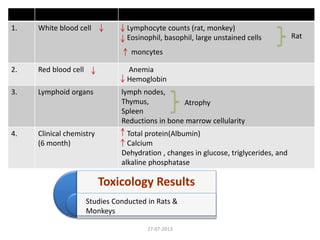
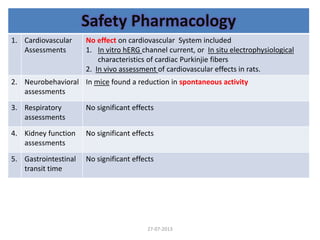
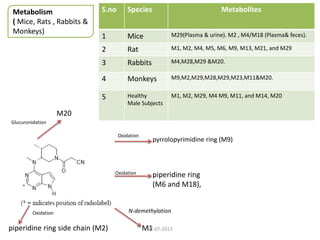
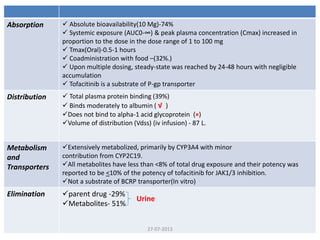
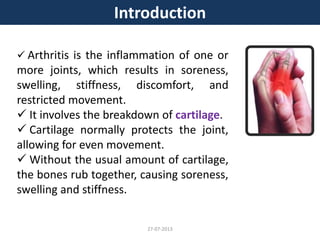
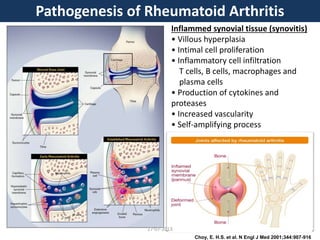
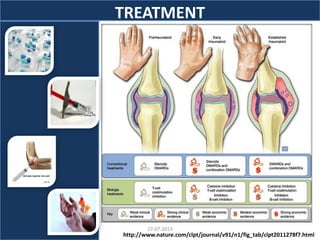
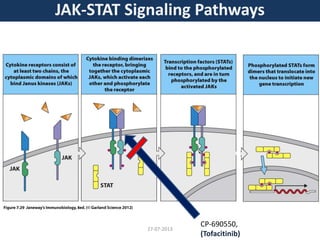
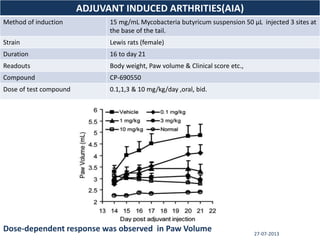
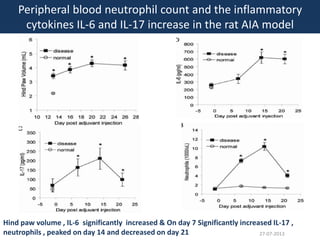
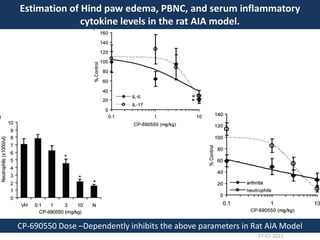
The document discusses tofacitinib, an oral JAK inhibitor drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. It provides background on arthritis, describing the signs and symptoms. It then discusses the mechanism of action of tofacitinib, inhibiting JAK-STAT pathways involved in inflammatory cytokine signaling. Data is presented from preclinical studies in animal models of arthritis showing tofacitinib reduced markers of inflammation and improved arthritis scores in a dose-dependent manner. Clinical trial results demonstrating the drug met efficacy endpoints at a 5 mg twice daily dose are also summarized.







