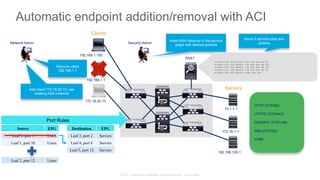
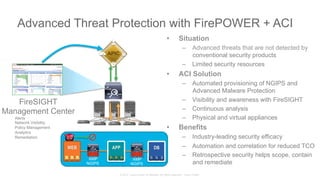
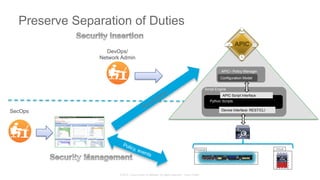
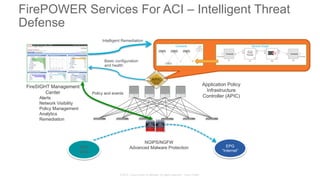
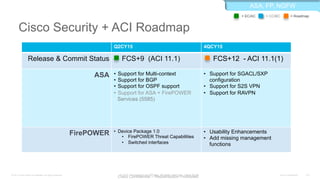
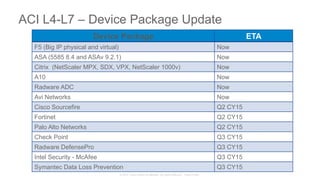
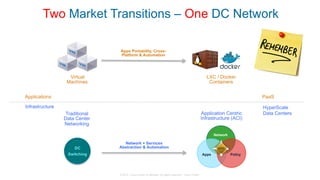
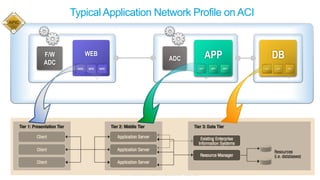
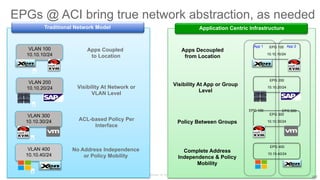
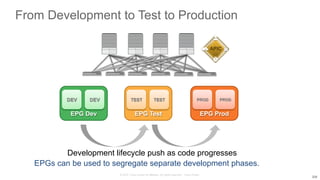
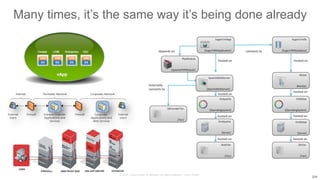
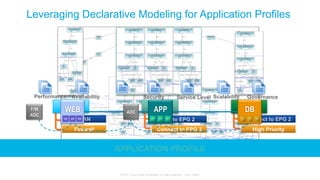
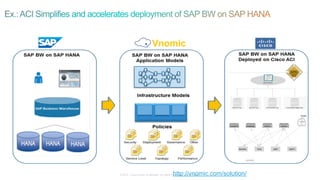
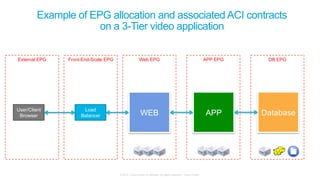
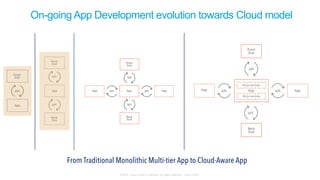
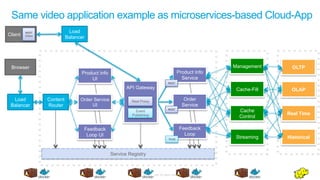
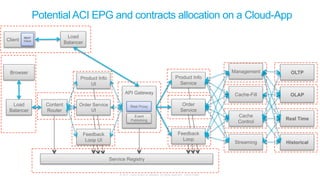
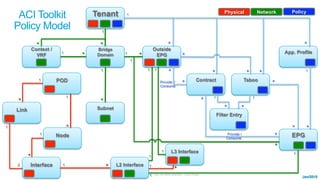
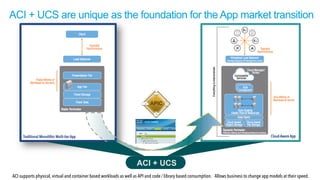
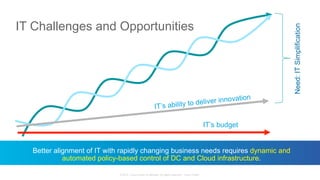
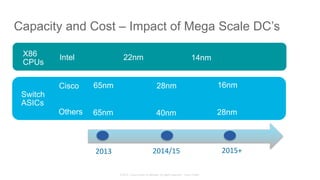
