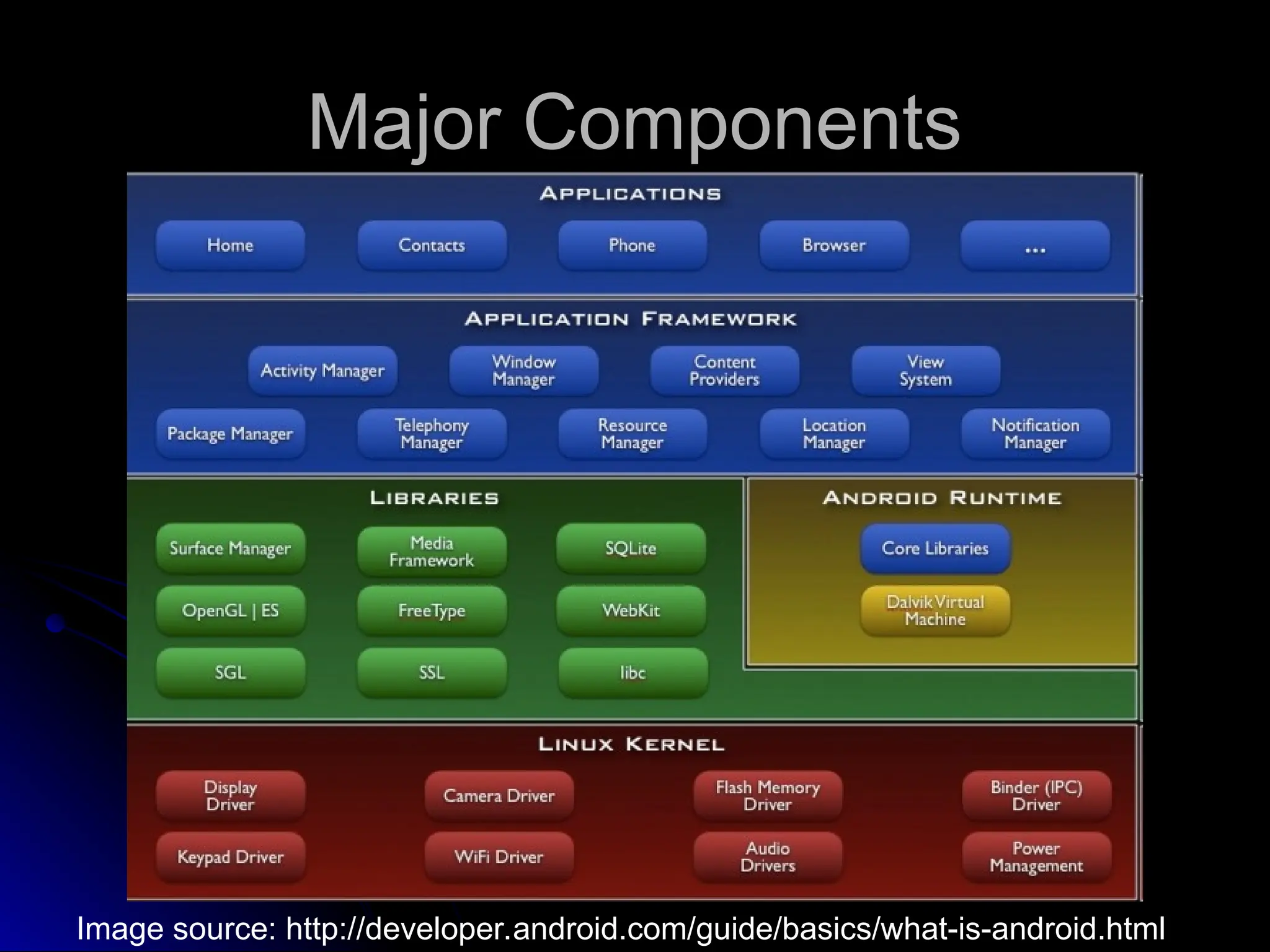
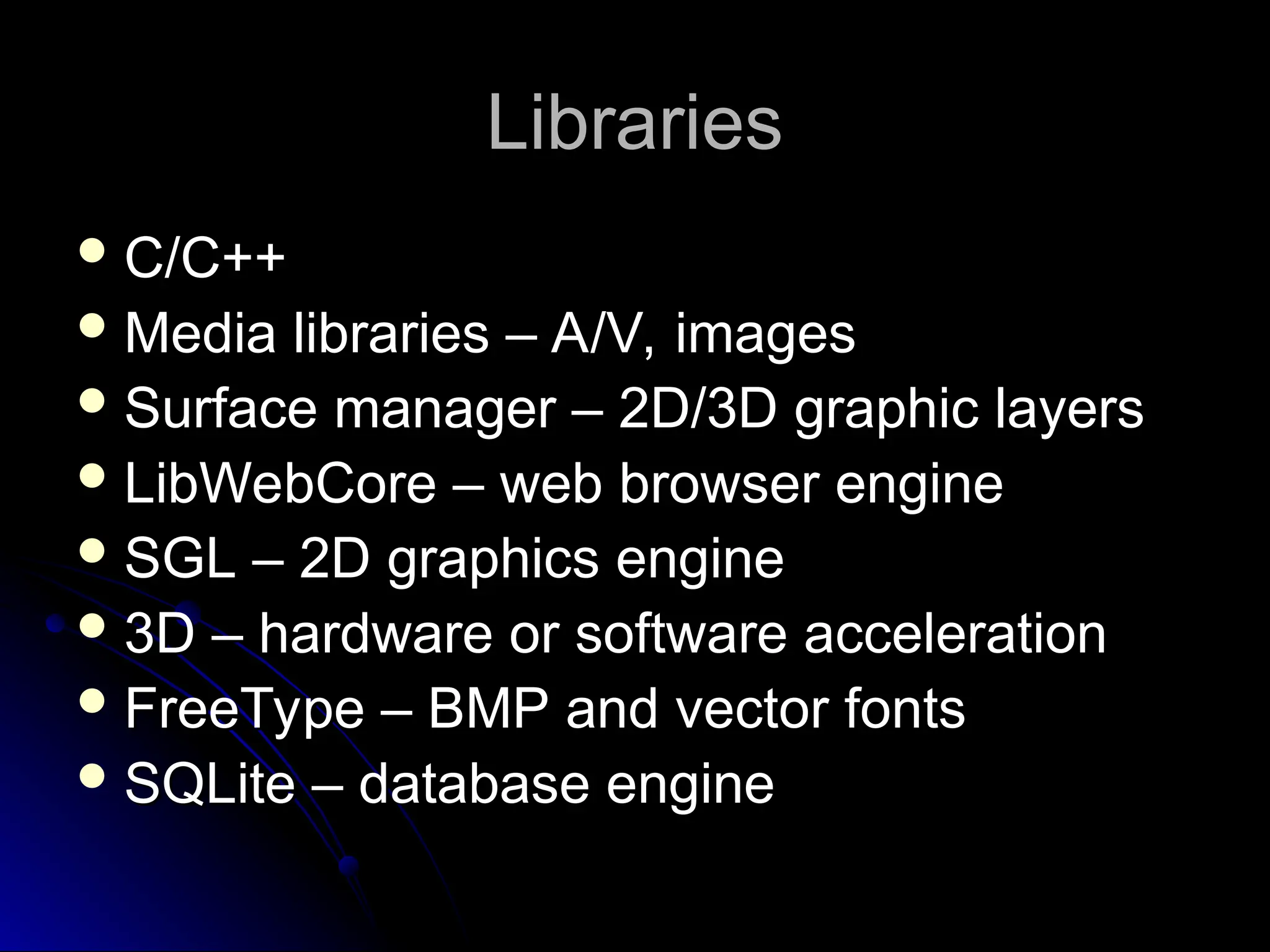