![IUPAC NAME :- 3-[(3R,4R)-4-methyl-3-[methyl(7H-
pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino]piperidin-1-yl]-3-
oxopropanenitrile
STRUCTURE OF CP-690550
CENTER FOR DRUG EVALUATION AND RESEARCH (NDA 213214)
27-07-2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swaroopjcfinal-200608064547/85/ARTHRITIS-and-TOFACITINIB-Discussion-12-320.jpg)
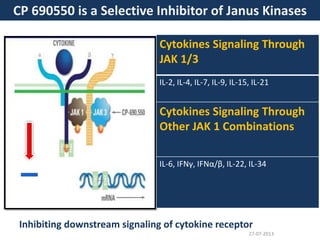
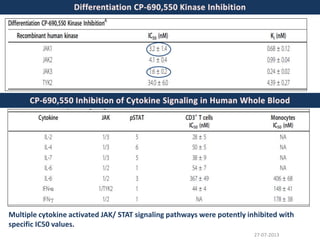
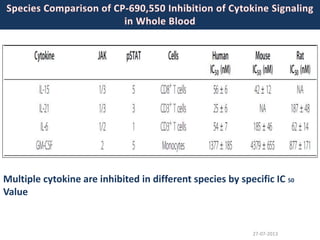
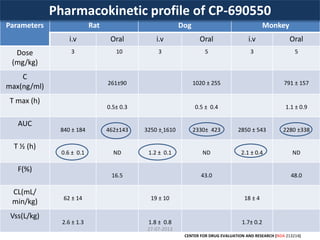
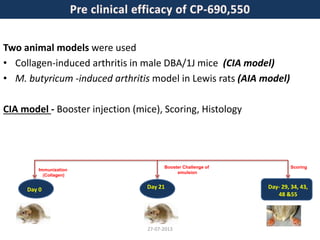
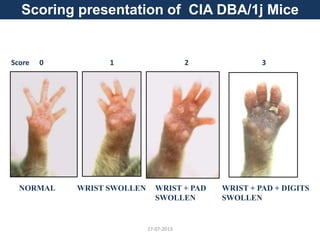
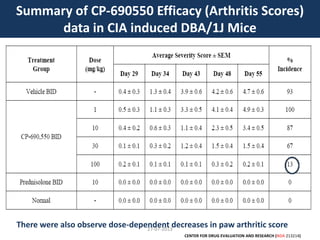
![27-07-2013
Modeled Human Pharmacokinetic Parameters and JAK1/3 and JAK2
IC50 Coverage for CP-690,550
At doses from 5 to 10 mg BID, JAK2 IC50 coverage is insignificant in comparison to JAK1/3
IC50 coverage
Doses as low as 5 mg BID are well-tolerated and efficacious in moderate to severe RA ,
suggesting the importance of JAK1 and JAK3 target coverage in the absence of JAK2
inhibition
A) JAK1/3 human whole blood IC50 (IL-21 dependent pSTAT3) = 25 ± 6 nM; B) Range based on the upper and lower error around the IC50
where available; C ) JAK2 human whole blood IC50 (GM-CSF dependent pSTAT5) = 1377 ± 185 nM; D) GM-CSF stimulated myelomonocytic
HUO3 cell JAK2 IC50 = 324 nM [1].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swaroopjcfinal-200608064547/85/ARTHRITIS-and-TOFACITINIB-Discussion-26-320.jpg)






![Tissue Distribution of CP-690550 (Pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine) in Long-
Evans Male Rats
Post Dosing in each time point One rat was euthanized by CO2 asphyxiation at
0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 72, 168, and 504 hr
Key Study Findings
The distribution of [14C]CP-690550 in blood and 57 tissues of male rats was studied
up to 504 hr following oral administration of 10.0 mg/kg (454 μCi/kg).
Maximum concentrations of [14C]CP-690550 occurred at 0.5 hr for 43 tissues, 1 hr
for 10 tissues and the whole-body, and 12 hr for the uvea.
It across the BBB by 0.5 hr and persisted in all CNS tissues for at least 4 hr.
It distributed into and was eliminated from 47 of 57 tissues by 24 hr following oral
administration.
By 72 hr, only the intervertebral discs, liver, vessel walls, kidneys, and ocular tissues
impregnated with melanin contained measurable levels of [14C]CP- 690550.
By168 and 504, only vessel walls and ocular tissues impregnated with melanin still
had measurable concentrations of [14C]CP-690550.27-07-2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swaroopjcfinal-200608064547/85/ARTHRITIS-and-TOFACITINIB-Discussion-39-320.jpg)