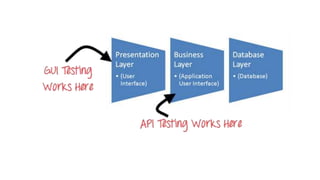
API testing validates application programming interfaces (APIs). API testing focuses on functionality, reliability, performance, and security of programming interfaces. Common protocols for API testing include HTTP, REST, SOAP, JMS, and UDDI. REST uses normal HTTP verbs like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE and supports data formats like plain text, HTML, XML, and JSON. CRUD (create, read, update, delete) operations can be performed through HTTP requests in API testing.