1) Combination therapy with two or more antihypertensive drugs from different classes is more effective at lowering blood pressure and helping more patients achieve target blood pressure goals than initiating treatment with a single drug alone (monotherapy).
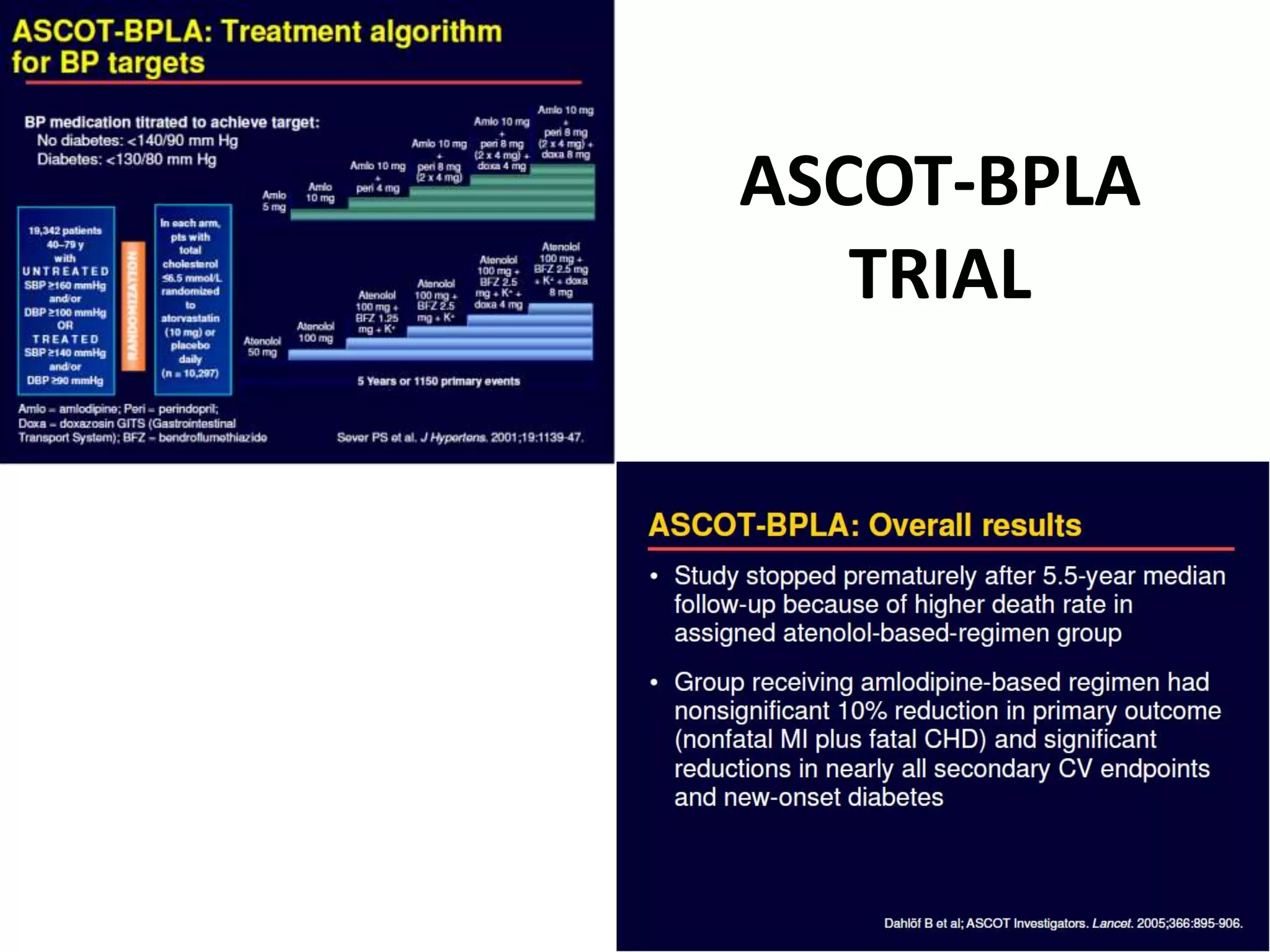
2) Several major clinical trials have demonstrated that initiating treatment for hypertension with combination therapy results in greater reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure compared to traditional stepped-care approaches starting with monotherapy.
3) Combination therapy may also help improve patient adherence and reduce withdrawals from therapy due to adverse effects compared to multiple medication changes involved in stepped-care approaches.

























































![Half the standard dose HCTZ – 6.25mg
• Enalapril + 6 mg HCTZ vs. Enalapril
– Significant reduction in mean BP (p<0.01) by 7.3mmHg (95% CI, -9.0; -6.2)
compared to Enalapril alone [4.1mmHg (-5.9; -2.9)]
– Synergistic with enalapril with absence of metabolic adverse effects
• Moexipril 3.75mg and 6.25 mg HCTZ
– Significantly reduced seating SBP and DBP (-7.6/-7.6mmHg) vs placebo (n=223;
+0.2/-3.9mmHg; p<0.05)
– 54% patients achieved good BP response (SDBP < or =90 mm Hg or > 10 mm
Hg decrease from baseline) vs 28% on placebo (p<0.001)
– Similar clinical and metabolic side-effects between the combination and
placebo groups
60
Am J Hypertens.1995 Jul;8(7):727-31, J CardiovascPharmacol. 1998 Mar;31(3):384-90](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approachtohypertension-combinationtherapy-220504162633/75/Approach-to-Hypertension-Combination-therapy-pptx-60-2048.jpg)

























