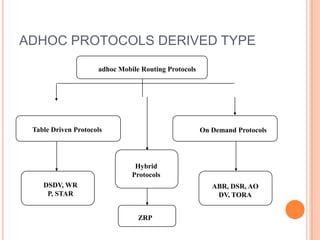
This document discusses routing in ad hoc networks. It begins by defining an ad hoc network as a collection of mobile wireless nodes that form a network without any infrastructure or centralized administration. It describes some key differences between ad hoc and normal wireless networks. It then discusses different types of routing protocols that can be used in ad hoc networks, including proactive, reactive, hybrid, and power-aware protocols. It also covers some security challenges in ad hoc networks and discusses energy efficient routing protocols like DSR and MBCR. It concludes by discussing advantages and disadvantages of ad hoc networks and opportunities for future research.