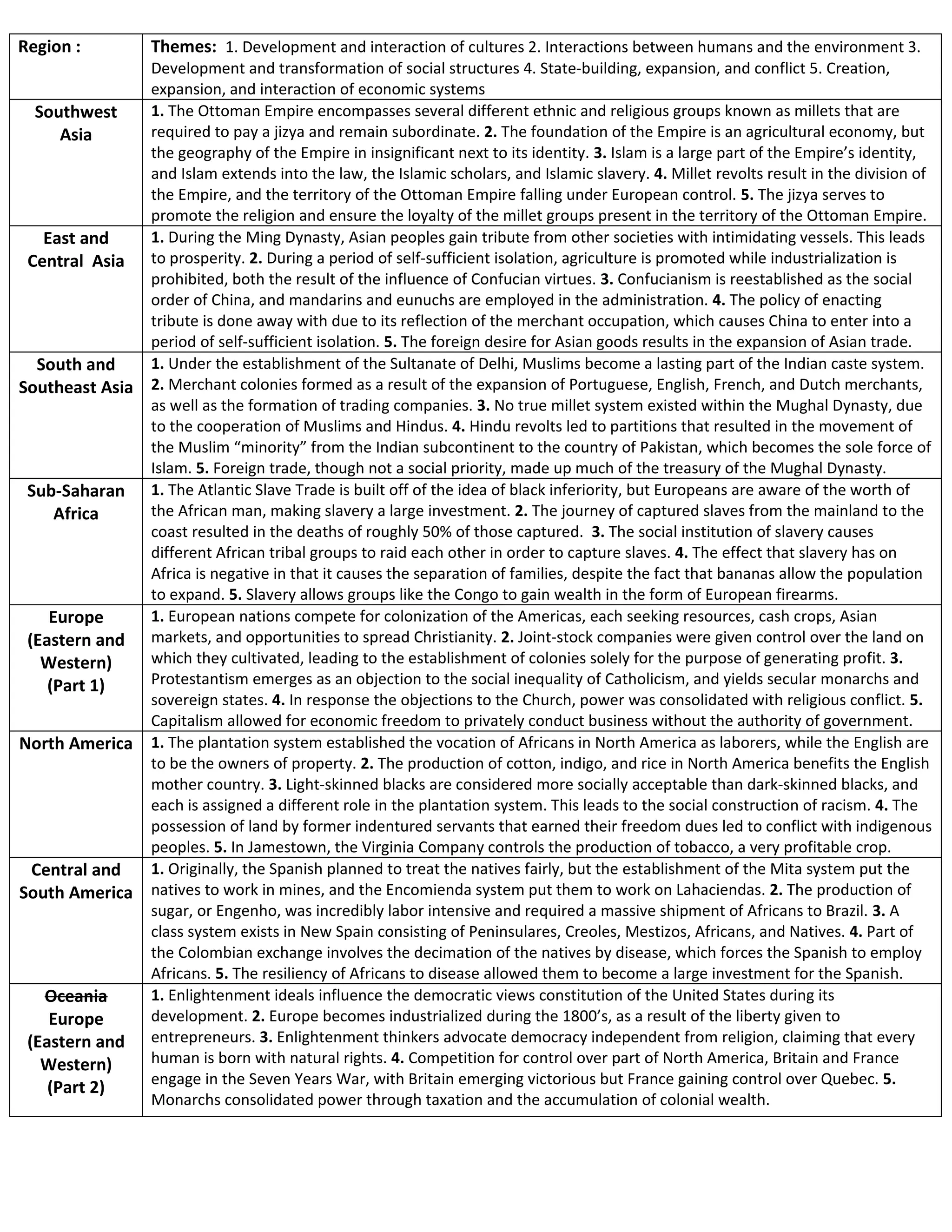
1. The document outlines key themes in the historical development of different regions of the world between 1500-1800.
2. These themes include the interaction of cultures, relationships between humans and the environment, transformations of social structures, state-building and conflict, and the creation and interaction of economic systems.
3. For each region, several bullet points provide examples of how these themes played out, such as the establishment of colonial trade networks and plantations in Africa and the Americas, the influence of religious and philosophical ideals in Europe, and the development of imperial and cultural institutions in Asia.