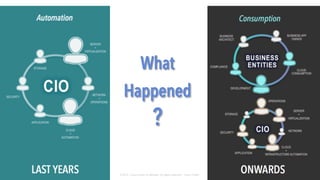
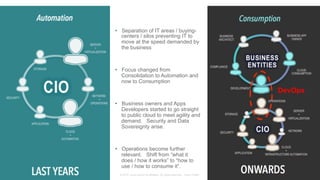
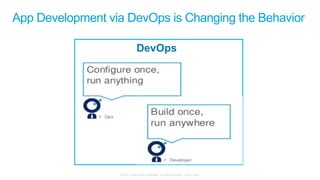
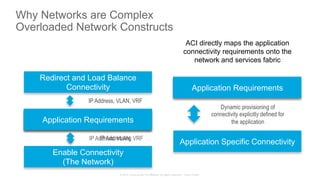
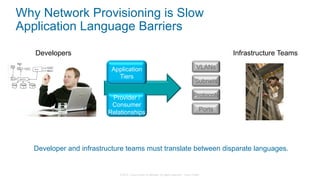
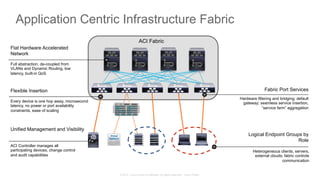
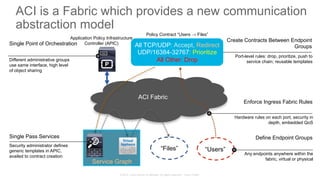
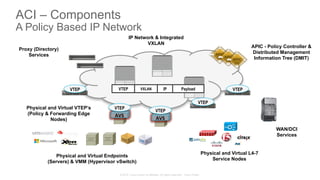
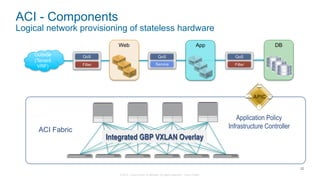
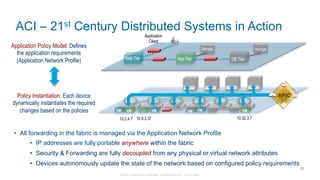
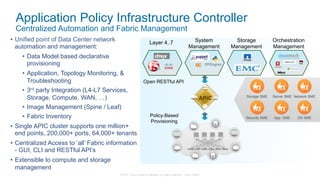
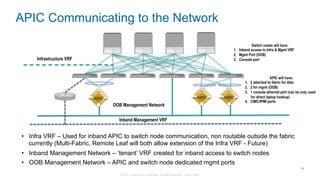
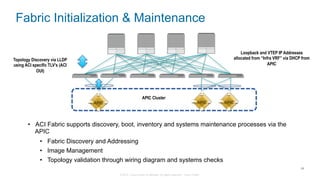
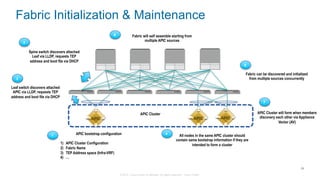
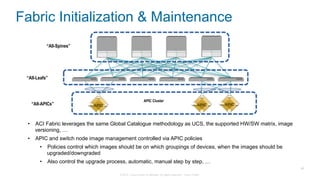
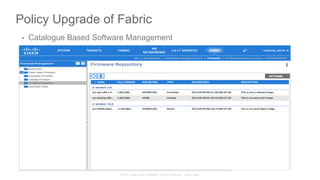
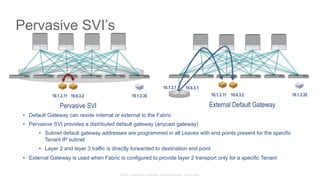
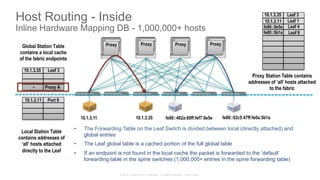
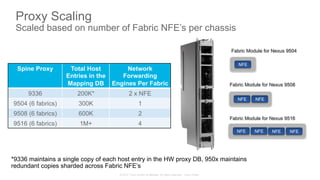
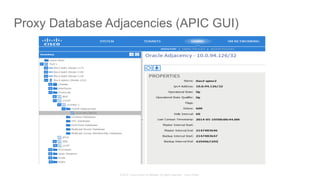
