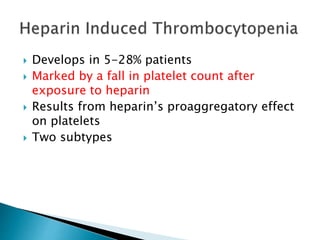
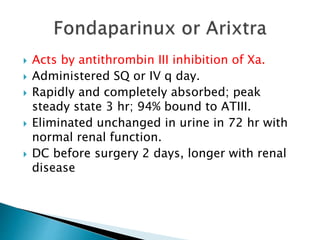
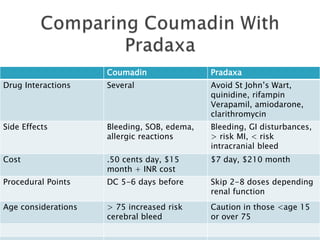
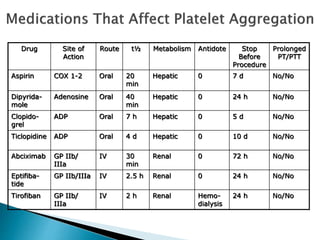
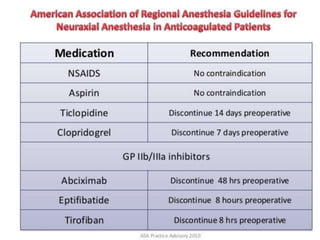
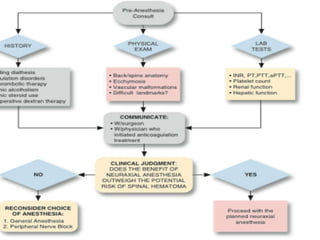
This document discusses the physiology of coagulation and various anticoagulant and thrombolytic agents. It covers the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways of coagulation and the mechanisms of several common anticoagulants including heparin, low molecular weight heparins, warfarin, and direct thrombin and factor Xa inhibitors. It also addresses considerations for reversing anticoagulation with protamine or newer antidotes and managing patients on anticoagulants who require surgery or procedures.