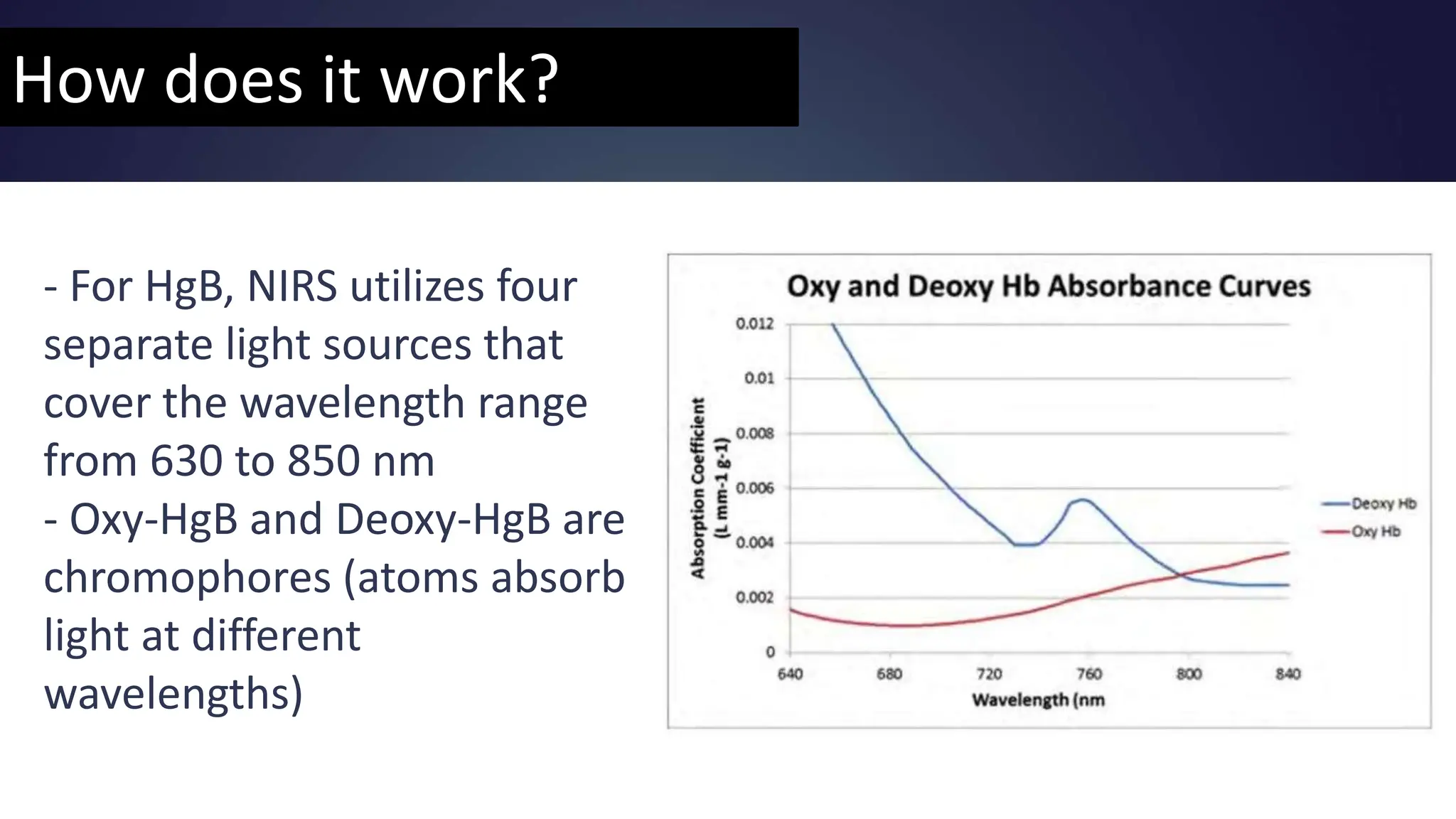
