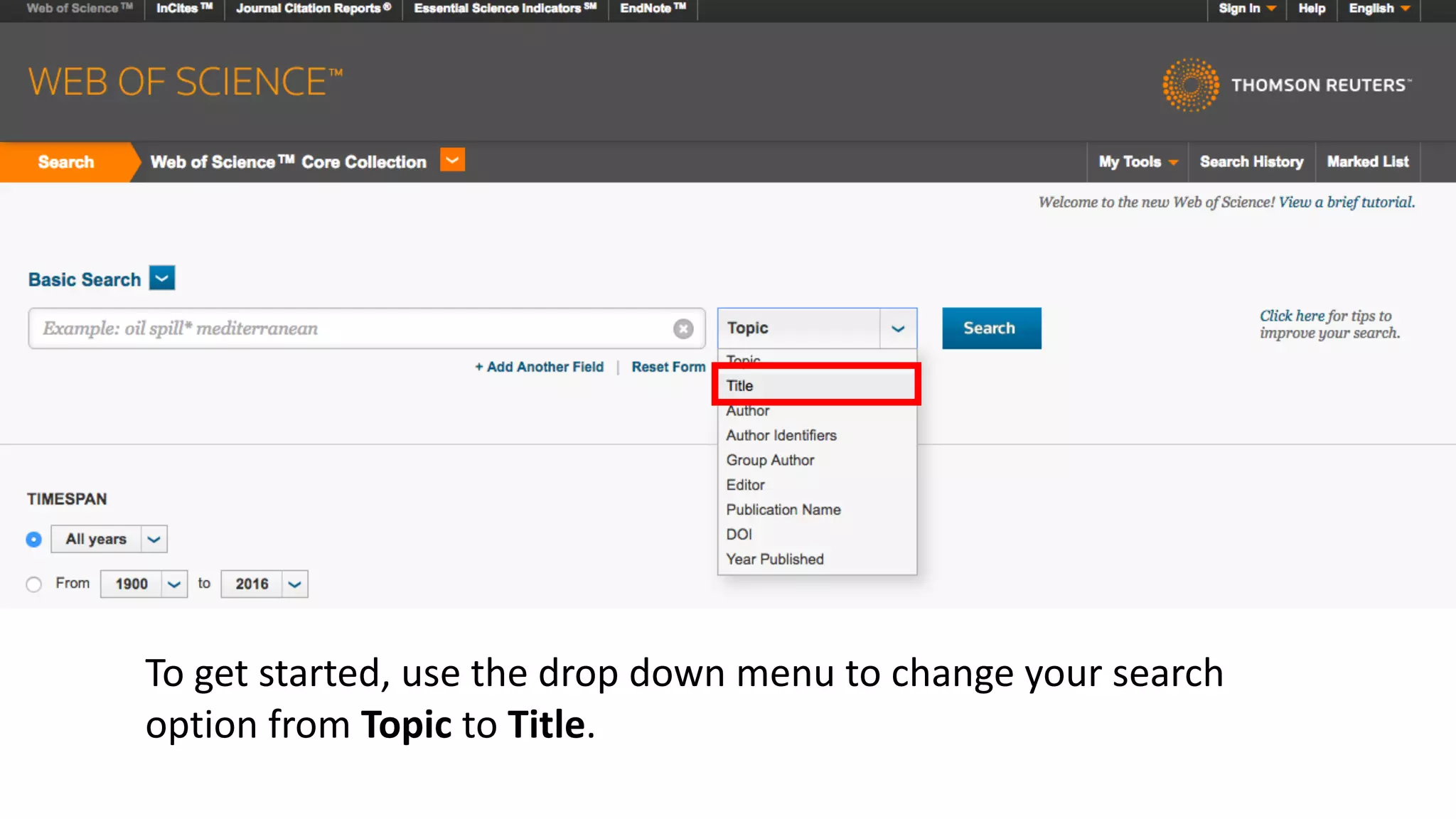
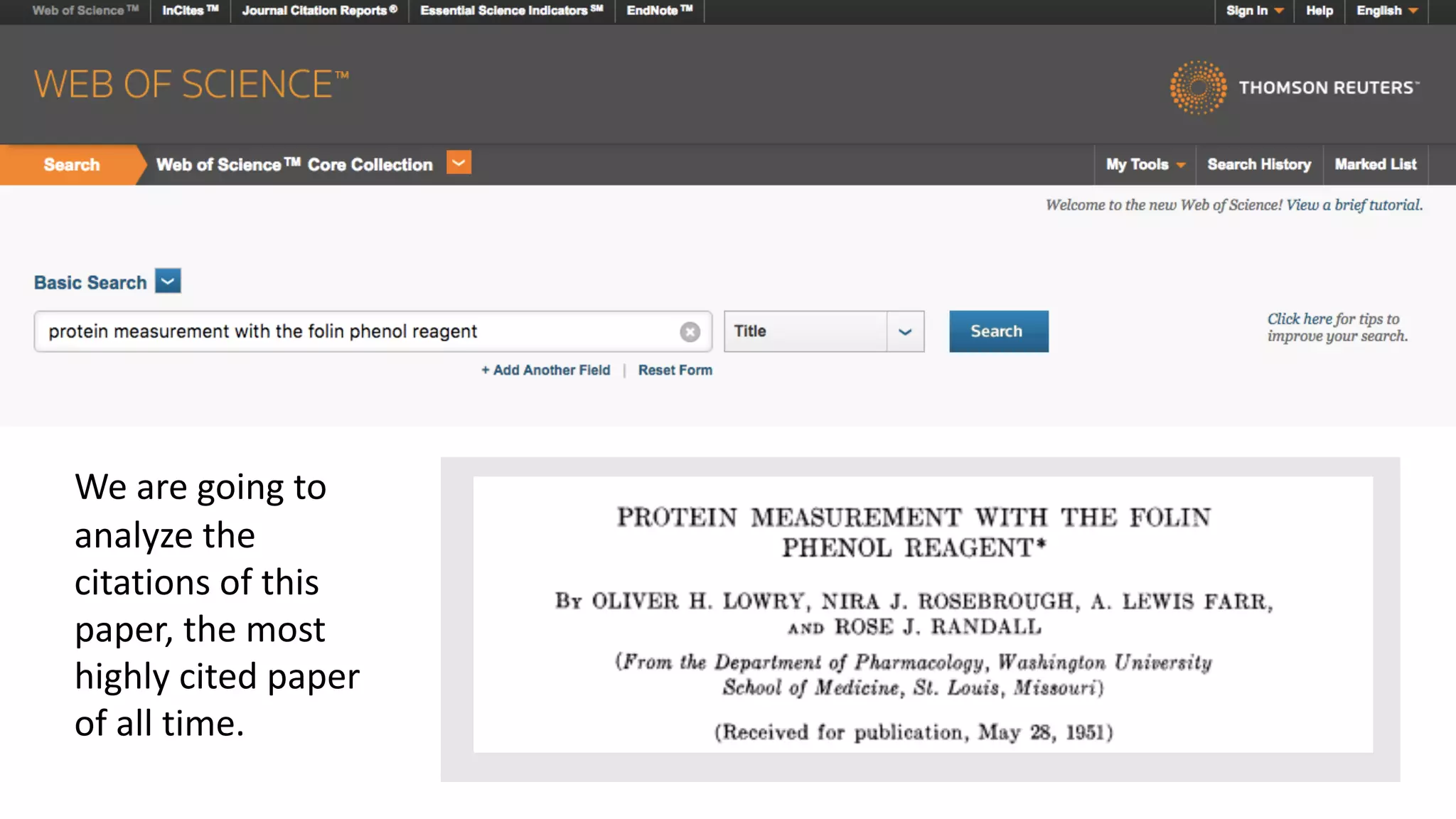
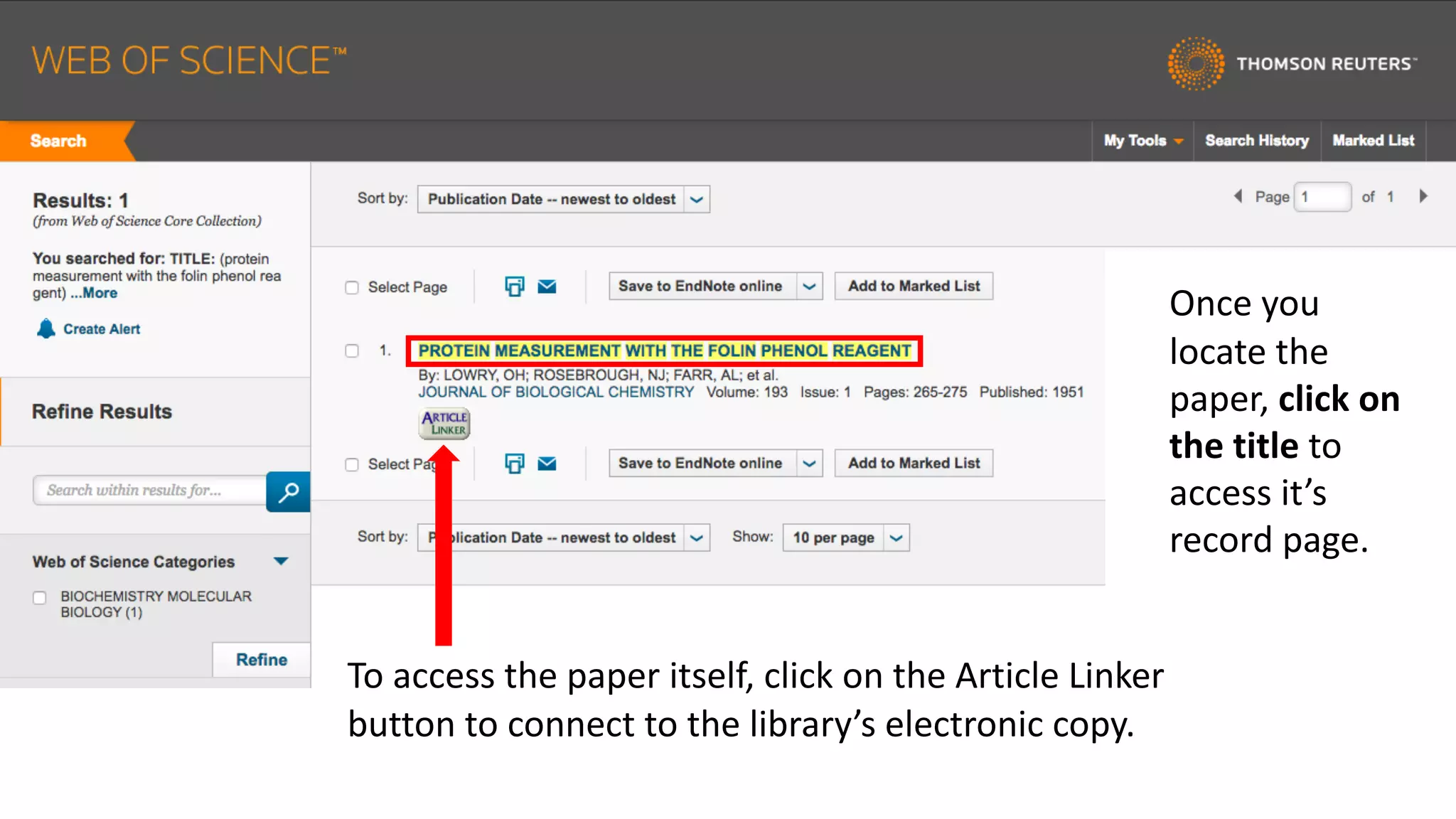