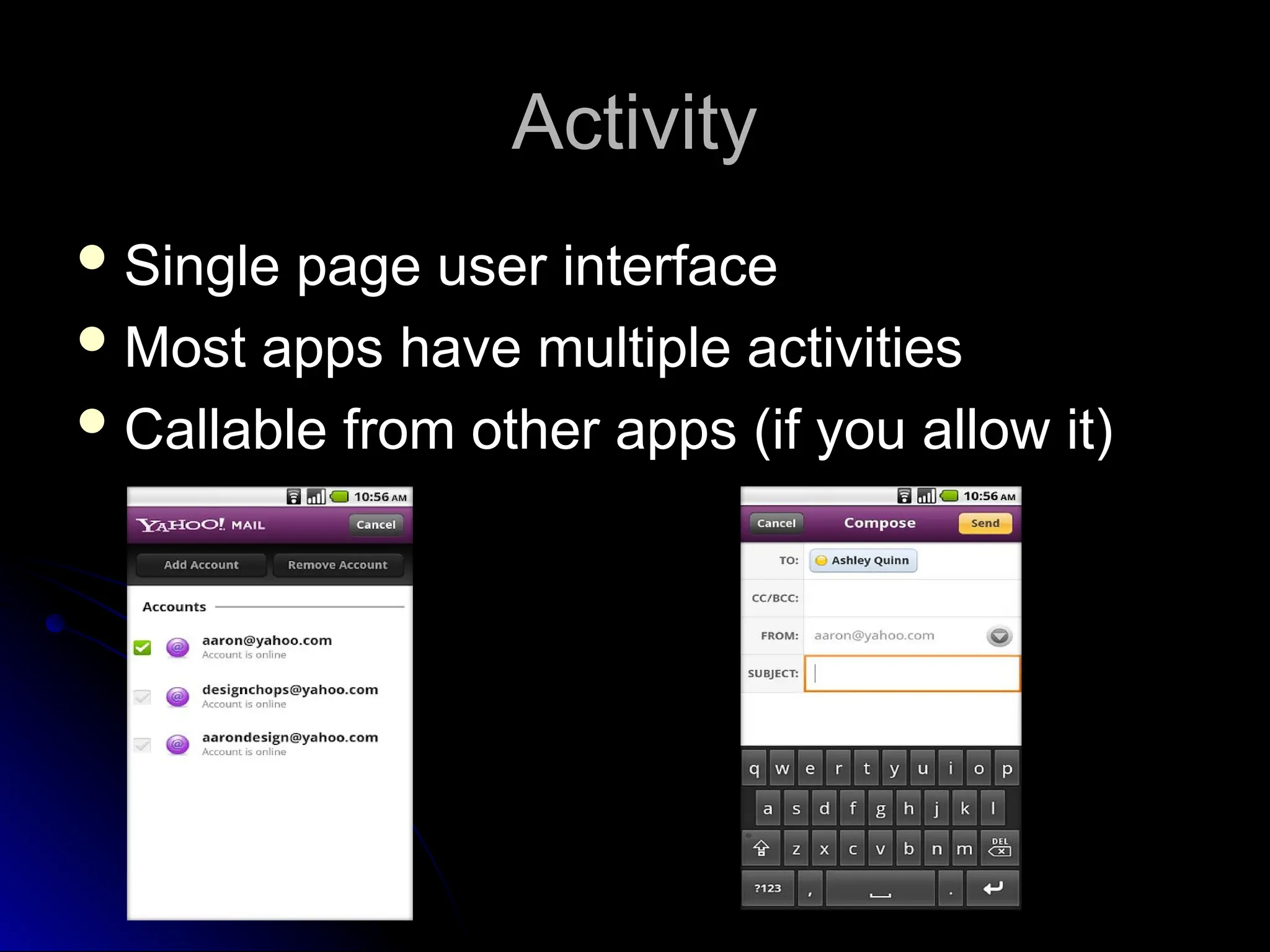
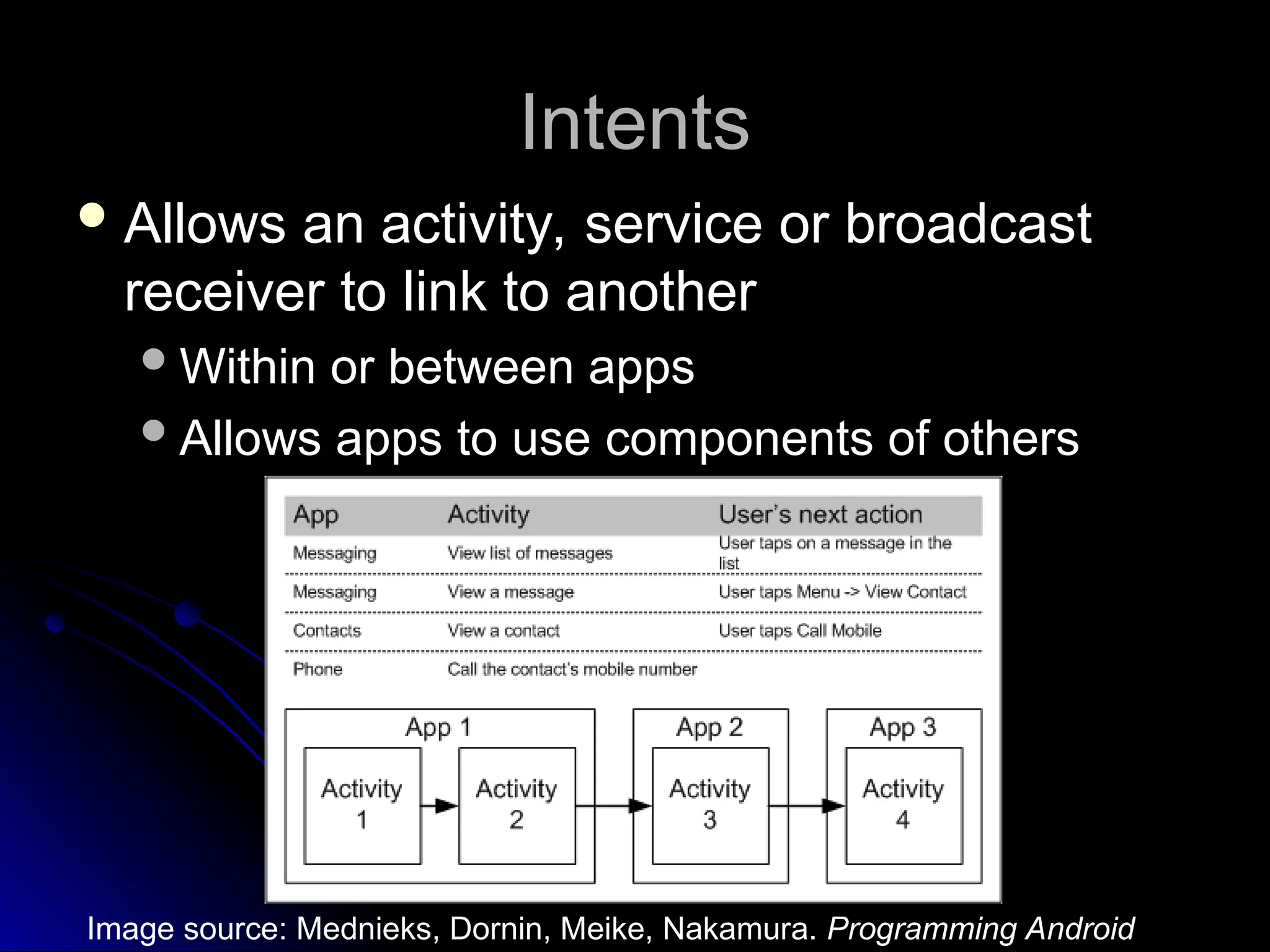
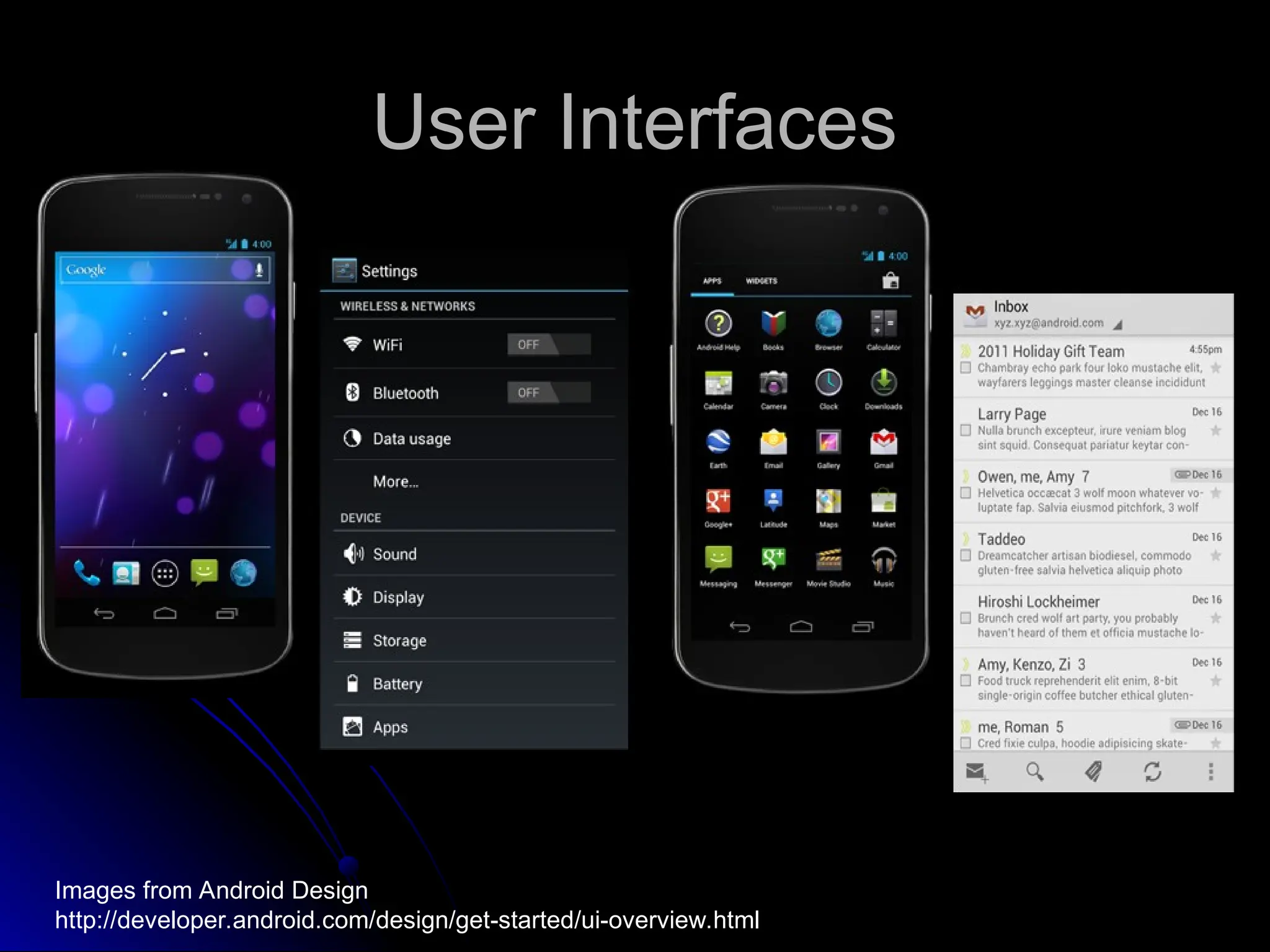
