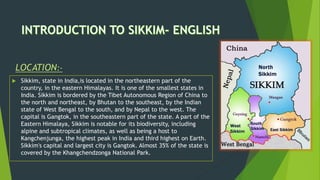
The document provides information about the Indian state of Sikkim through several sections. It discusses Sikkim's location in the eastern Himalayas and shares its official languages which include Nepali, Sikkimese, and Lepcha. The summary also describes Sikkim's traditional dress called Kho or Bakhu worn by Sikkimese people and provides examples of popular tourist destinations in Sikkim like Gangtok, Yumthang Valley, and Tsomgo Lake. In addition, the summary mentions that Sikkim has a largely organic farming system growing crops like rice, potatoes and cardamom and cash crops like bananas which are a nutritious food source. Finally, it highlights how S