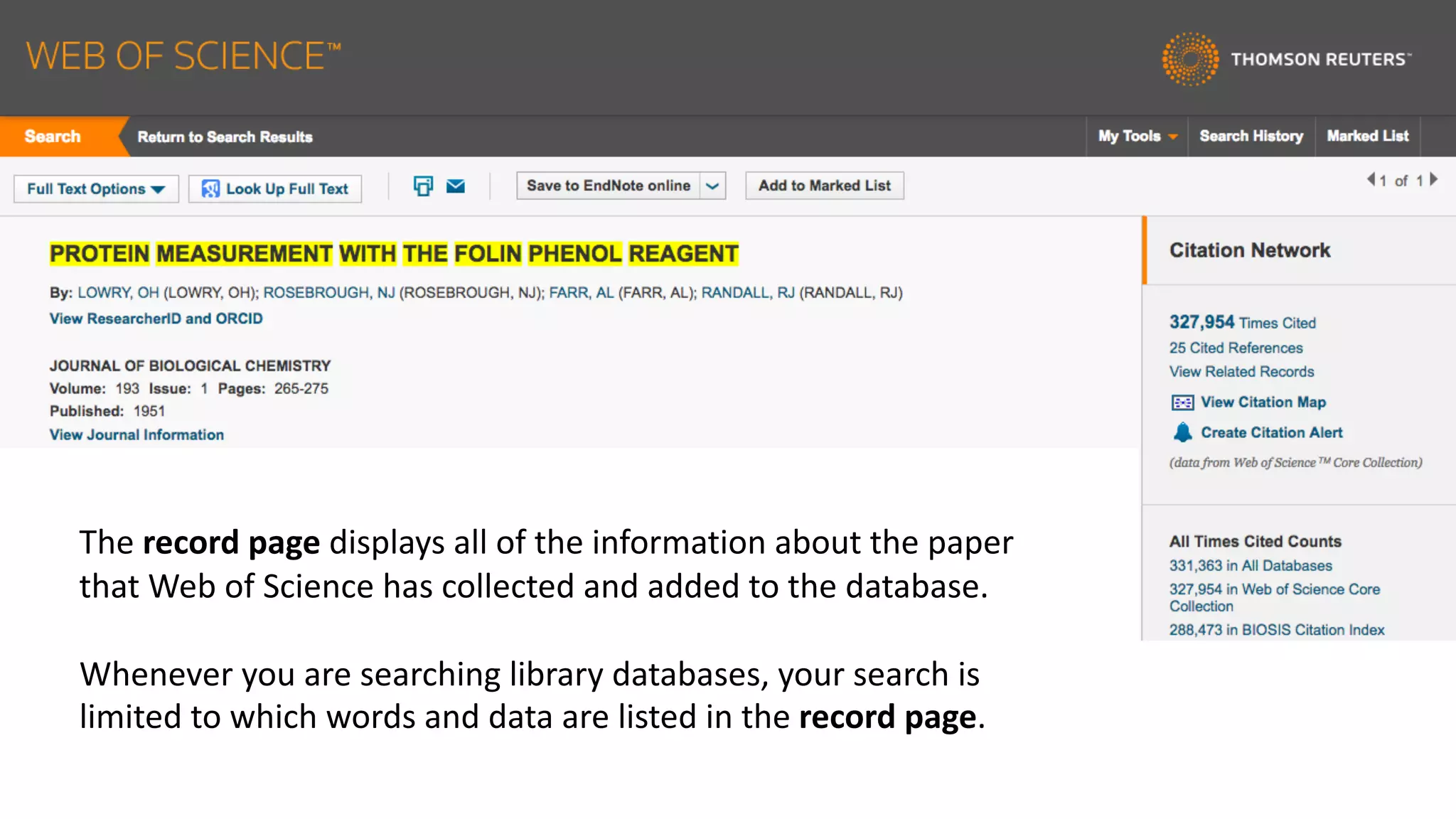
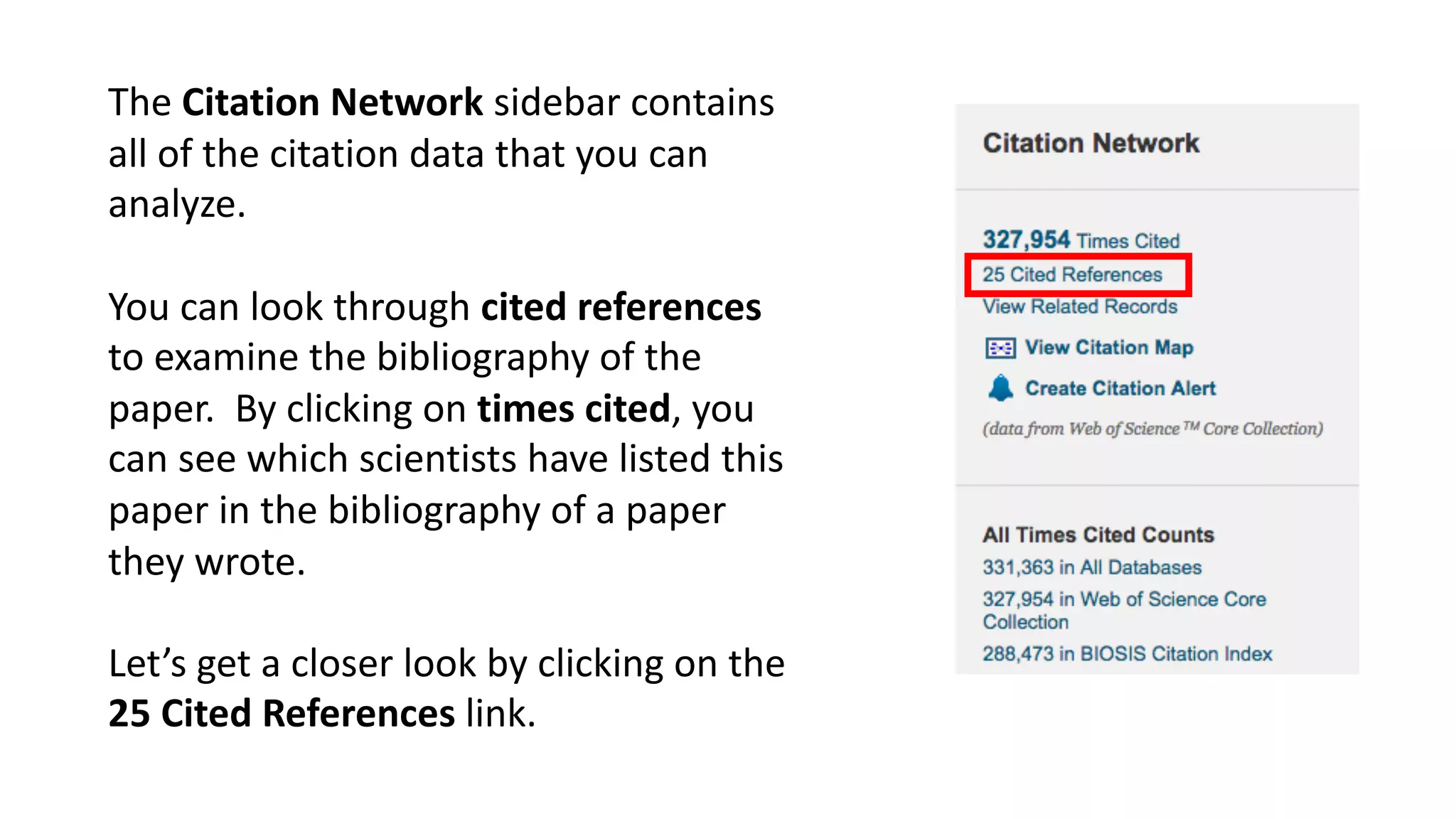
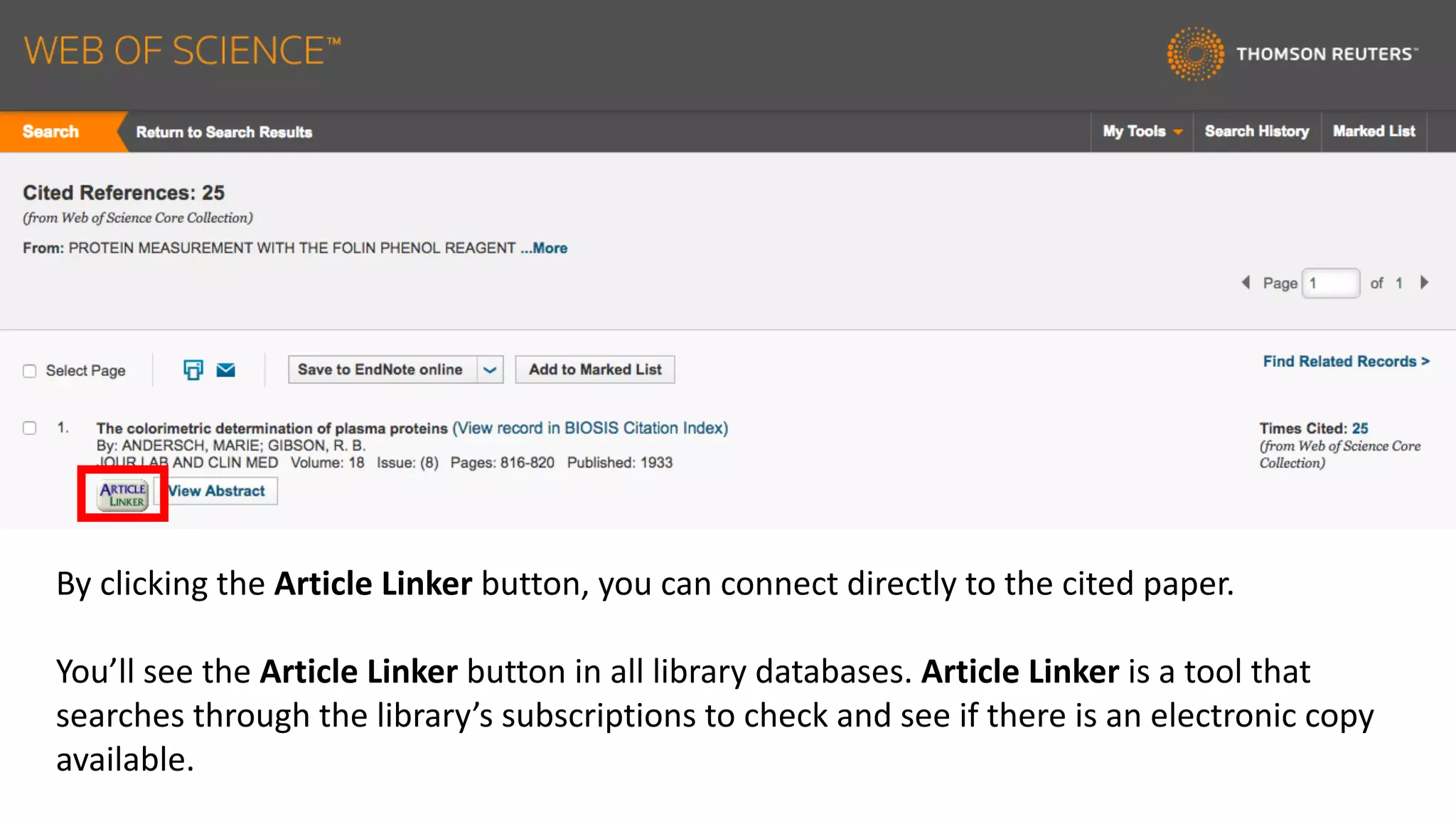