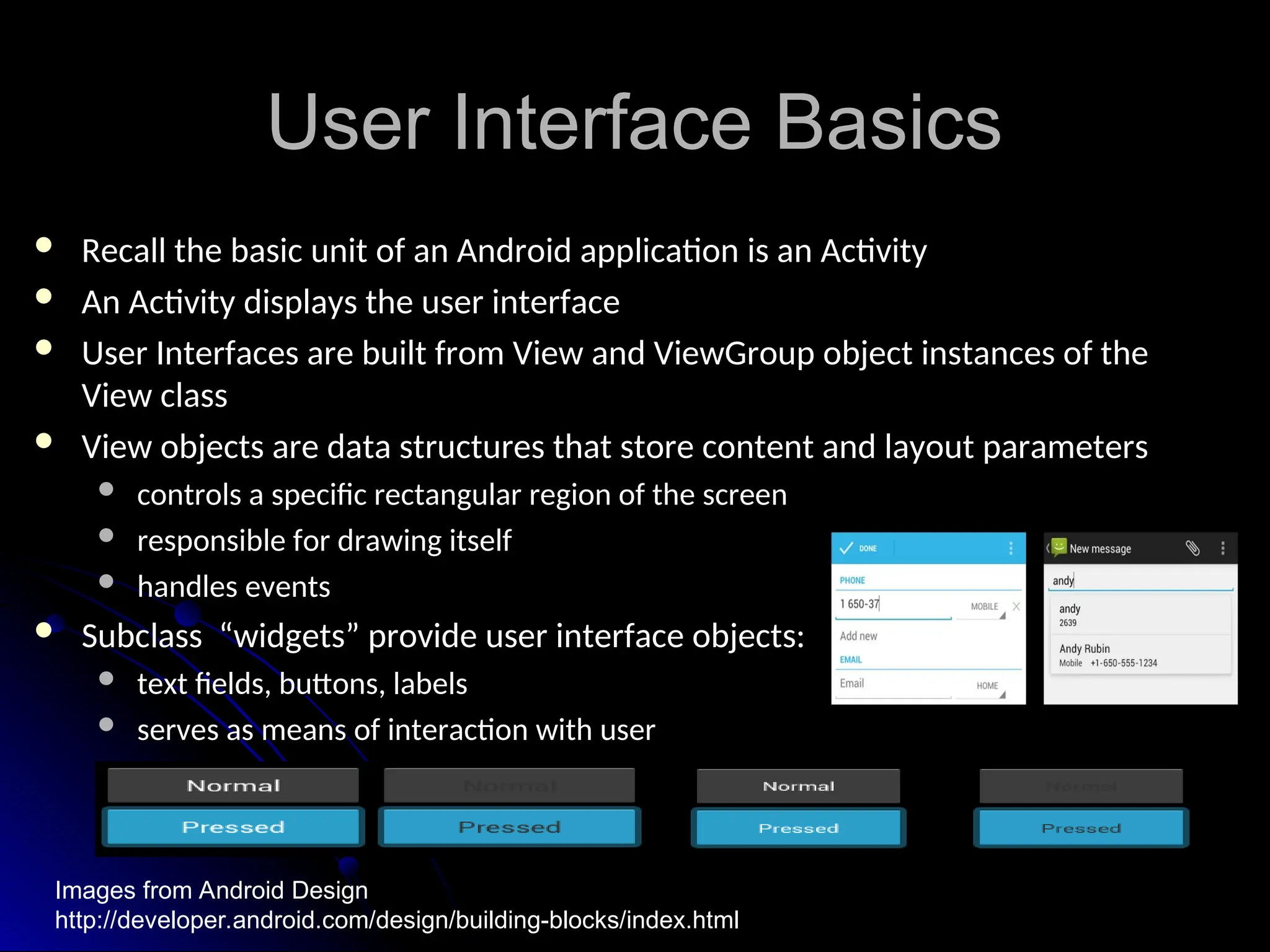
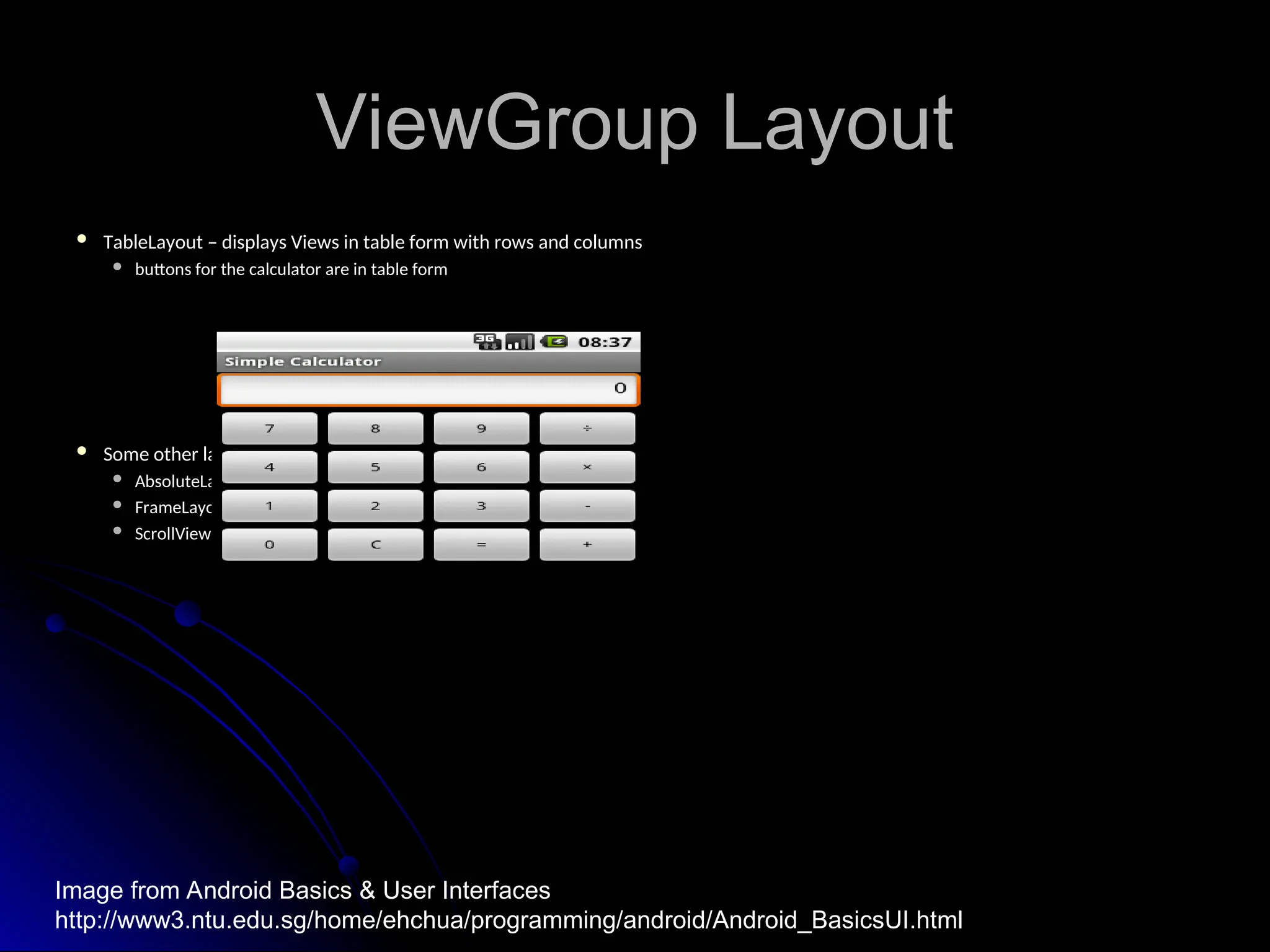
