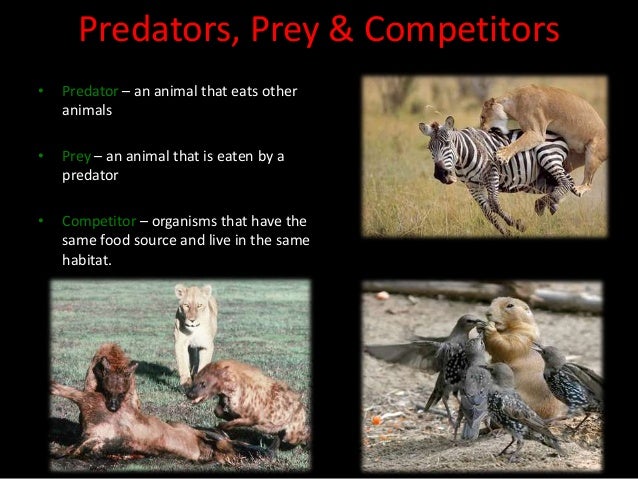
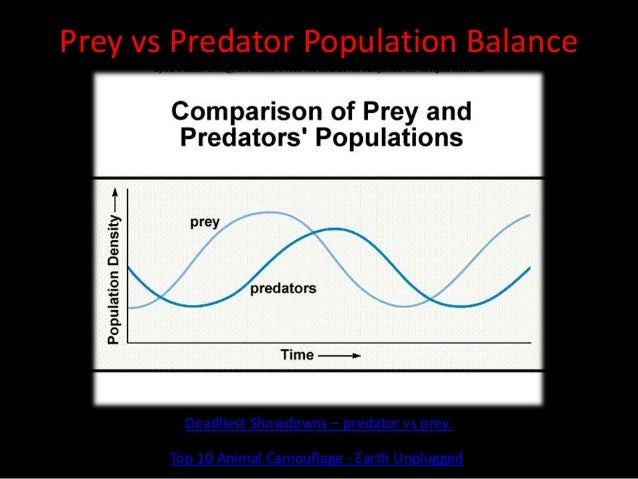
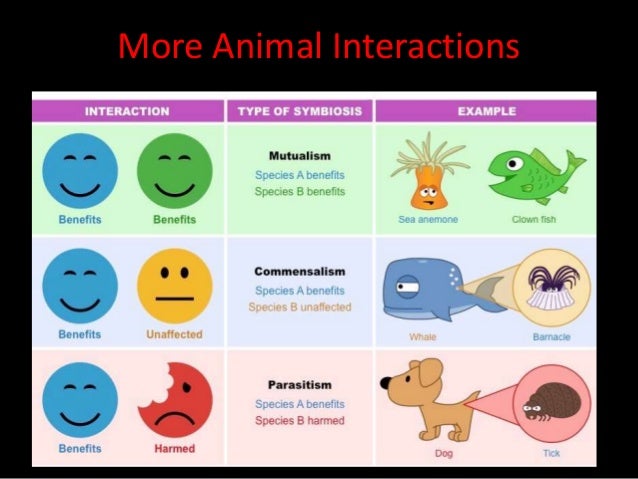
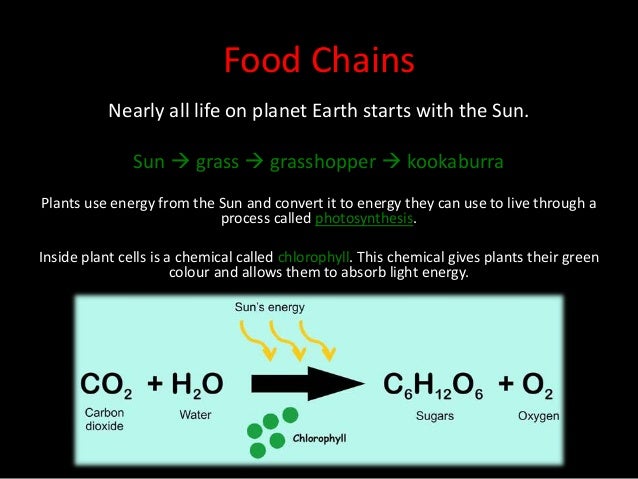
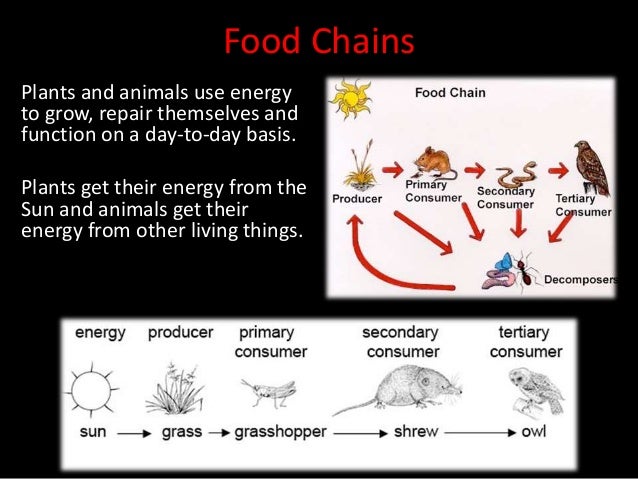
This document discusses different types of interactions between organisms in an ecosystem. It explains that organisms have feeding relationships where some organisms obtain food by eating other organisms. It then defines several key relationship types between organisms, including predator-prey relationships, competition for resources, mutualism, parasitism, and commensalism. Food chains and food webs are also discussed as a way that energy passes between organisms in an ecosystem.