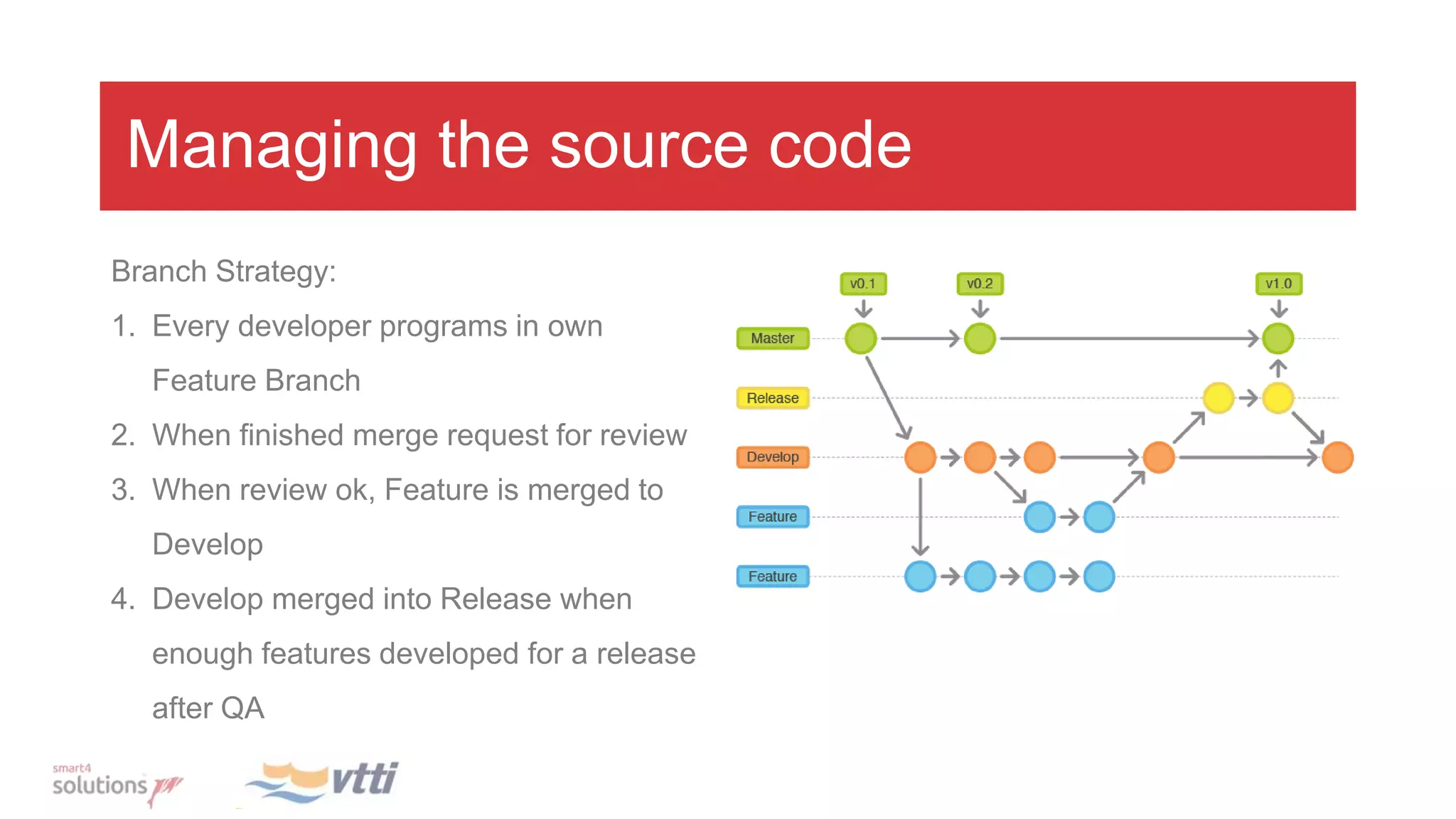
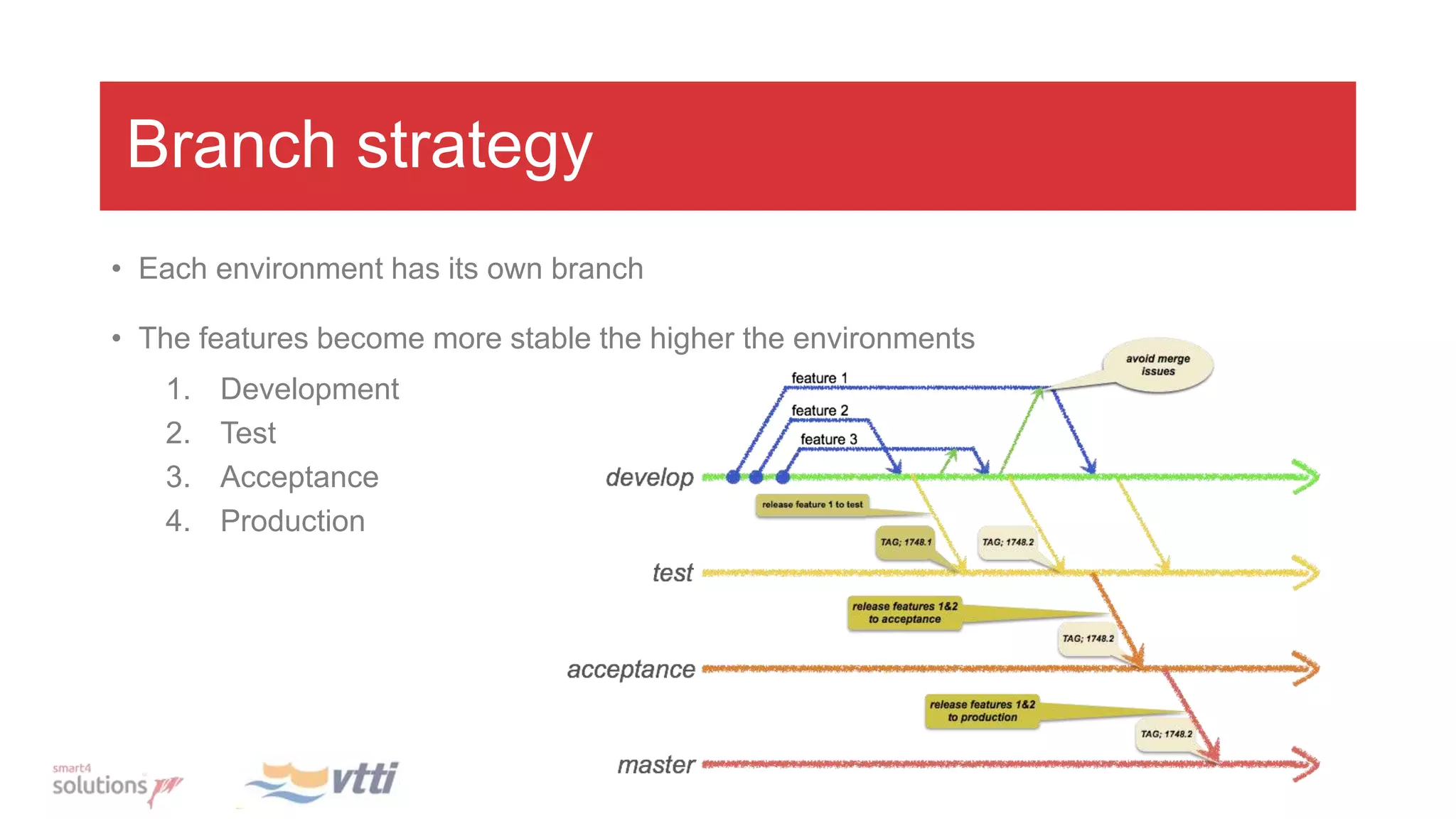
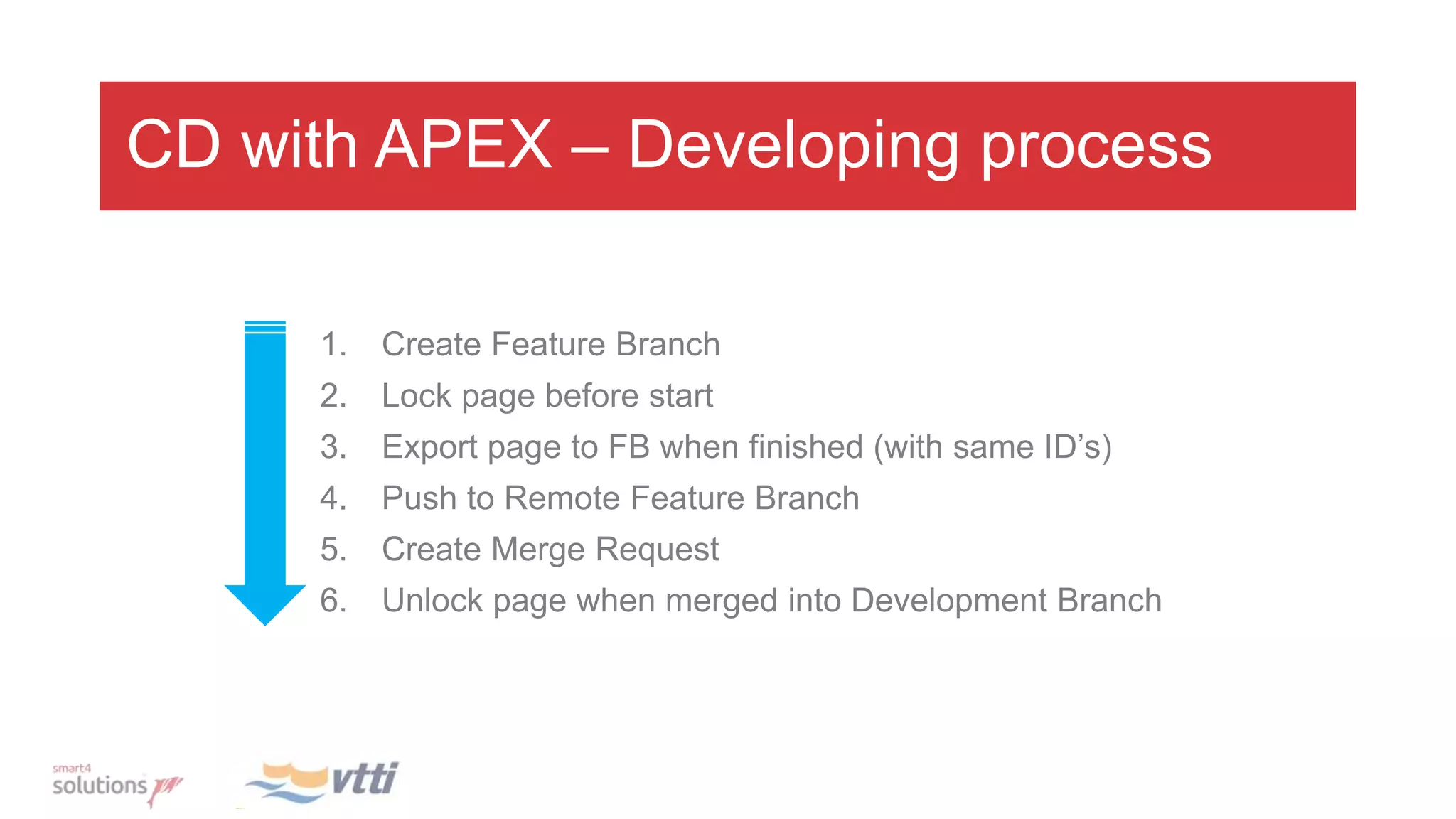
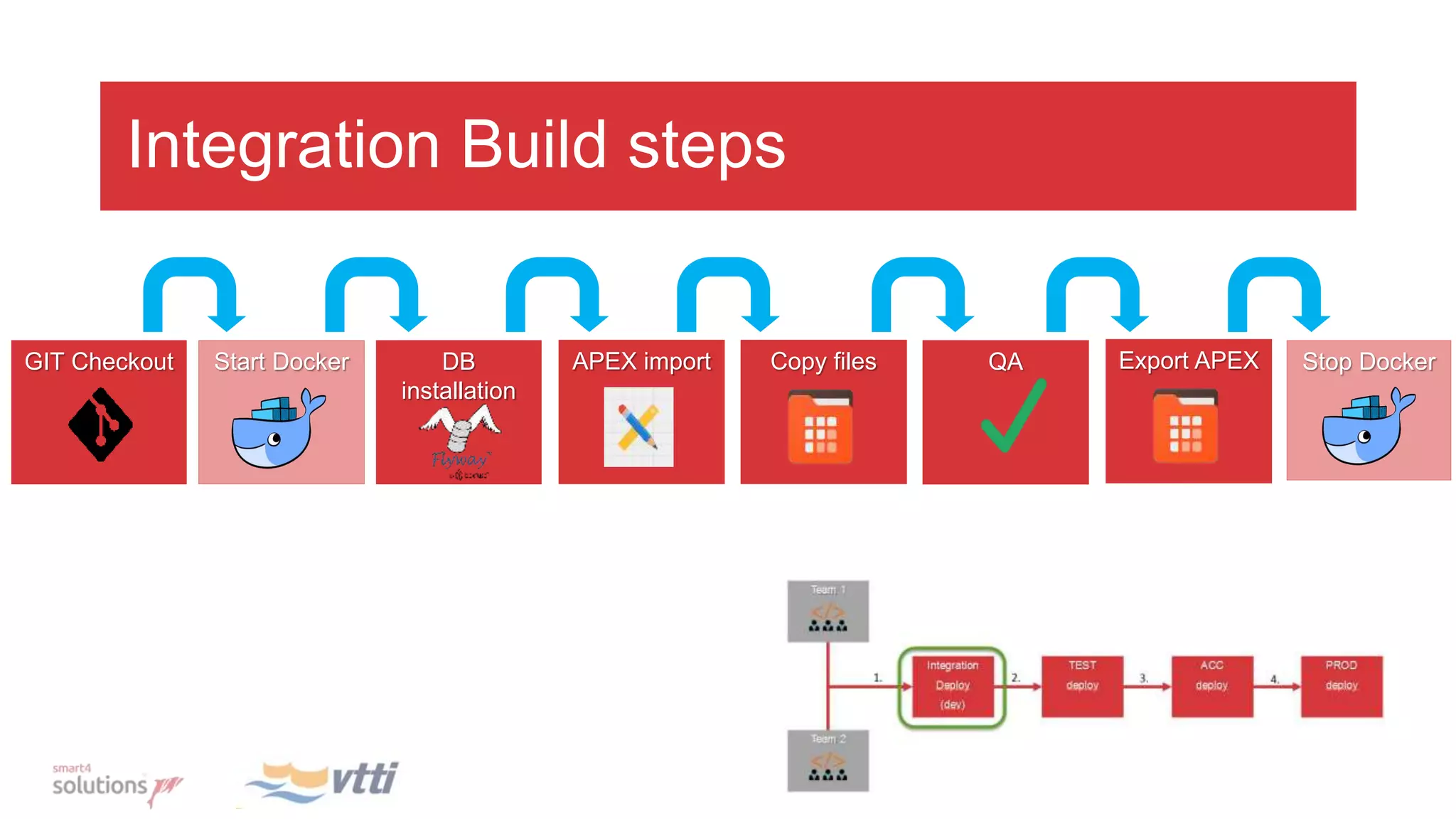
