1. Pulmonary hypertension is not as rare as previously thought and can be diagnosed using echocardiography. Survival rates decrease significantly as estimated right ventricular systolic pressure increases.
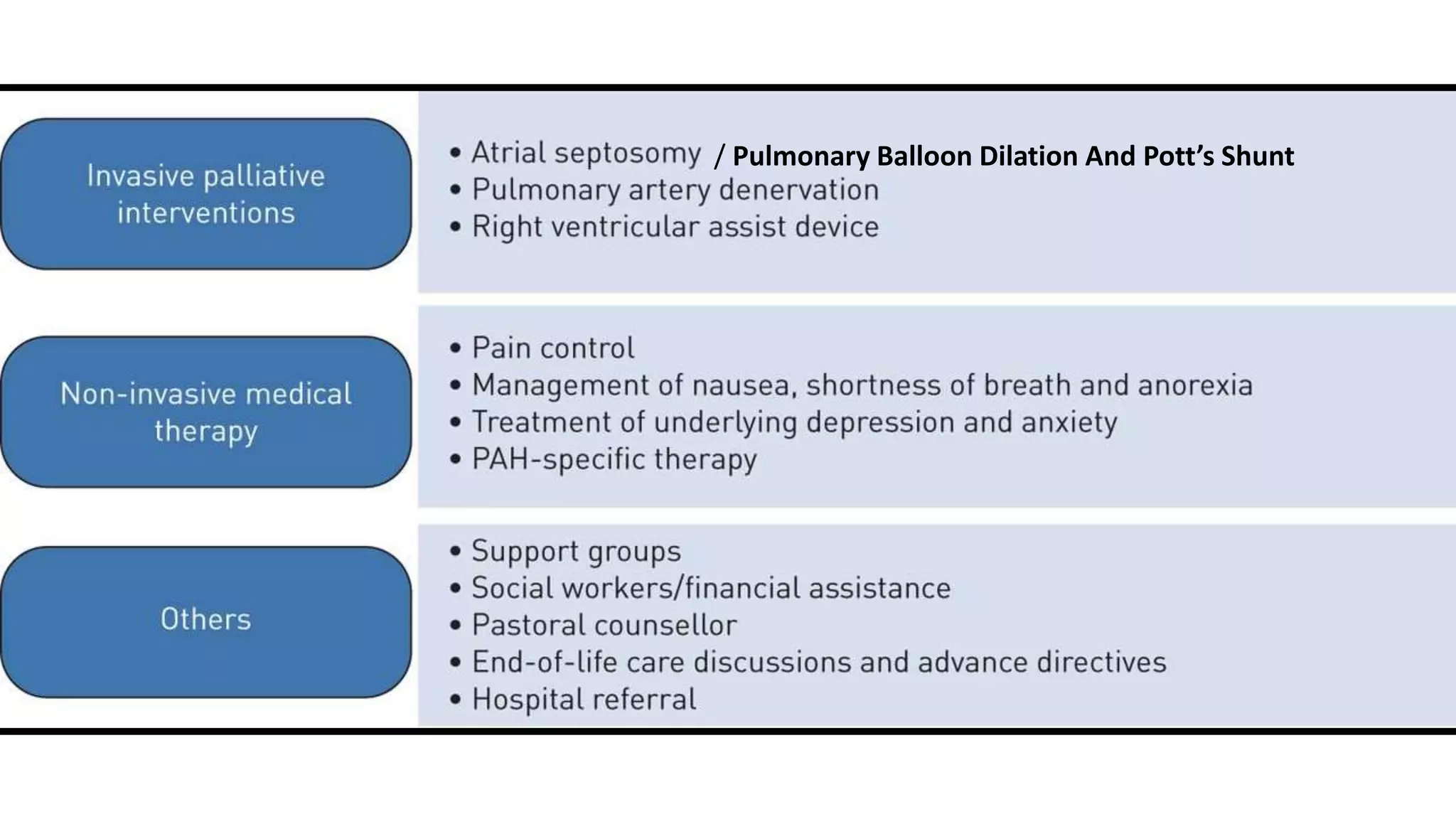
2. While pulmonary hypertension remains largely untreatable, treatment options include pulmonary vasodilator medications, balloon dilation, surgical shunts, and newer interventions like pulmonary artery denervation.
