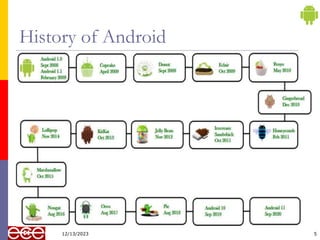
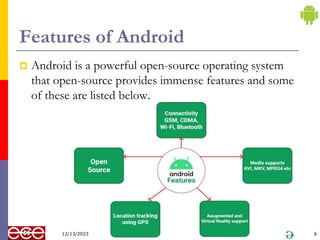
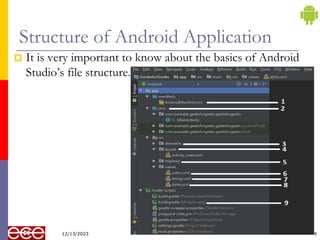
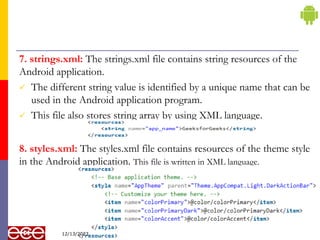
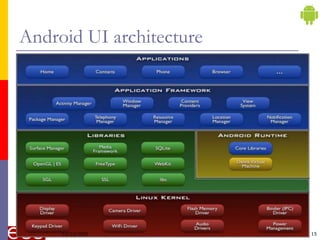
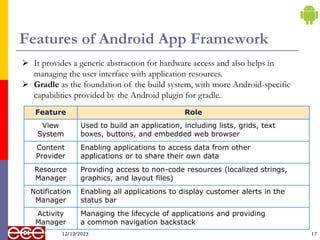
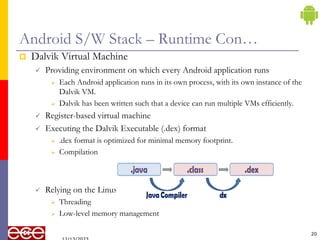
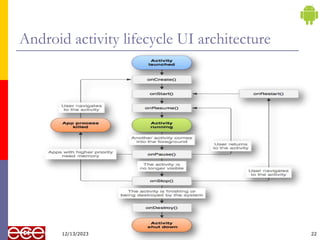
The document provides an introduction to Android, a mobile operating system based on Linux, highlighting its features, benefits, and structure. It outlines key elements such as the application structure, UI components, and the software stack. The document serves as a foundational resource for understanding mobile application development using Android.