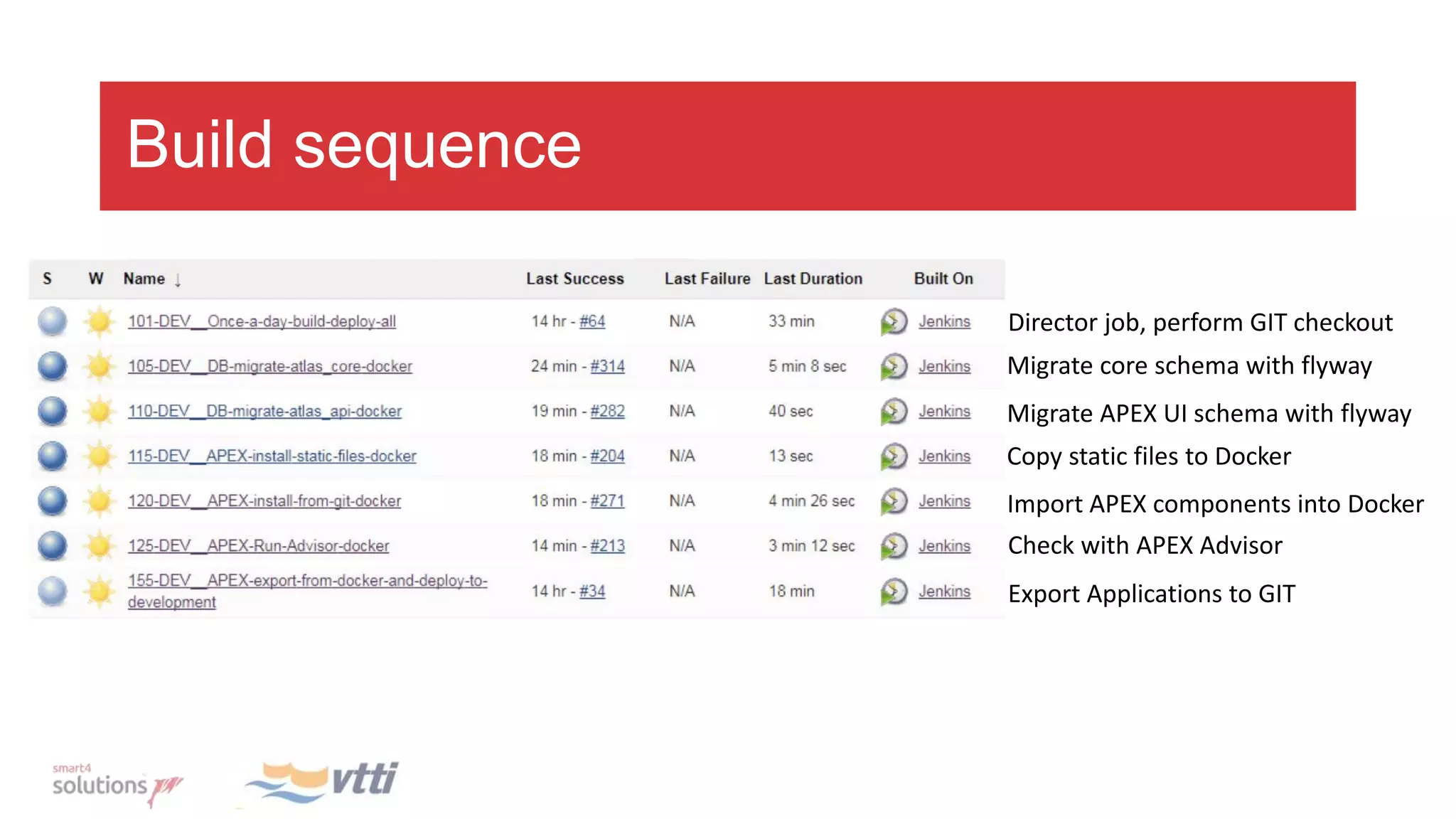
This document discusses continuously delivering APEX applications. It outlines managing source code using feature branches and merging into development, test, acceptance, and production branches. Flyway is introduced for database version management and tracking changes. The development process involves locking pages during development, exporting on completion, and merging to remote branches. Integration builds involve checking out code, installing the database with Flyway, importing and exporting APEX, and using Docker and Jenkins for automation and rollback capabilities.