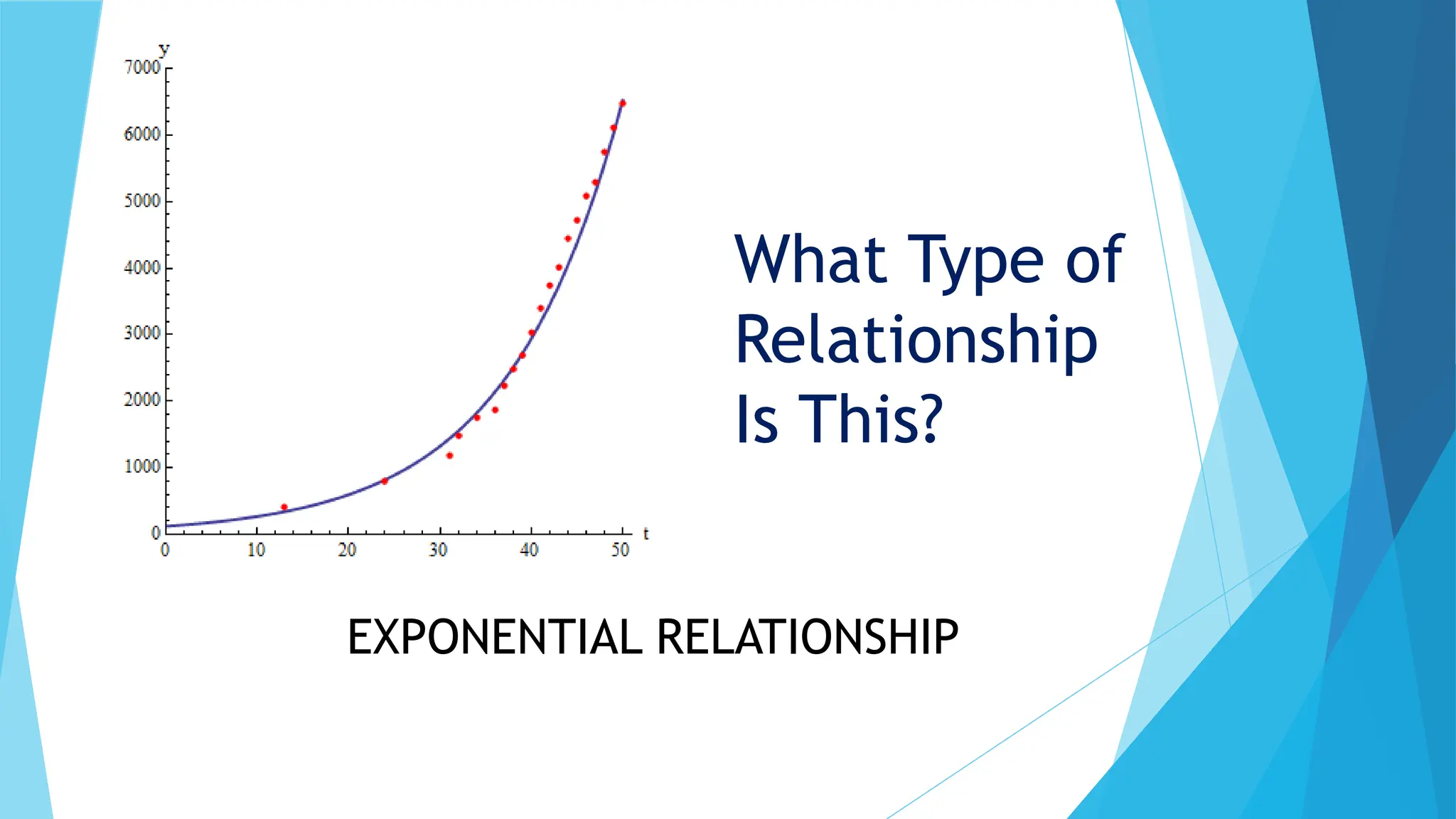
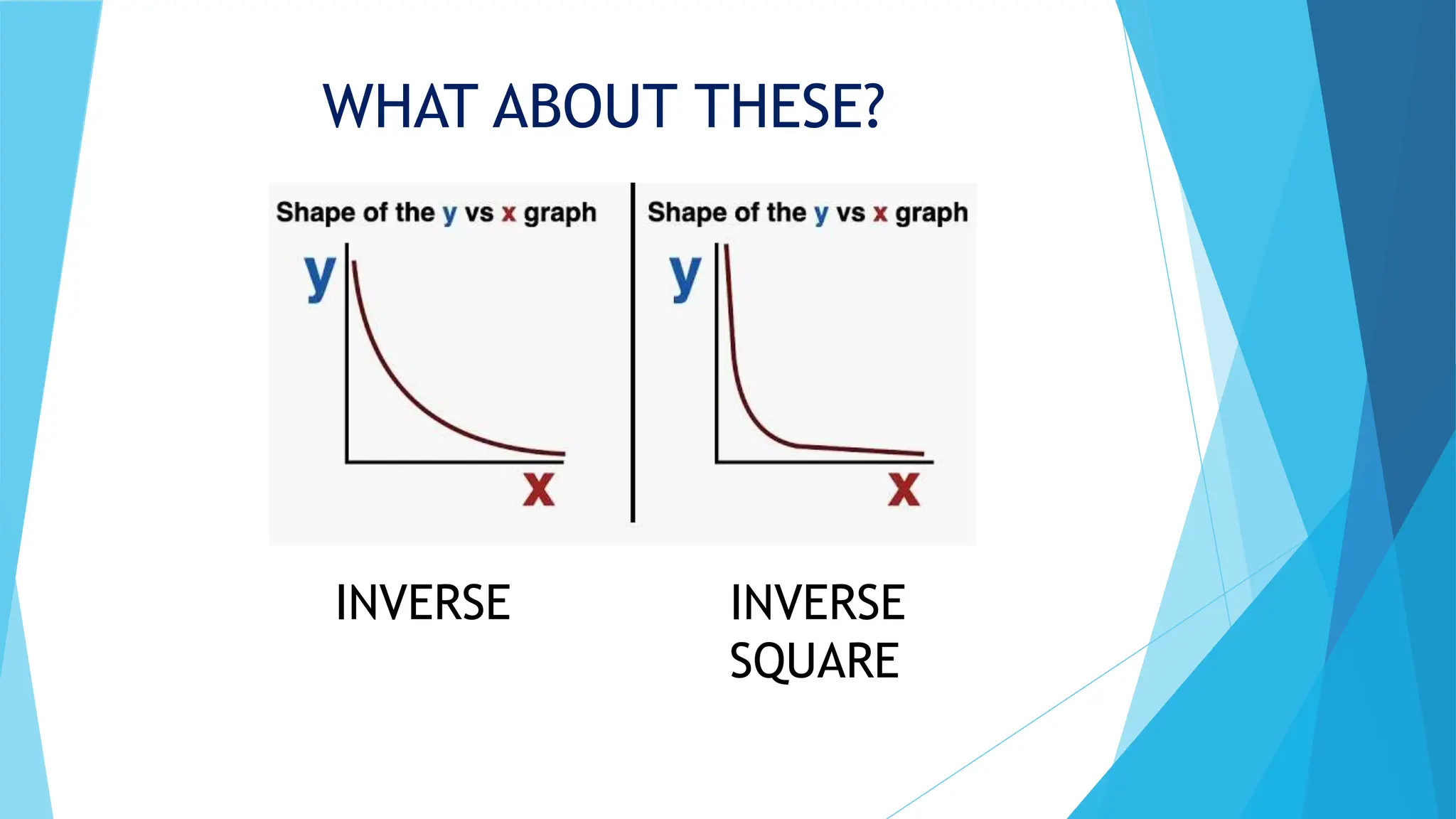
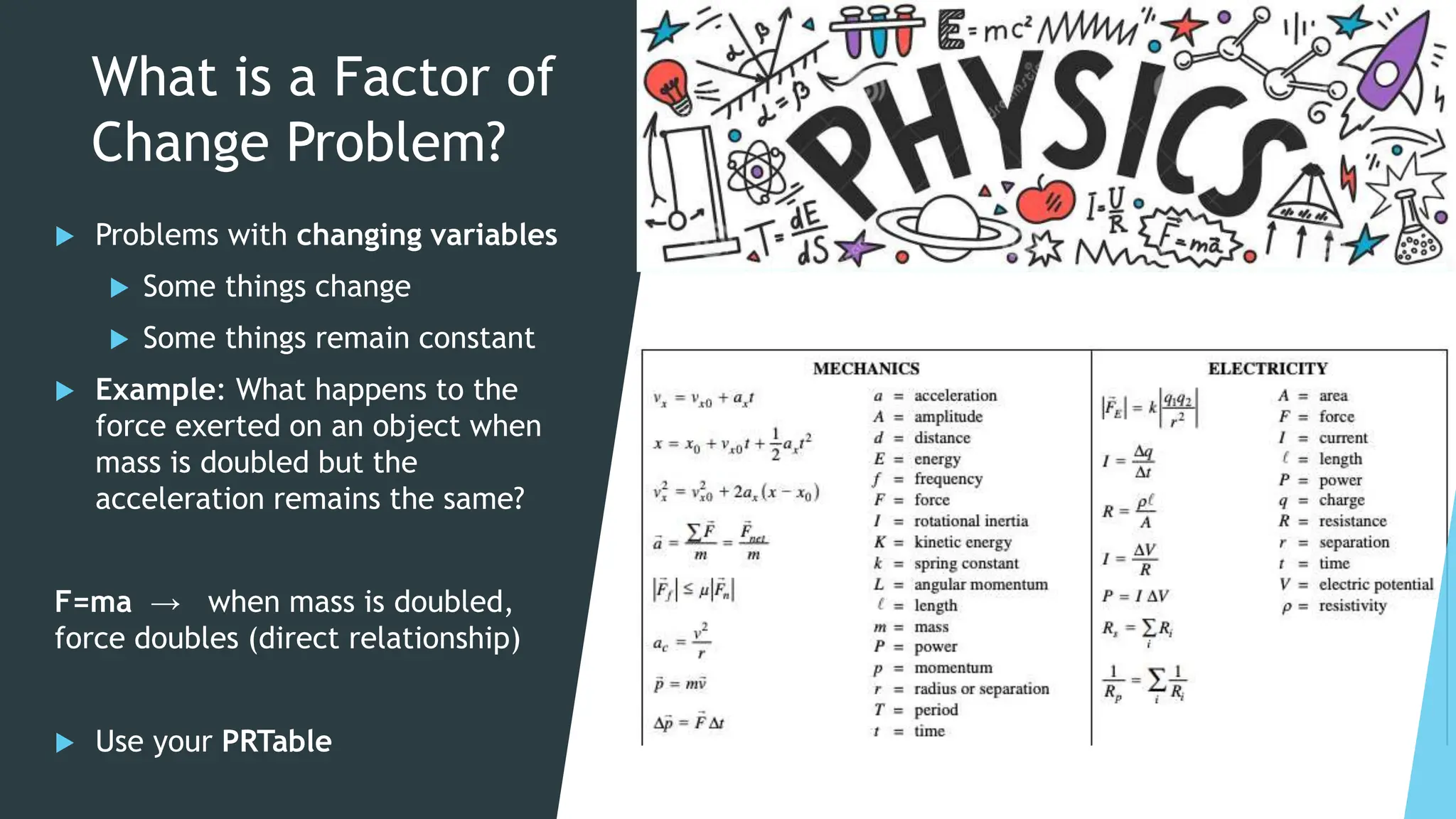
This document discusses factor of change problems in AP Physics. It defines factor of change problems as those involving changing variables while others remain constant. Examples are provided of determining how force, stopping distance, angular speed, and surface gravity change when variables like mass, speed, angular acceleration, volume, and mass are altered. Key steps are outlined: identify relevant equations; determine changing and constant variables; and write the unknown variable in terms of known quantities using relationships like direct, inverse, or exponential. Solving these problems involves understanding variable relationships and applying equations while accounting for changes.