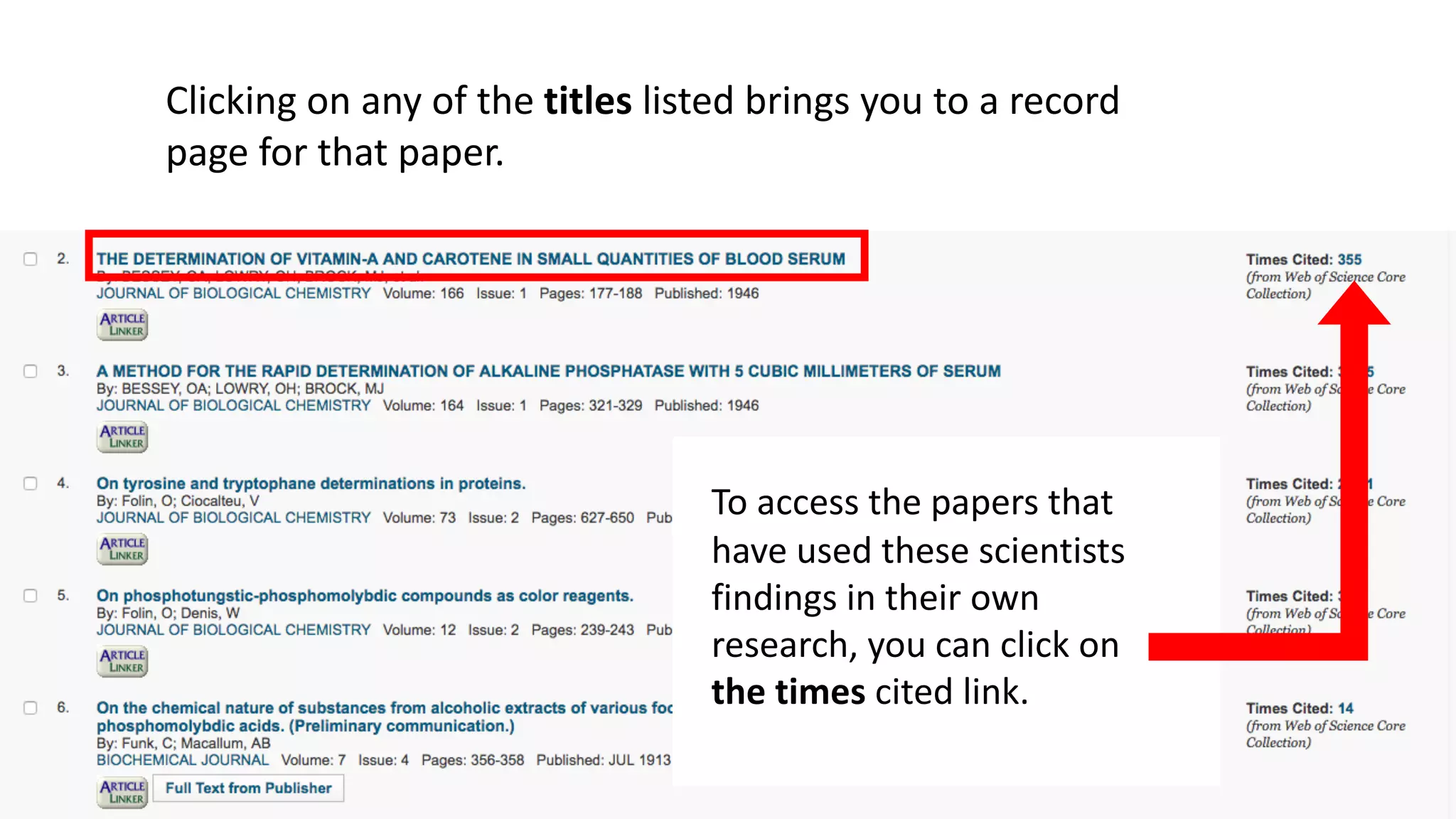
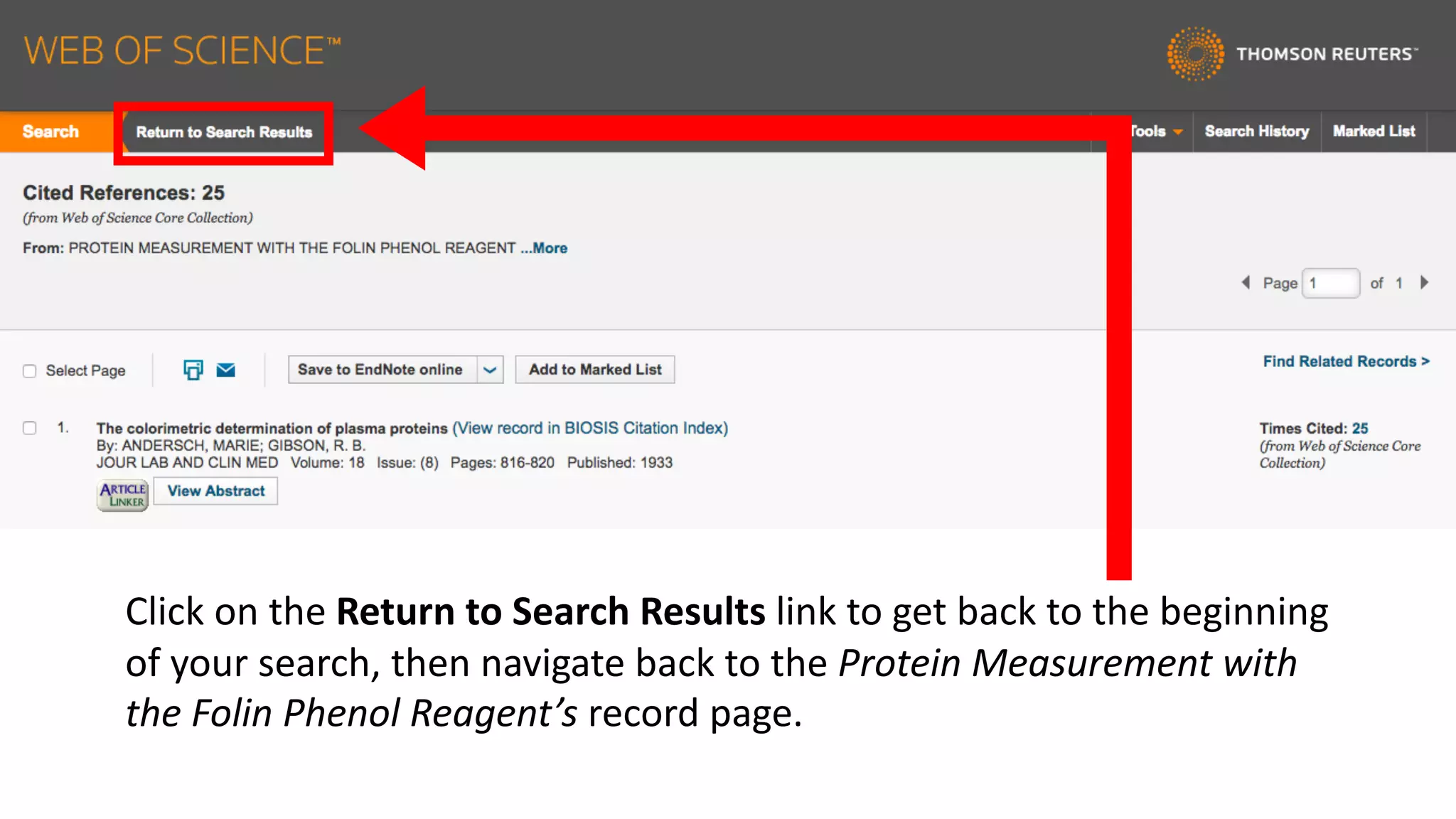
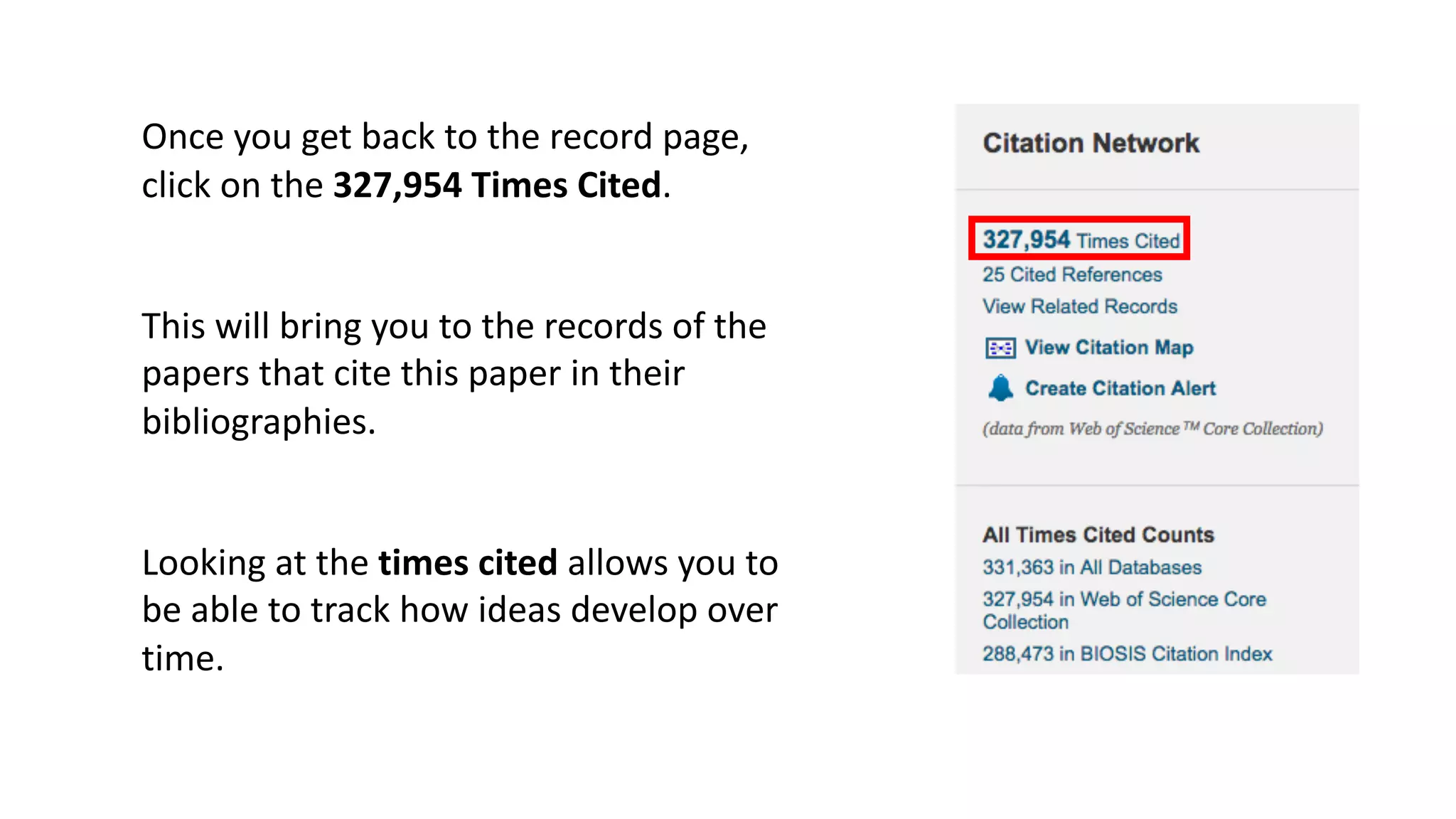