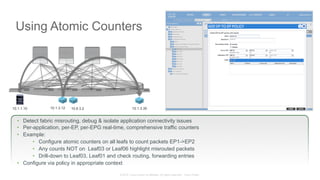
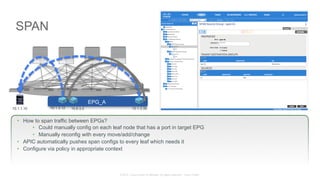
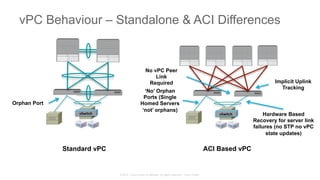
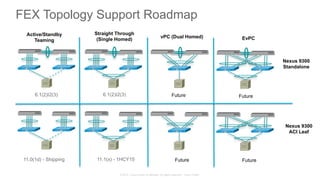
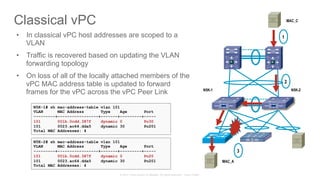
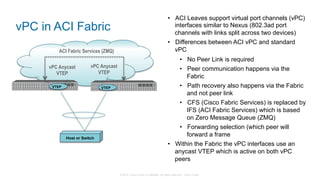
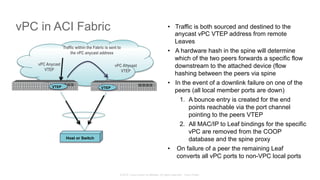
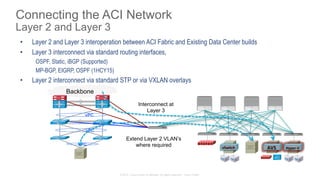
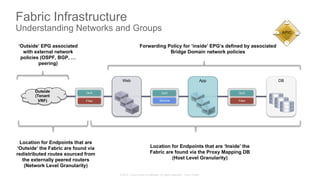
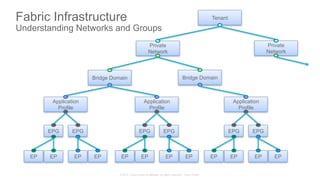
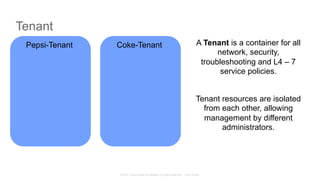
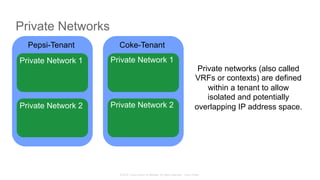
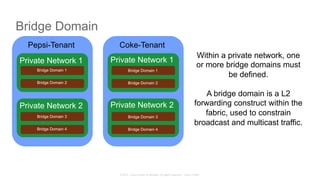
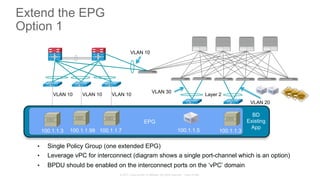
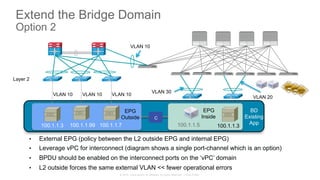
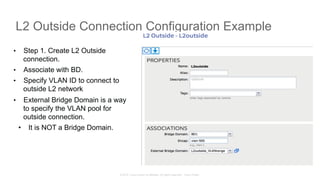
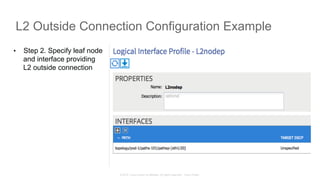
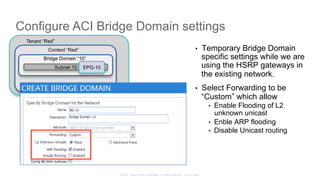
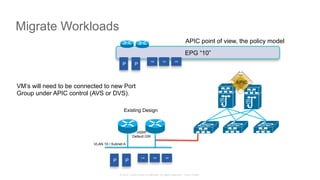
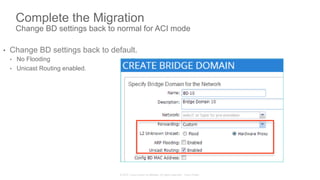
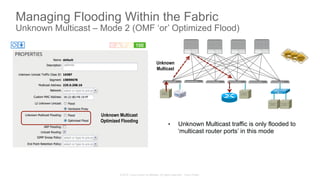
