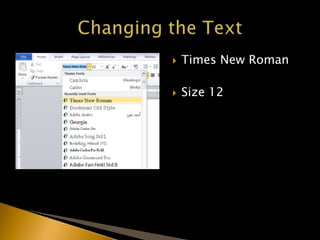
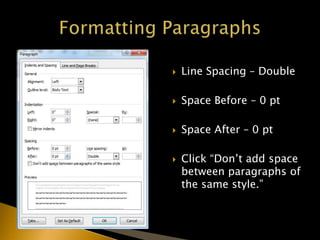
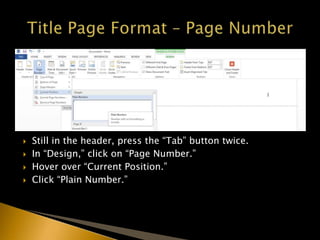
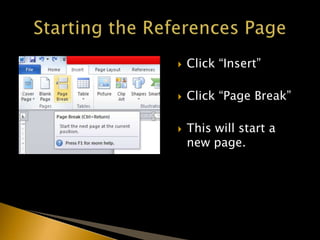
The document outlines the APA citation style including guidelines on formatting, in-text citations, and referencing sources. It emphasizes the importance of proper citations to avoid plagiarism and to give credit for ideas and work. Additionally, it provides detailed instructions on how to structure papers, create a references page, and implement various citation formats.