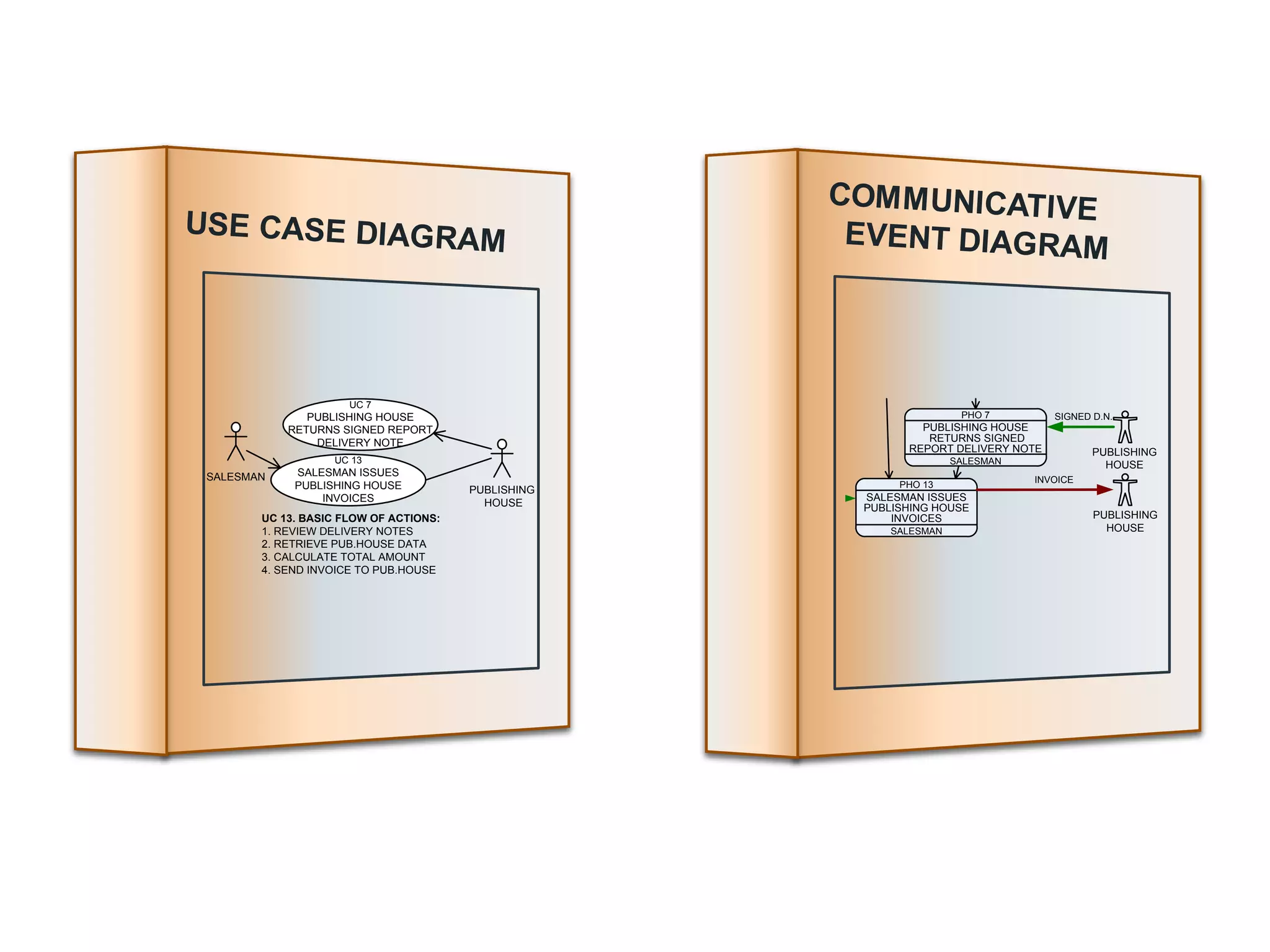
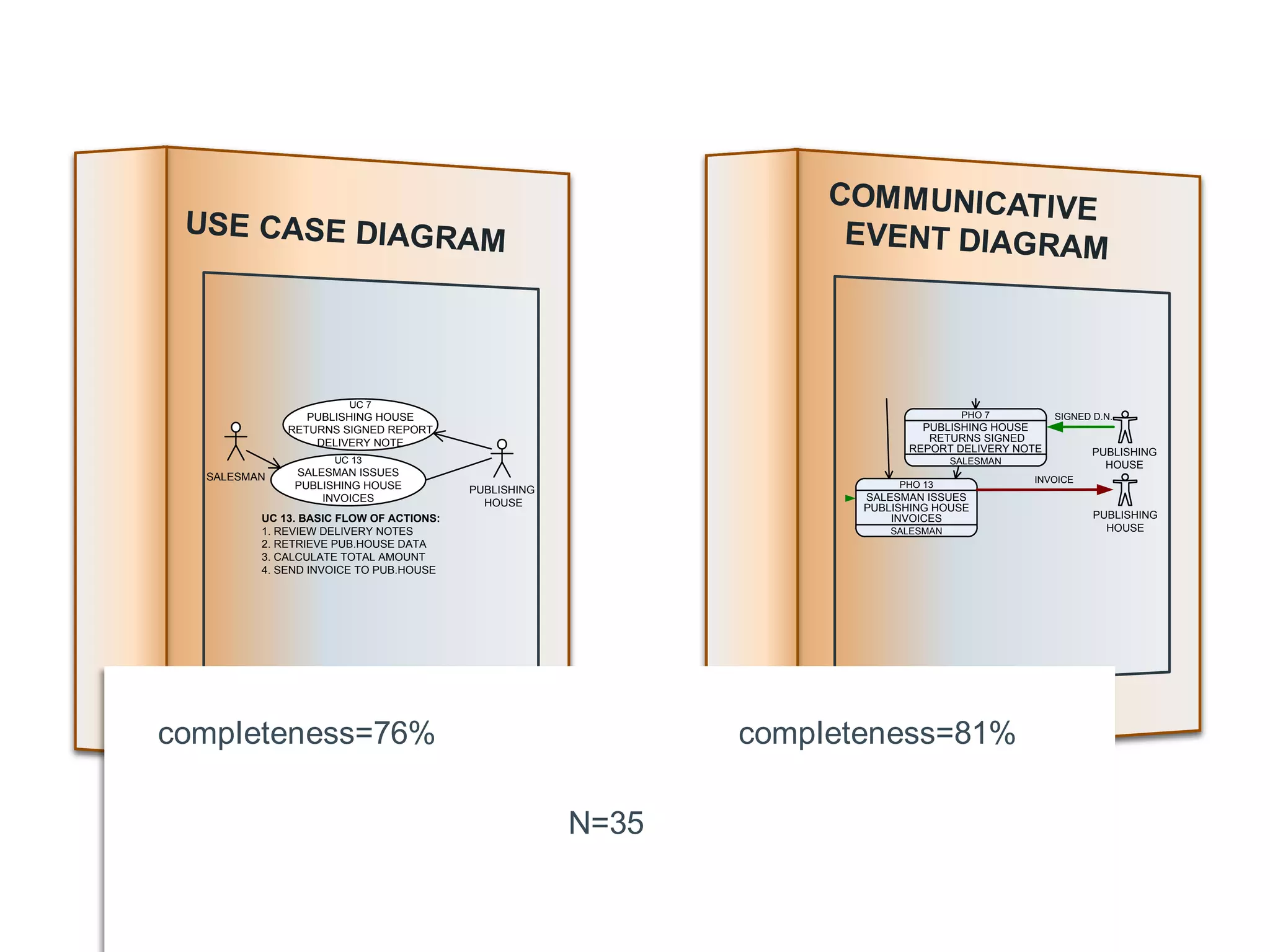
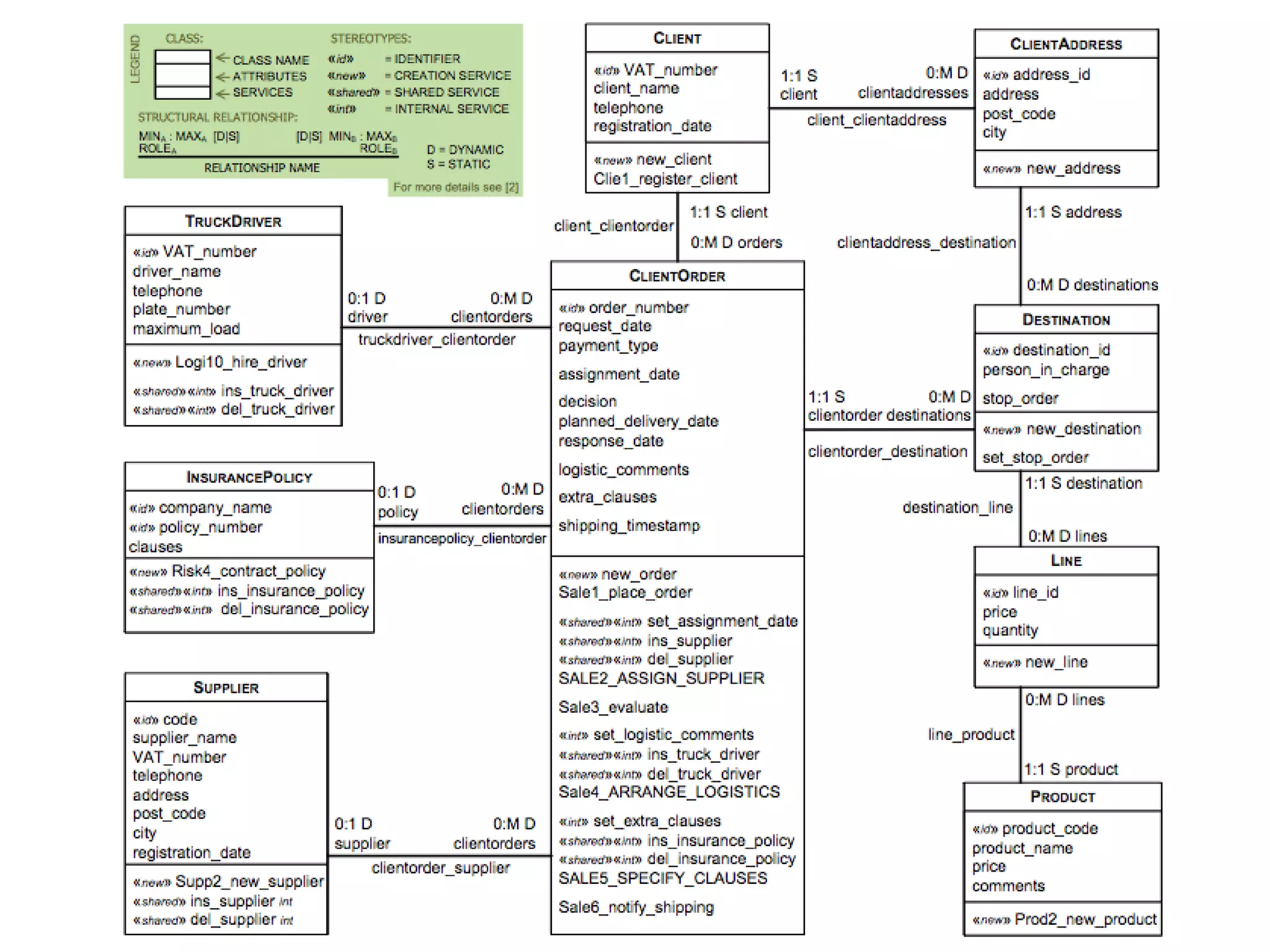
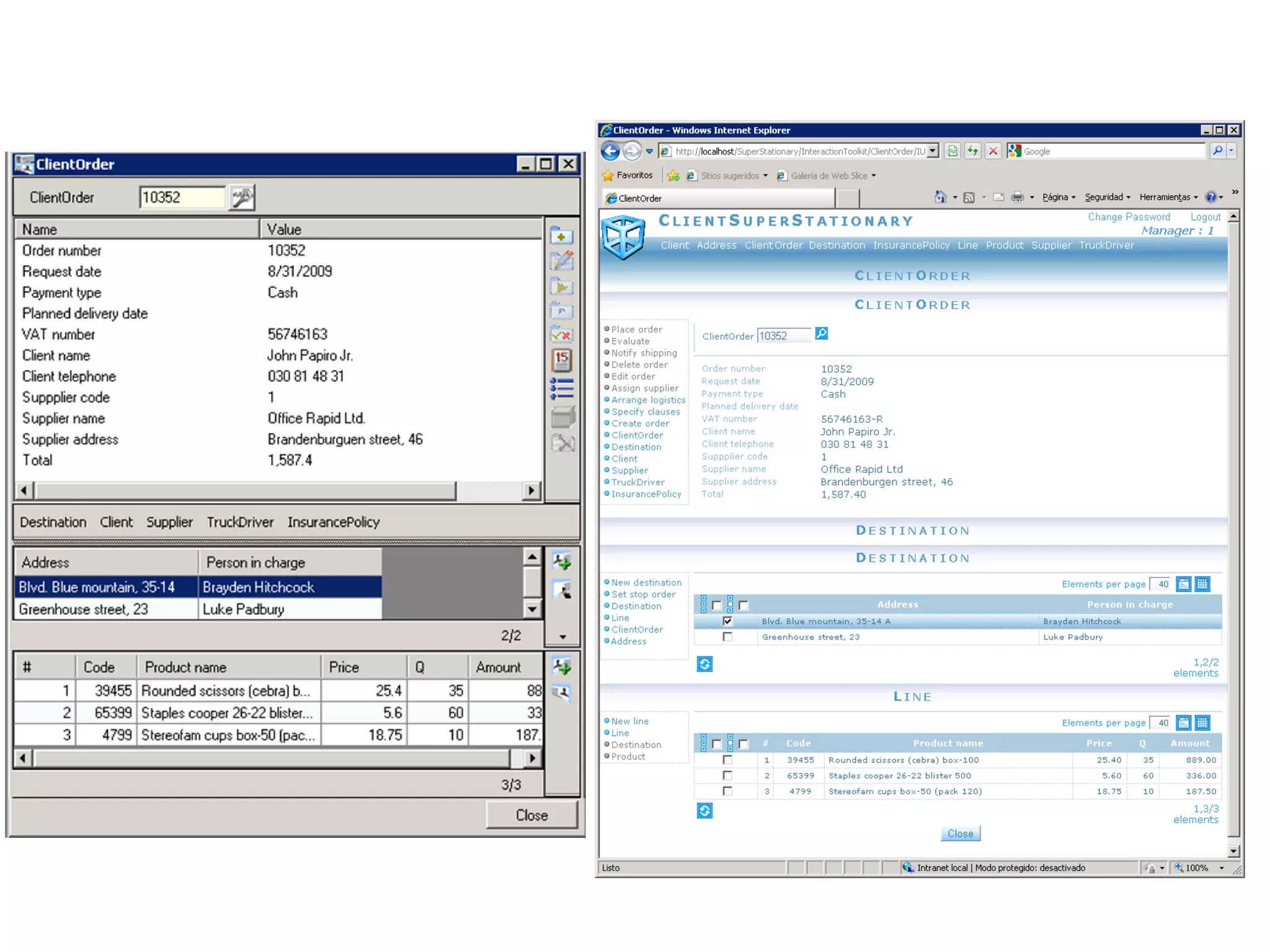
This document summarizes a systematic review of literature on the concept of quality in model-driven engineering. The review aimed to analyze definitions of quality, how quality relates to model-driven engineering principles, and whether current methods can assess quality across multiple modeling languages. The review found that there is no agreed-upon definition of quality and few methods consider model-driven engineering features or sets of languages. Overall, the assessment of quality across modeling languages remains an open research question.



![Framework by Lindland,Sindre and Sølvberg [1994]
LANGUAGE
AUDIENCE
INTERPRETATION
DOMAIN MODEL
PRAGMATICS
SYNTAX
SEMANTICS
completeness=77% completeness=85%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rcis2014slidesdeploy-140605134631-phpapp02/75/Analysing-the-concept-of-quality-in-model-driven-engineering-literature-a-systematic-review-8-2048.jpg)