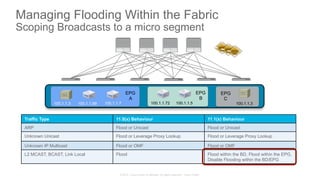
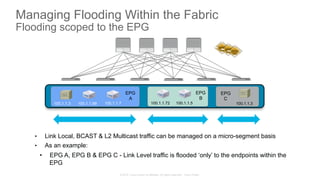
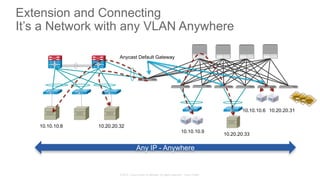
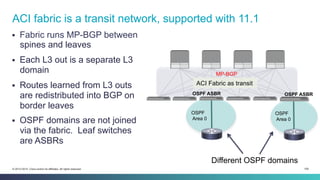
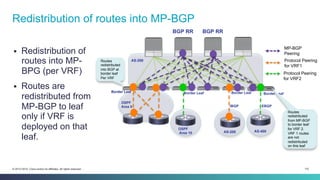
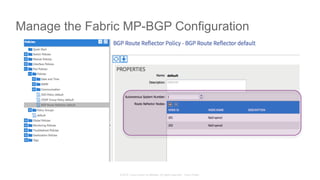
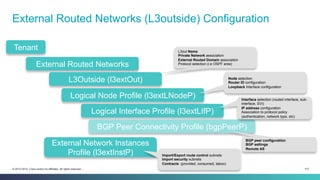
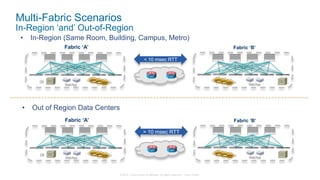
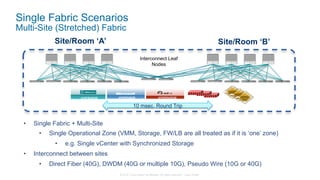
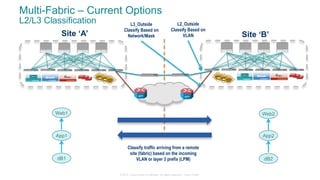
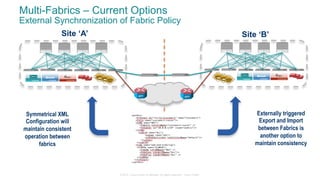
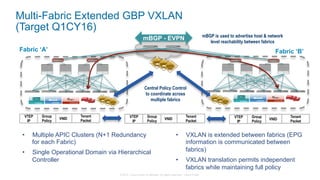
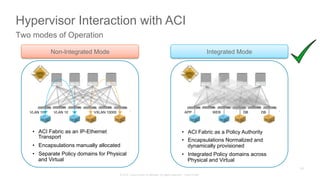
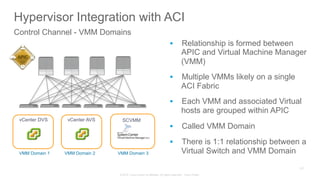
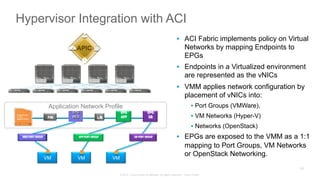
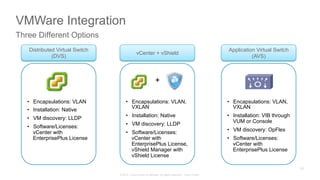
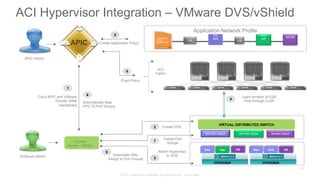
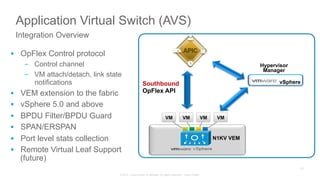
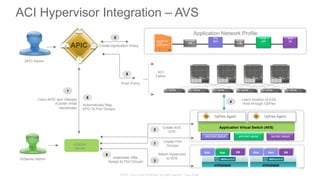
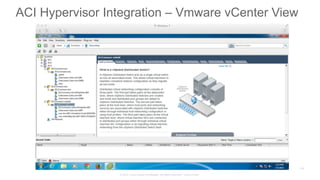
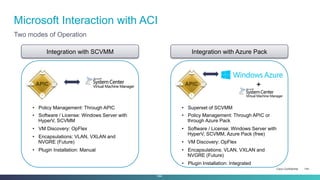
