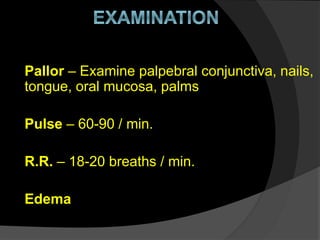
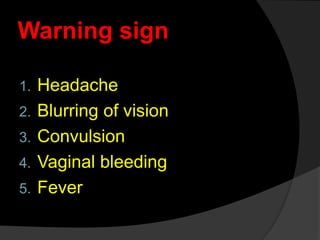
This document outlines the goals and procedures of antenatal care (ANC). ANC involves regular checkups during pregnancy to monitor the health of the mother and baby. It aims to screen for high-risk cases, prevent or treat any complications, ensure ongoing risk assessment, and educate mothers. Checkups include medical history, physical exam measuring vitals and fetal growth, and lab tests. Women are advised to attend 4 ANC visits - at 16, 24-28, 32 and 36 weeks - where the above procedures and health education are provided to monitor pregnancy and ensure normal delivery of a healthy baby.




![Antenatal care comprises
of-
1.Registration of pregnancy
2. History taking
3. Antenatal examinations
[general and obstetrical]
4. Laboratory investigations
5. Health education](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antenatalcare-161230151017-200817224545/85/Antenatalcare-161230151017-6-320.jpg)