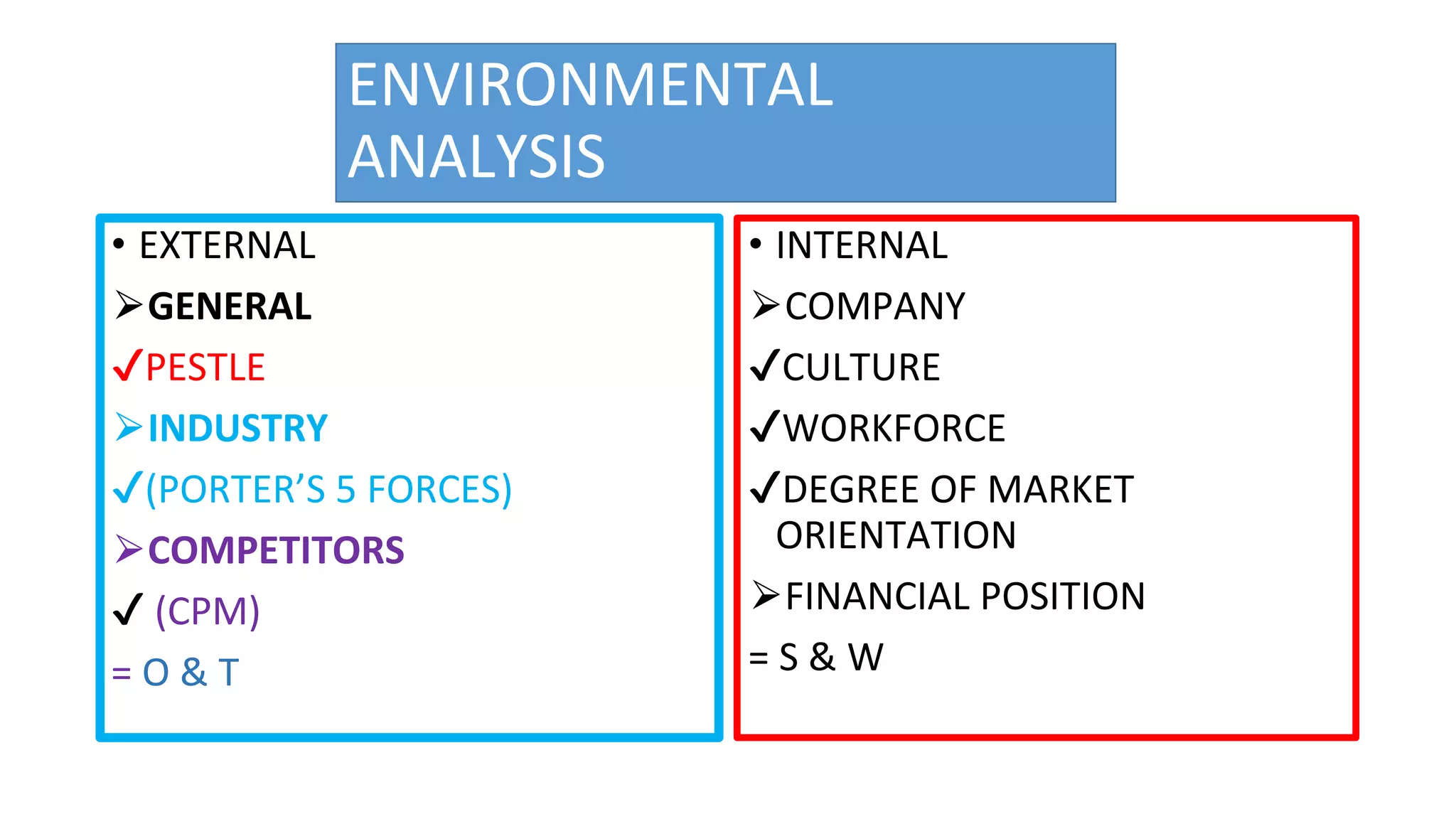
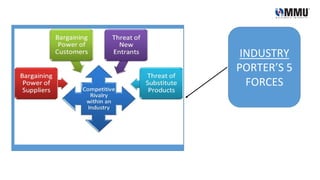
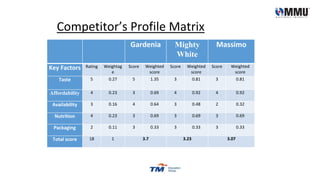
The document provides an analysis of Malaysia's external and internal environment for business planning purposes. Externally, it examines political, economic, social, technological, legal and environmental factors in Malaysia using PESTLE and Porter's Five Forces frameworks. Internally, it considers the company's culture, workforce, financial position and degree of market orientation. The analysis finds that while Malaysia provides economic opportunities, businesses must be aware of potential corruption and environmental issues.