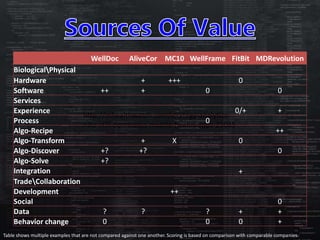
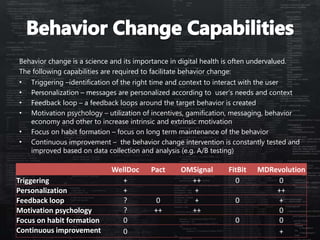
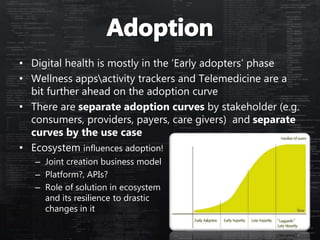
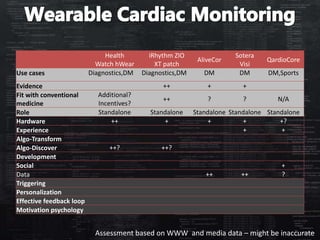
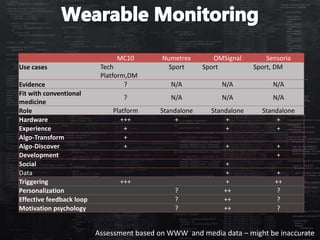
This document defines categories and matrices to evaluate digital health solutions. It discusses category definitions, sources of value, behavior change capabilities, fit with conventional medicine, business models, adoption, and potential revenue streams. Examples of digital health solutions are also provided and evaluated based on these criteria. The document emphasizes the importance of behavior change capabilities for digital health solutions to be effective.