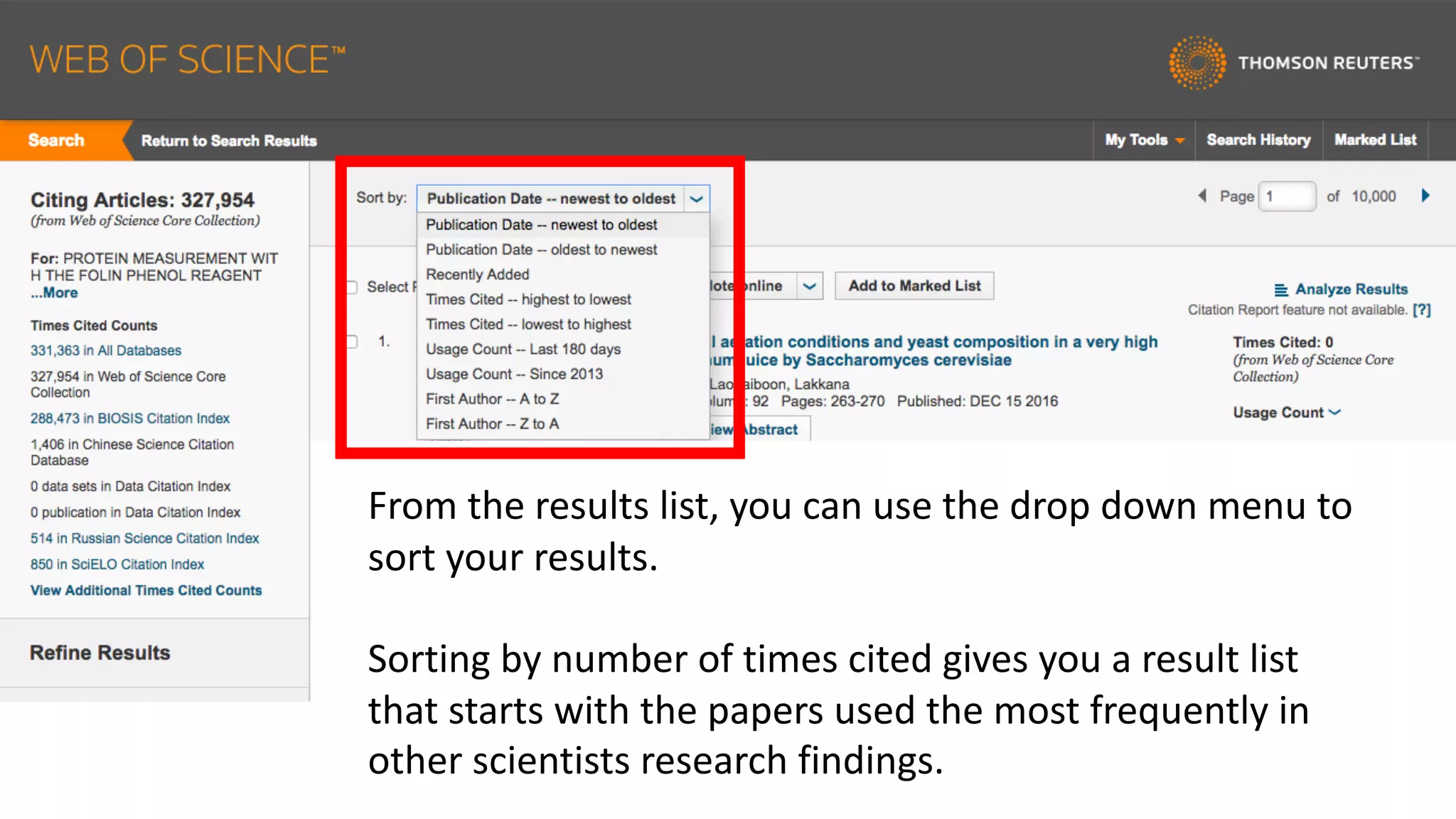
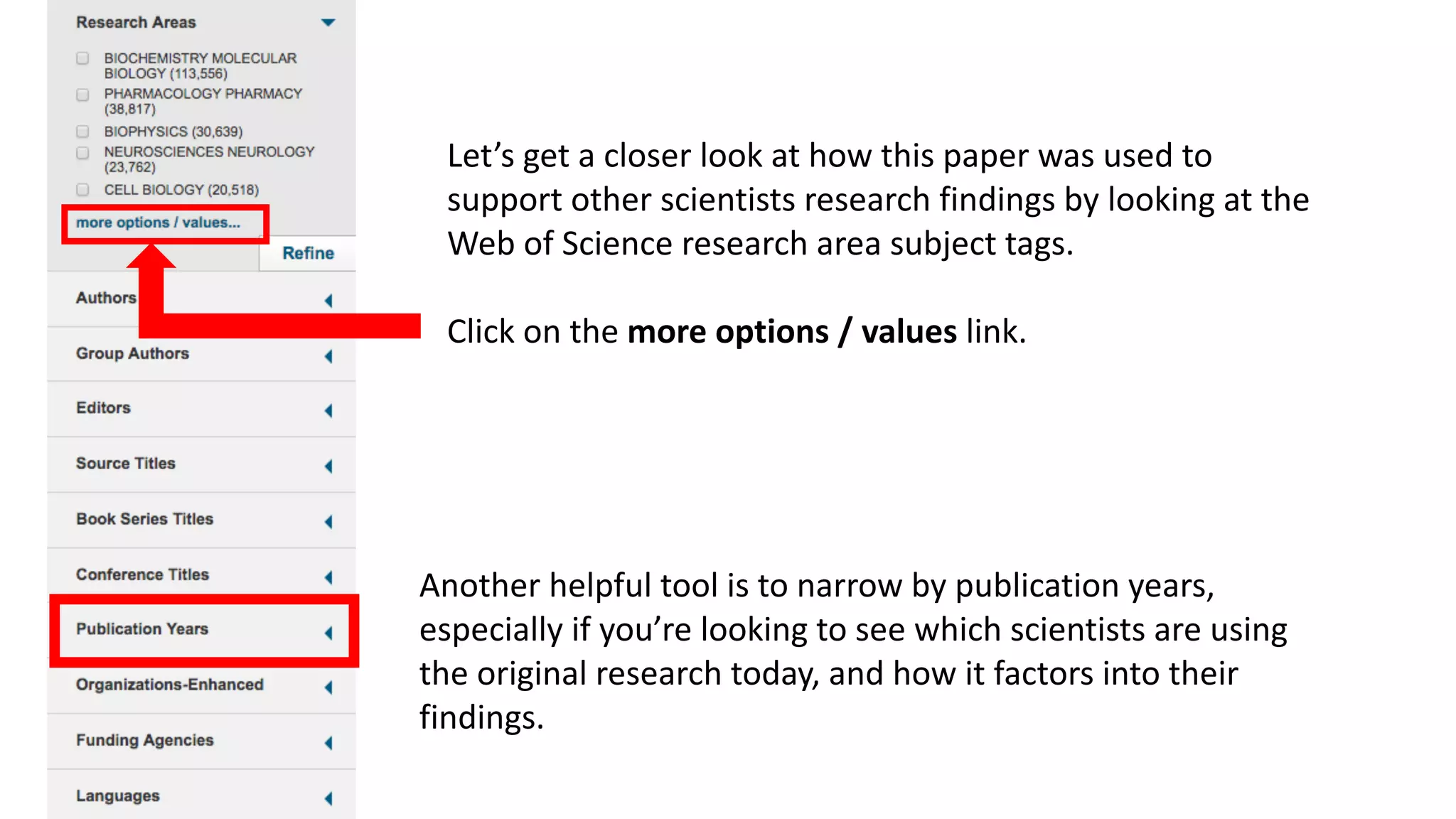
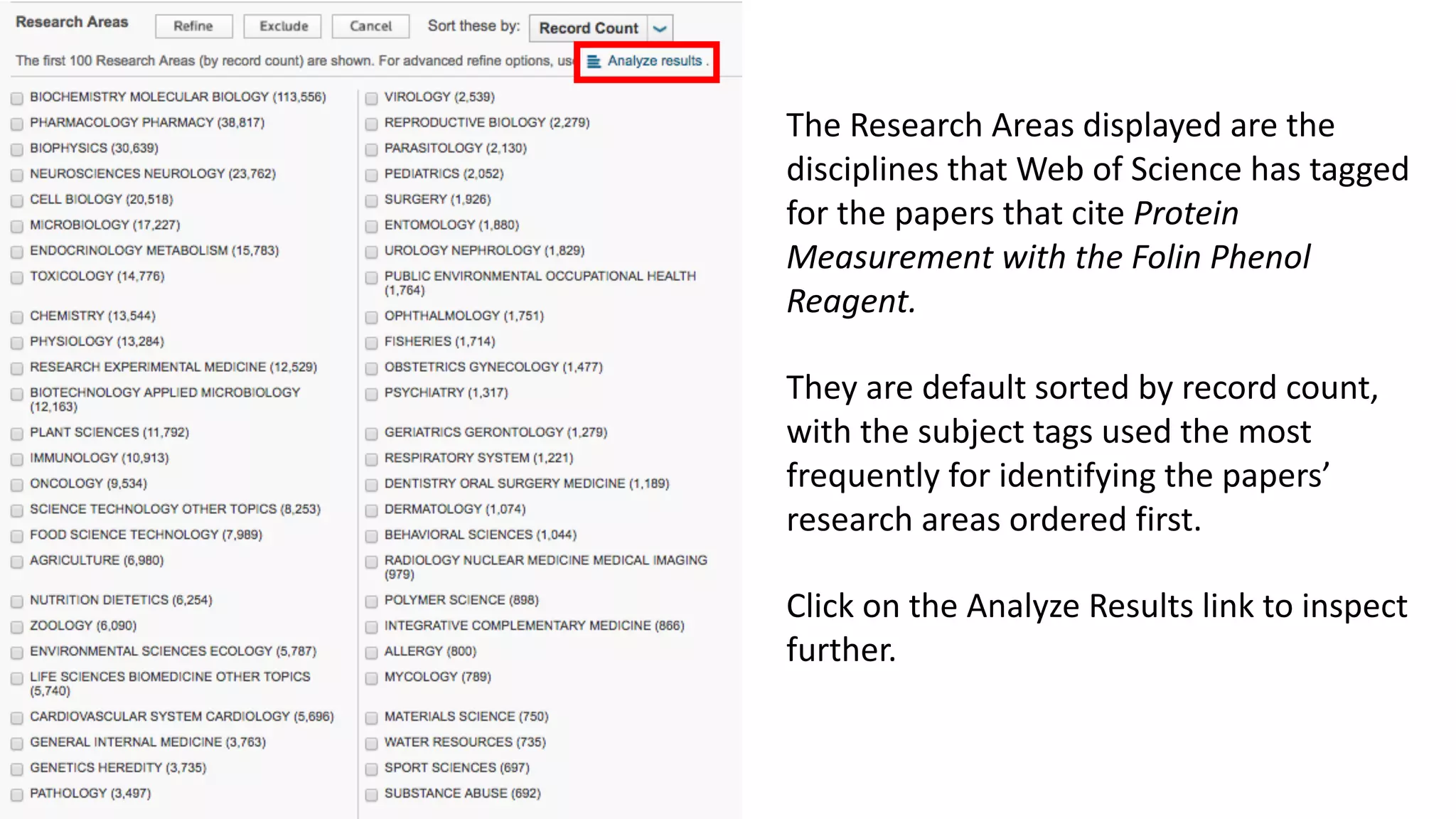
