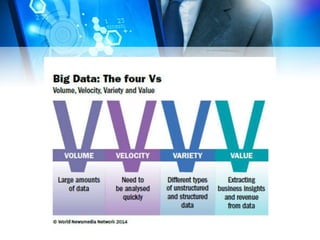
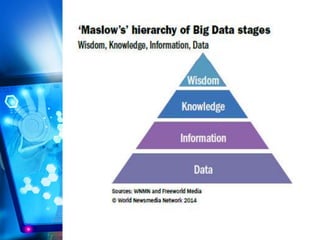
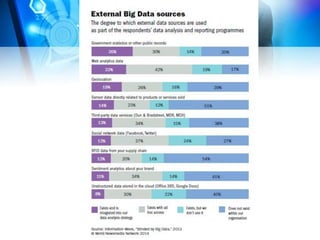
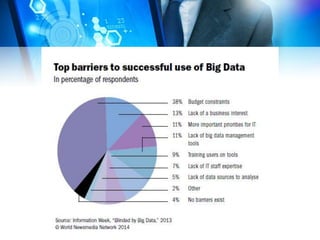
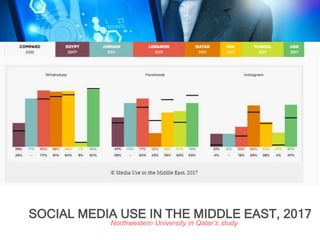
This document discusses big data and computational journalism. It defines big data as large volumes of data that require new technologies to analyze effectively. Computational journalism is described as journalistic work that combines traditional journalism and computing, using tools like data analysis and automation. The document then examines how media organizations can use big data strategies for audience analytics, database mining for stories, managing large amounts of content, and targeted advertising. It provides an overview of social media use and data journalism development in the Middle East and North Africa region, including examples from Tunisia, Egypt, and training programs since the Arab Spring.