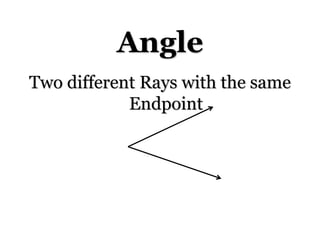
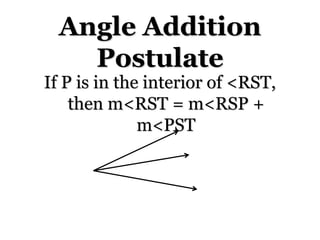
1. The document defines key angle concepts such as acute, obtuse, right, and straight angles. It also introduces the protractor and angle addition postulate.
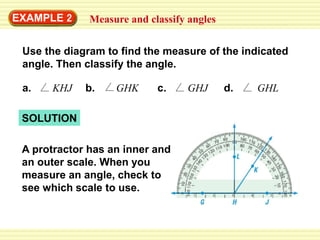
2. The examples demonstrate how to name angles, measure angles using a protractor, find missing angle measures using the angle addition postulate, identify congruent angles, and double an angle measure when the angle is bisected.
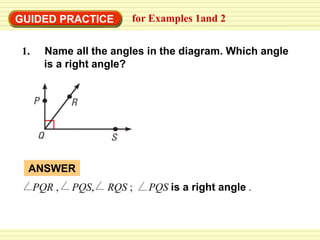
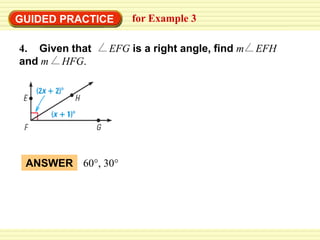
3. The guided practice problems apply the concepts taught in the examples to find missing angle measures, identify congruent angles, and draw and label diagrams related to bisected and straight angles.