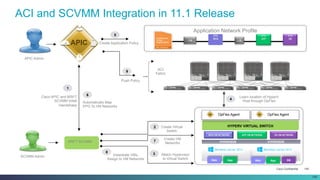
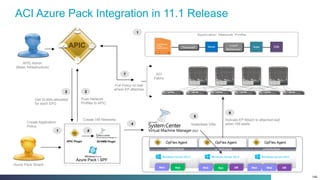
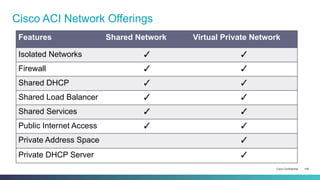
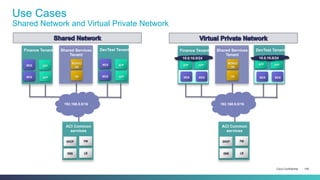
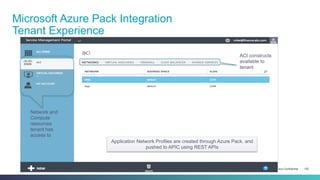
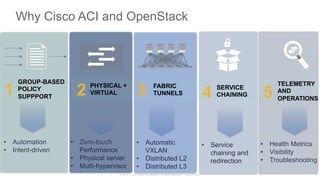
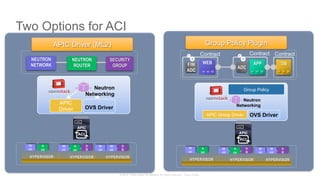
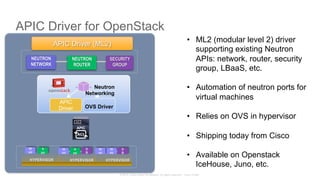
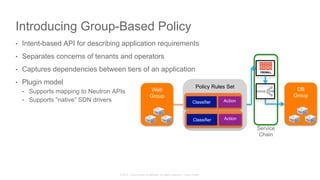
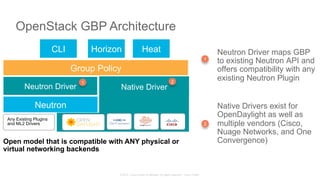
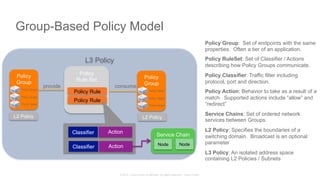
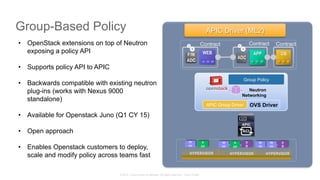
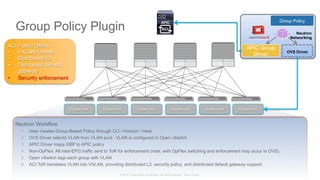
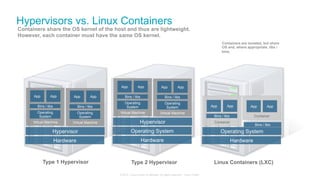
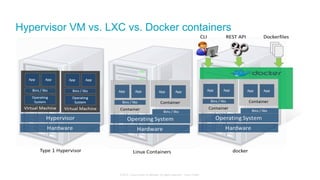
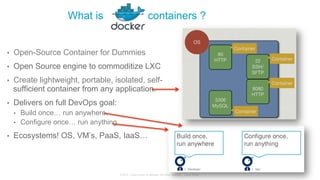
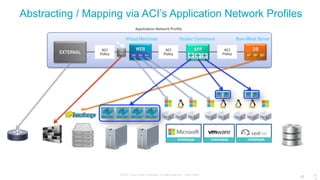
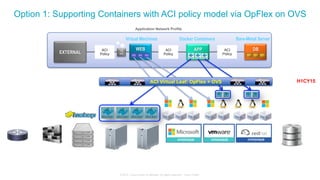
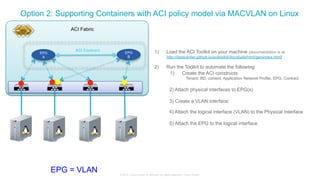
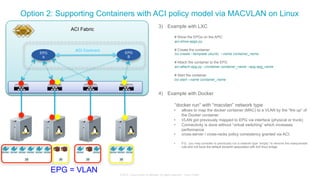
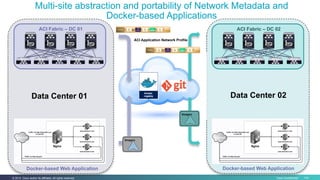
