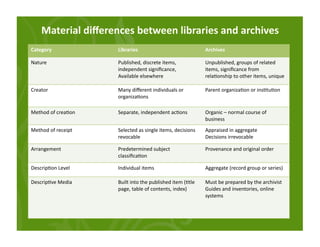
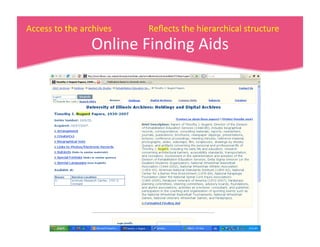
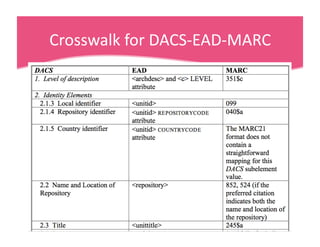
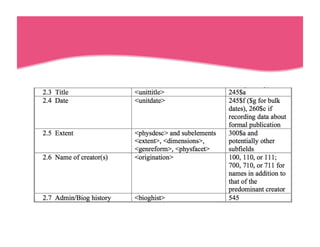
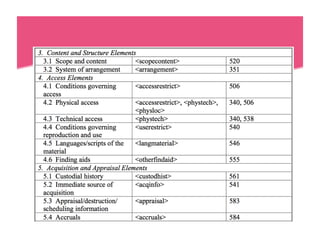
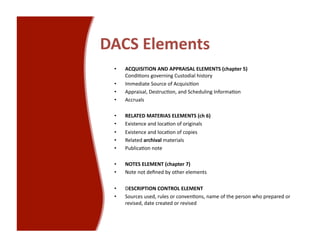
This document provides an overview of archives, archival description standards, and finding aids. It defines what archives are, distinguishing them from libraries. It describes the archival mission to identify, preserve, and provide access to materials of enduring value. Key aspects covered include the Descriptive Archival Content Standard (DACS), the Encoded Archival Description (EAD) standard for encoding archival finding aids, and how EAD maps to MARC21 fields. The document compares the differences between libraries and archives and outlines the core elements in DACS for archival description.