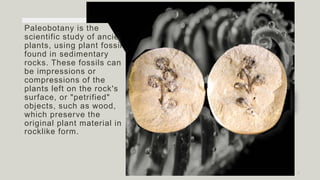
Paleobotany is the study of ancient plants through fossils found in sedimentary rocks. Archaeologists use various techniques like dry and wet screening to process artifacts, which provide insights into past human life. The conservation of archaeological records is crucial for understanding history and is guided by ethical principles.