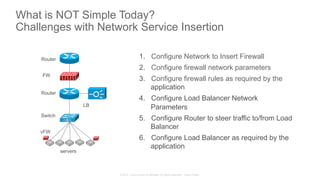
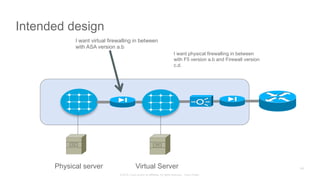
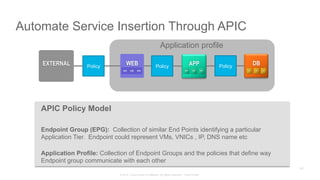
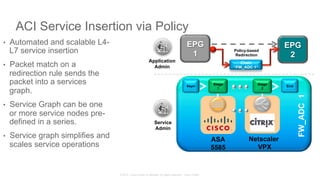
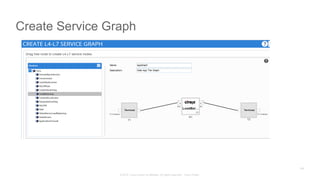
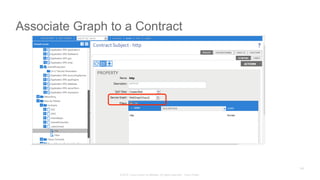
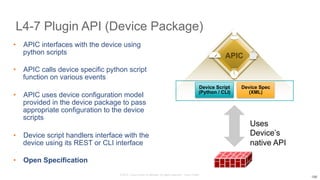
The document discusses Cisco's Application Centric Infrastructure (ACI), which aims to simplify and automate data center and cloud infrastructure management through a policy-driven model. It highlights the challenges faced by IT in adapting to rapid business changes and the shift towards automated, consumption-based models in application development. ACI's architecture emphasizes decoupling application requirements from physical network constraints and provides a unified management platform for enhanced visibility and control across devices.








