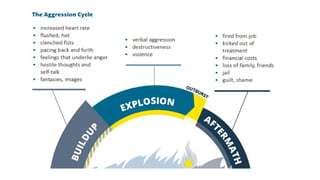
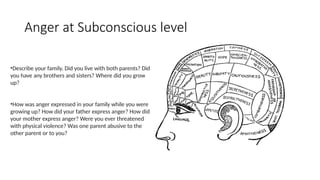
Anger is a natural human emotion, but when it is uncontrolled, it can lead to stress, conflicts, and negative consequences. Anger management involves recognizing triggers, controlling reactions, and expressing anger in a healthy way.
1. Understanding Anger
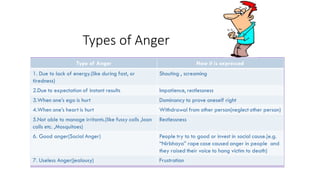
Types of Anger:
Passive Anger: Suppressed emotions that may lead to resentment.
Aggressive Anger: Explosive outbursts or hostile behavior.
Assertive Anger: Expressing feelings constructively.