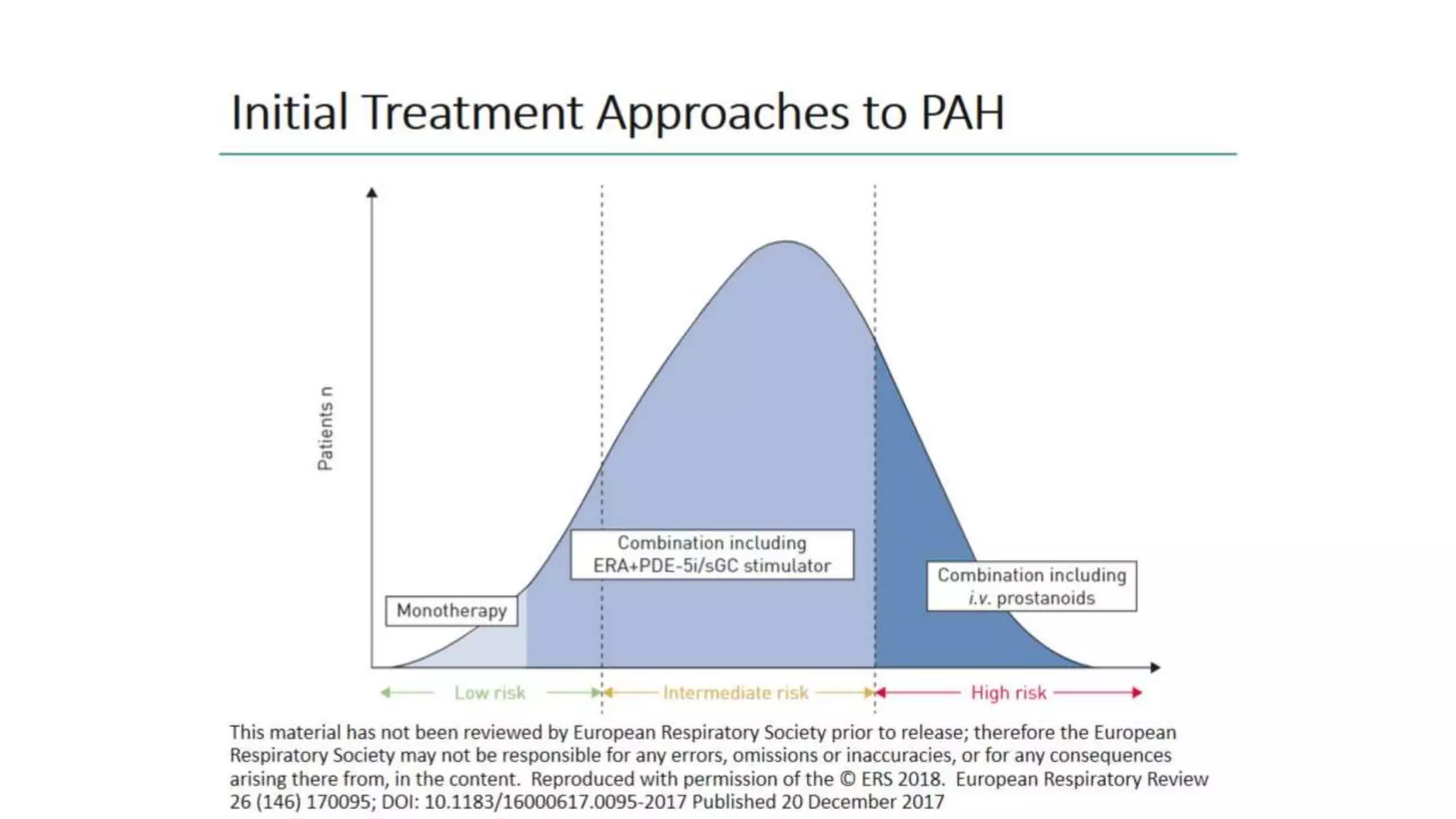
3. Combination drug therapy using multiple pulmonary vasodilators is now the standard of care approach and has been shown in studies to reduce clinical worsening events and improve survival compared to monotherapy. Initial triple oral therapy may provide additional benefits over initial double therapy.









































![Combination therapy versus monotherapy for pulmonary
arterial hypertension: a meta-analysis Lancet Respir Med 2016
Combined therapy was associated with significant risk
reduction for clinical worsening compared with monotherapy
(combined therapy 17% [332 of 1940 patients] vs
monotherapy 28% [517 of 1862 patients], risk ratio [RR] 0·65
[95% CI 0·58–0·72], p<0·00001).
Combination therapy, either upfront or sequential, is progressively
becoming the standard of care in PAH. This meta-analysis provides
strong evidence supporting this treatment strategy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managementofpah-220504162753/75/Management-of-PAH-pptx-43-2048.jpg)








![Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Oral Versus Initial
Double Oral Combination Therapy in Patients with
Newly Diagnosed Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
(PAH): Results of the Randomized Controlled TRITON Study
POSTER AT ESC 2020 - 29 AUG 2020
Initial triple oral therapy was associated with a 41 % reduction in the risk of
first disease progression event compared to initial oral double therapy at an
average follow up of 77.6 and 75.8 weeks, respectively.
Sixteen initial disease progression events were observed in patients taking
initial triple oral therapy, and 27 events were observed in patients taking initial
double oral therapy (hazard ratio 0.59; [CI]; 0.32, 1.09).
Two patients died in the initial triple therapy group (1.7 percent) compared to
nine (7.1 percent) in the initial double therapy group up to the end of the main
observation period (hazard ratio 0.23; CI 0.05, 1.04).
These results are not statistically significant and should be interpreted as
exploratory considering the primary endpoint was not met.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managementofpah-220504162753/75/Management-of-PAH-pptx-53-2048.jpg)



