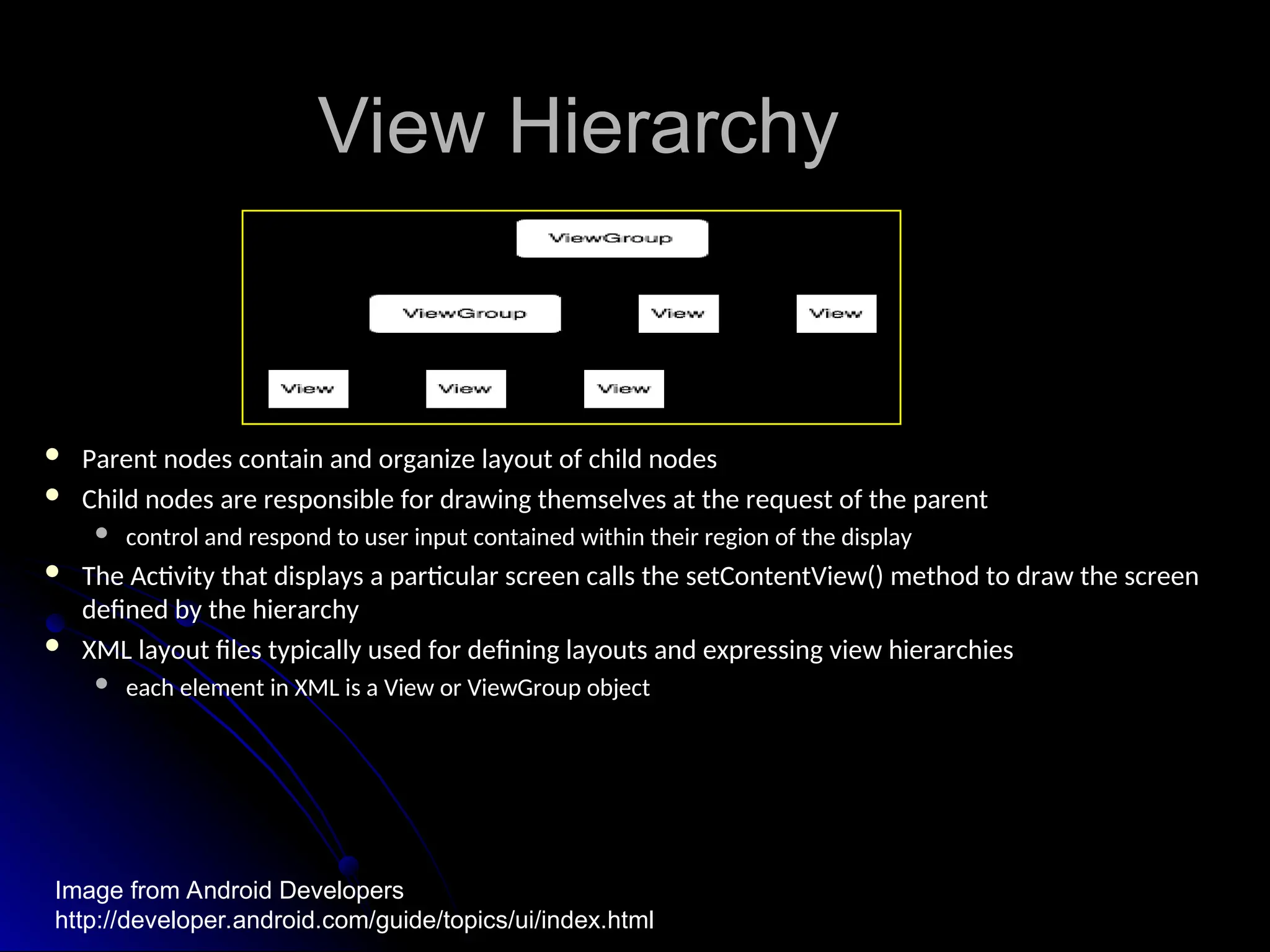
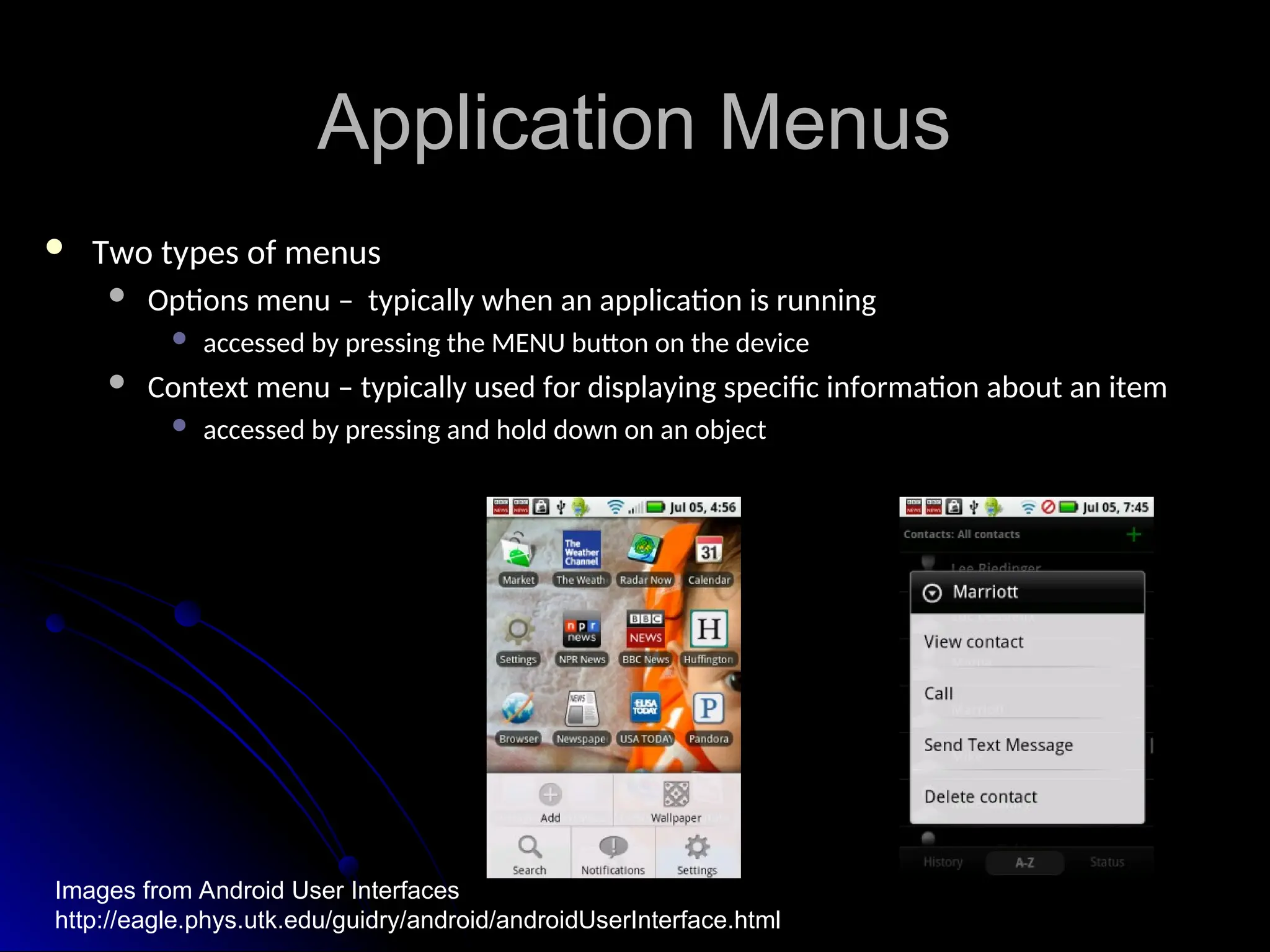
The document outlines the fundamentals of Android, detailing its software stack, major components like activities, services, and content providers, and the use of APIs for app development. It explains user interface basics, including the structure of view and viewgroup objects, various layouts, as well as input events and application menus. Additionally, it covers hardware interactions such as sensors and Bluetooth management.