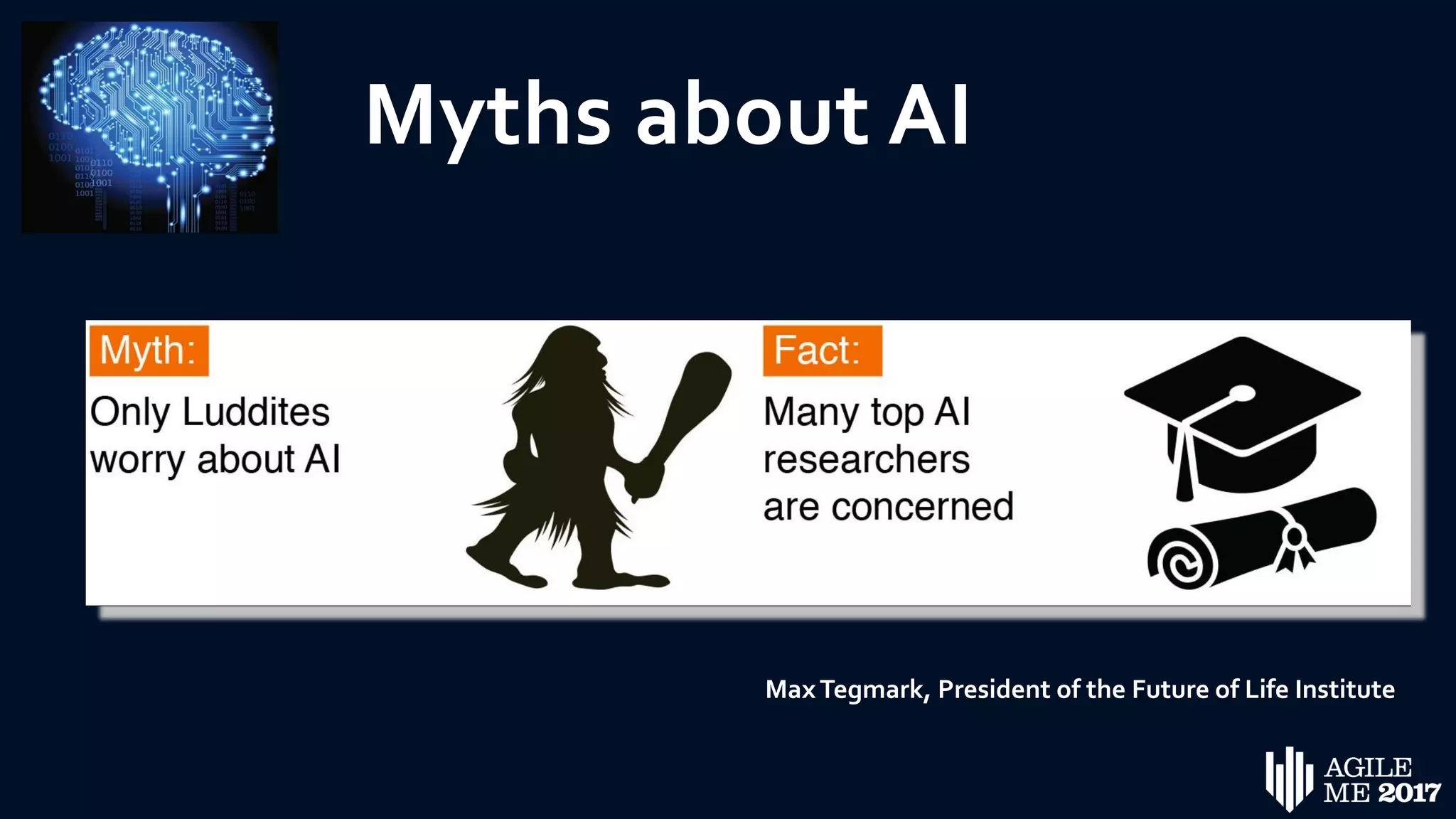
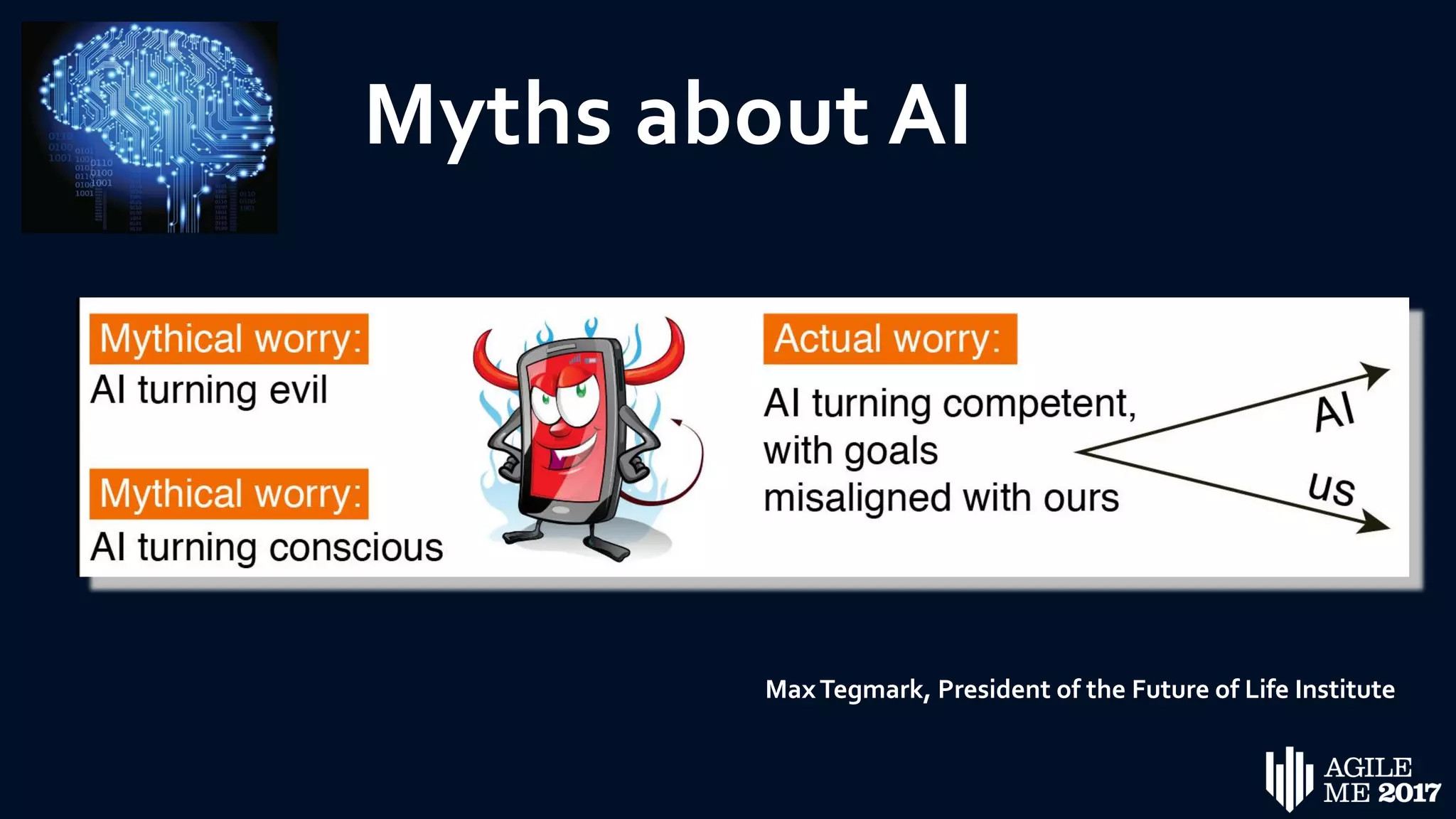
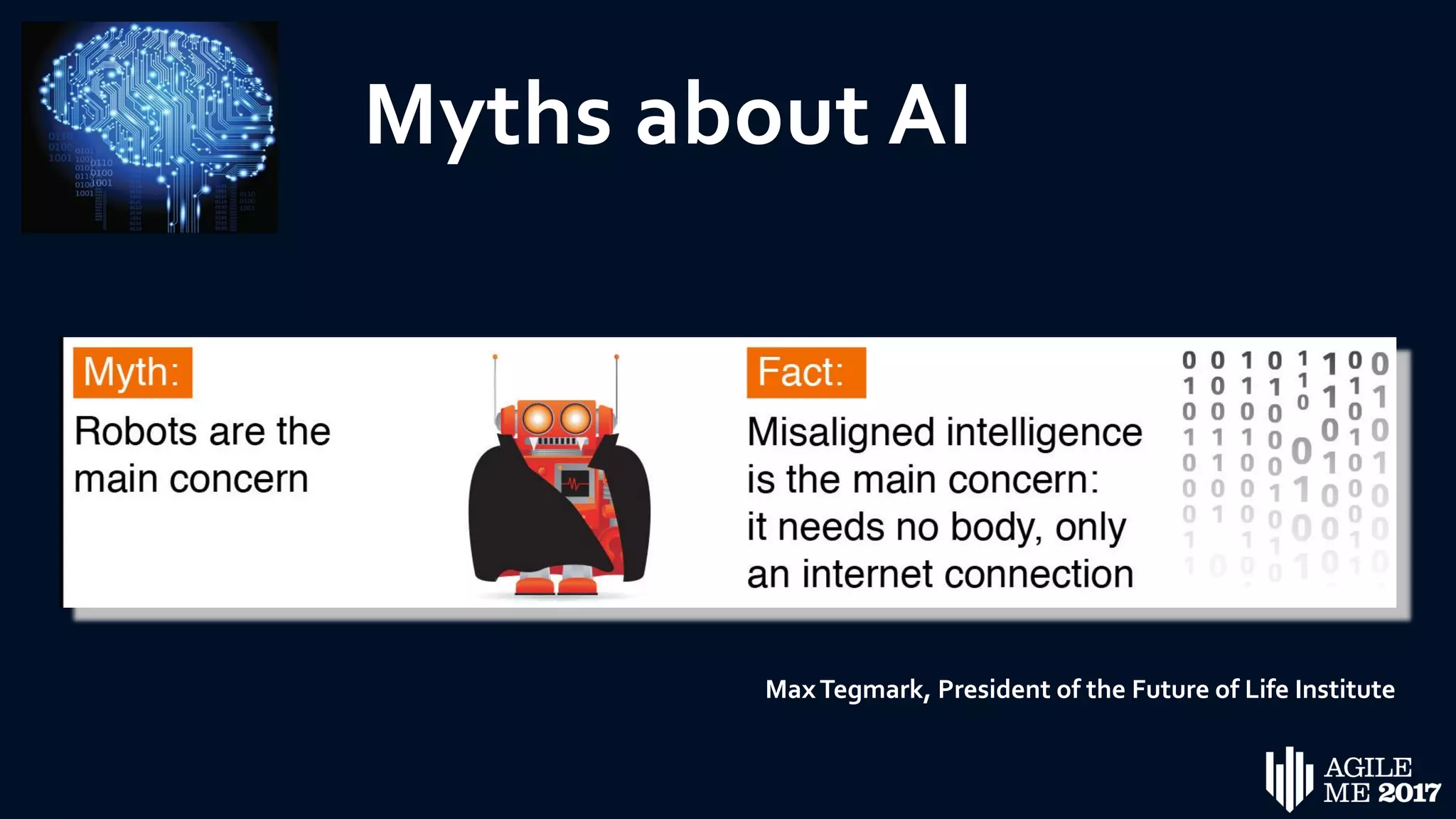
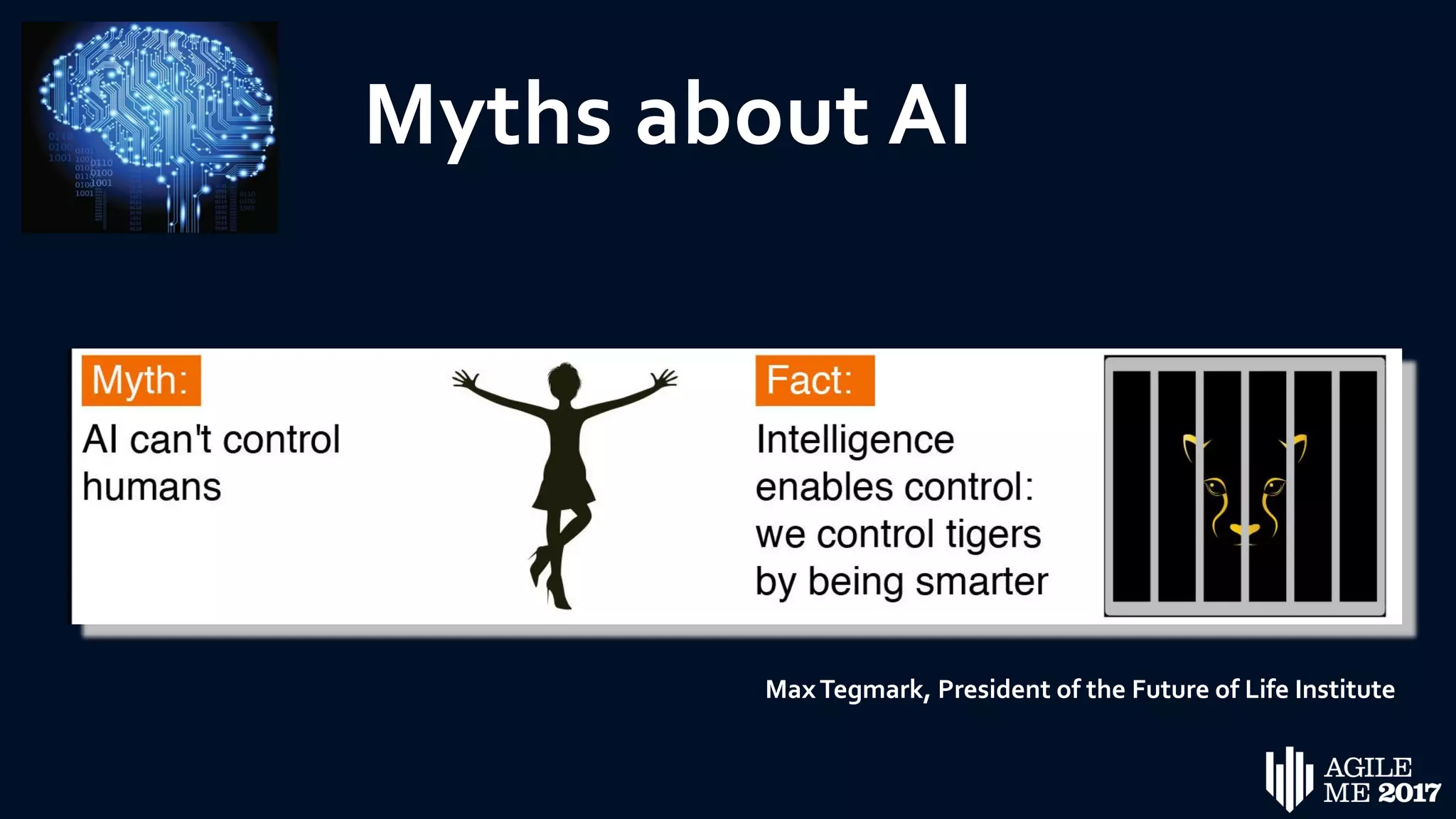