![© 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
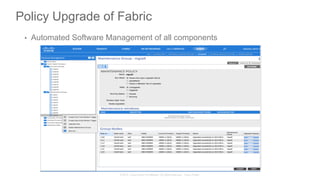
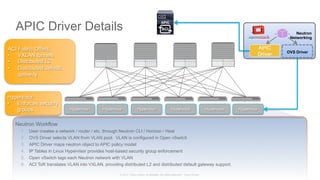
APIC first time Setup
• APIC one time setup is via UCS console access
• Cluster configuration
• Fabric Name
• Number of controllers [1..9]
• Controller ID [1..9]
• TEP Address pool [10.0.0.1/16]
• Infra VLAN ID [4093]
• Out-of-band management configuration
• Management IP address [192.168.10.1/254]
• Default gateway [192.168.10.254]
• Admin user configuration
• Enable strong passwords (Y/N)
• Password
After first time setup, APIC UI is
accessible via URL
https://<APIC-mgmt-IP>
APIC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationcentricinfrastructurethepolicydrivendatacenter-150610171635-lva1-app6892/85/Application-Centric-Infrastructure-ACI-the-policy-driven-data-centre-26-320.jpg)




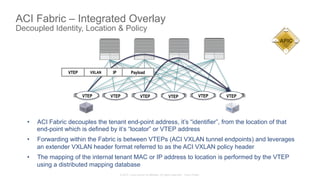

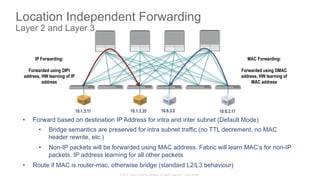
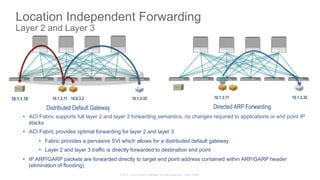



























![© 2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Cisco Public
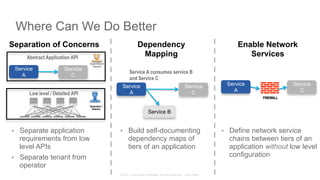
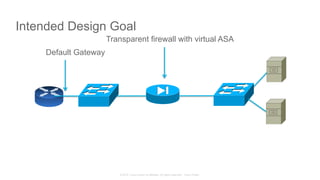
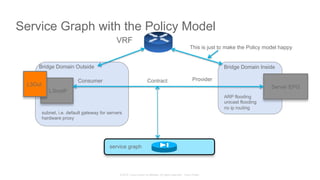
Service Configuration before the Service Graph
192.168.1.1 192.168.1.100
10.1.1.1
172.16.1.1
192.168.100.1
HTTP (TCP/80)
HTTPS (TCP/443)
DCERPC (TCP/135)
SSH (TCP/22)
ICMP
access-list OUT permit tcp host 192.168.1.1 host 10.1.1.1 eq 80
access-list OUT permit tcp host 192.179.1.1 host 10.1.1.1 eq 443
[…]
access-list OUT permit icmp host 192.168.1.100 host 192.168.100.1
30 ACL Rules
172.18.20.13
access-list OUT permit tcp host 172.18.20.13 host 10.1.1.1 eq 80
access-list OUT permit tcp host 172.18.20.13 host 10.1.1.1 eq 443
[…]
access-list OUT permit icmp host 172.18.20.13 host 192.168.100.1
15 ACL Rules
45 ACL Rules
Network Admin Security Admin
Add client 172.18.20.13,
call Security Admin to
enable access
Remove client 192.168.1.1, “no
other action necessary”
Add ASA rules for client
172.18.20.13
Original ASA rules never
change4
1
2
2
3
4
Files
Users](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationcentricinfrastructurethepolicydrivendatacenter-150610171635-lva1-app6892/85/Application-Centric-Infrastructure-ACI-the-policy-driven-data-centre-190-320.jpg)