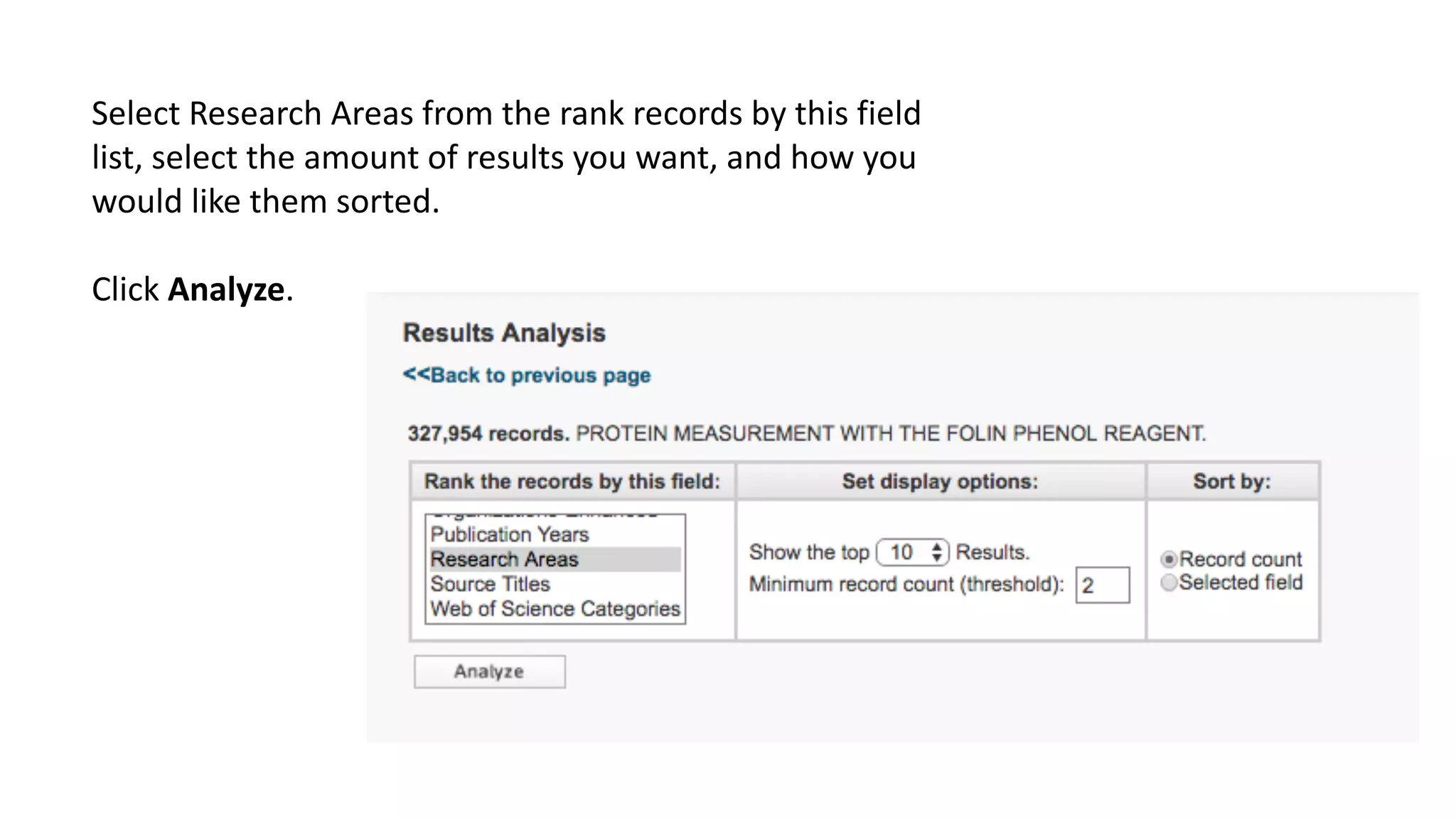
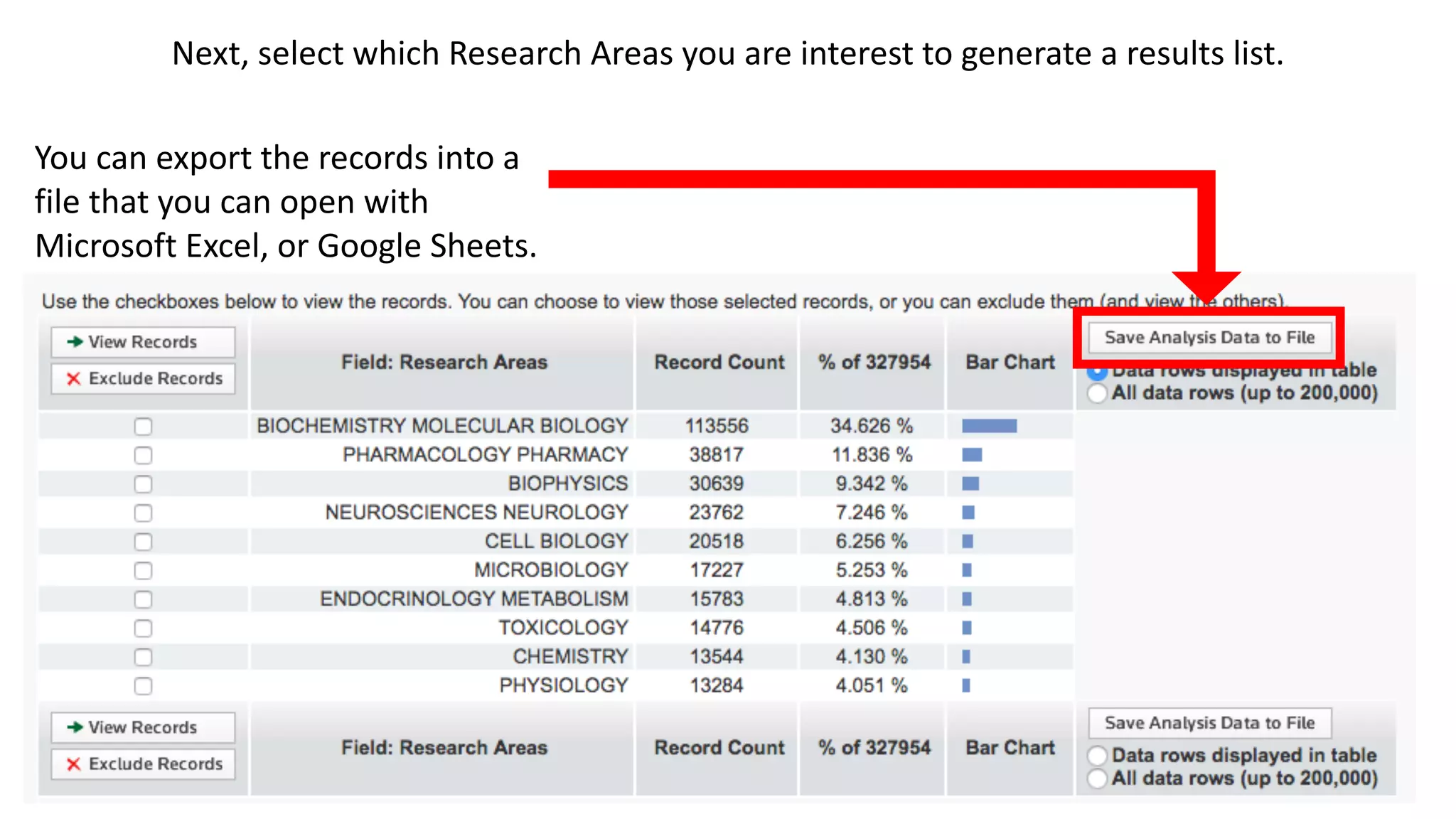
Web of Science is a multi-disciplinary database containing millions of published scholarly works from 1900 to present. It allows users to analyze citations in depth for specific papers, including viewing citing references, cited references, and times cited counts. The document provides a step-by-step guide to using Web of Science's citation analysis tools to explore how a highly cited paper has been used and built upon by other research over time.