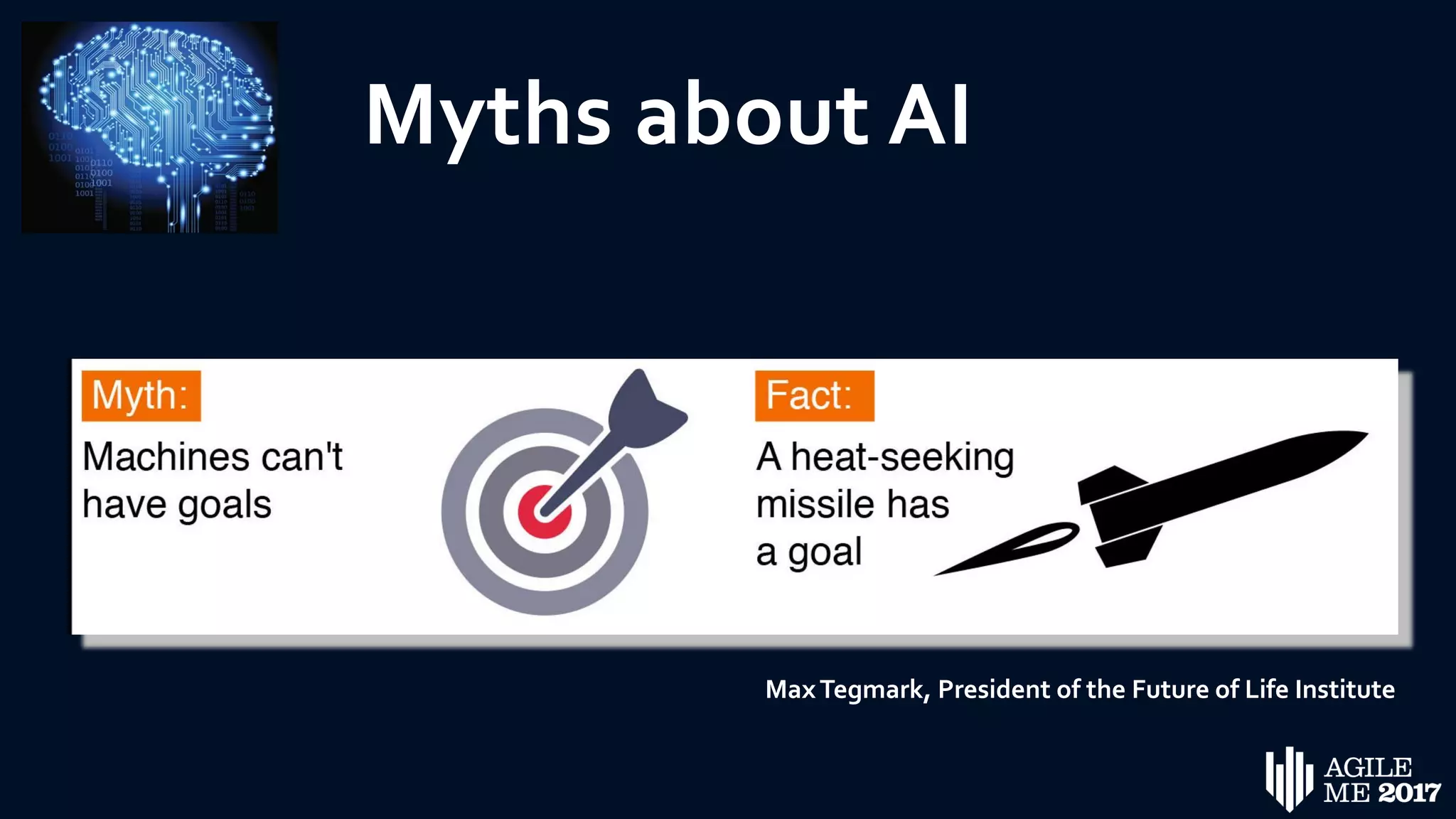
The document discusses the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in project management, including its definitions, history, and various applications such as engineering design, cost estimation, risk management, and performance management. It highlights different AI technologies like expert systems, artificial neural networks, genetic algorithms, and fuzzy logic, emphasizing their potential to improve project efficiency and outcomes. Additionally, it addresses the importance of data mining and knowledge engineering in enhancing resource management practices within the field.