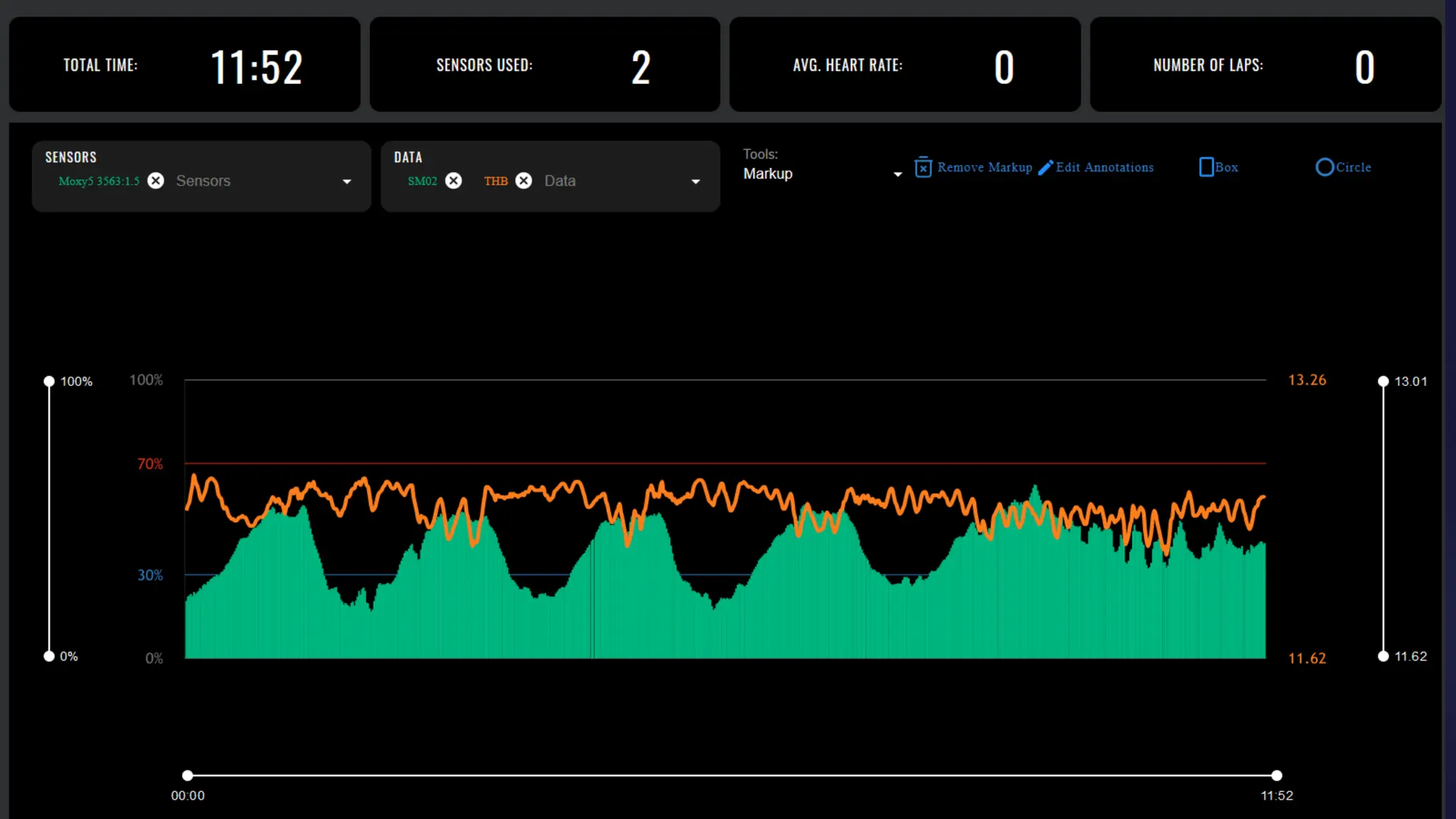
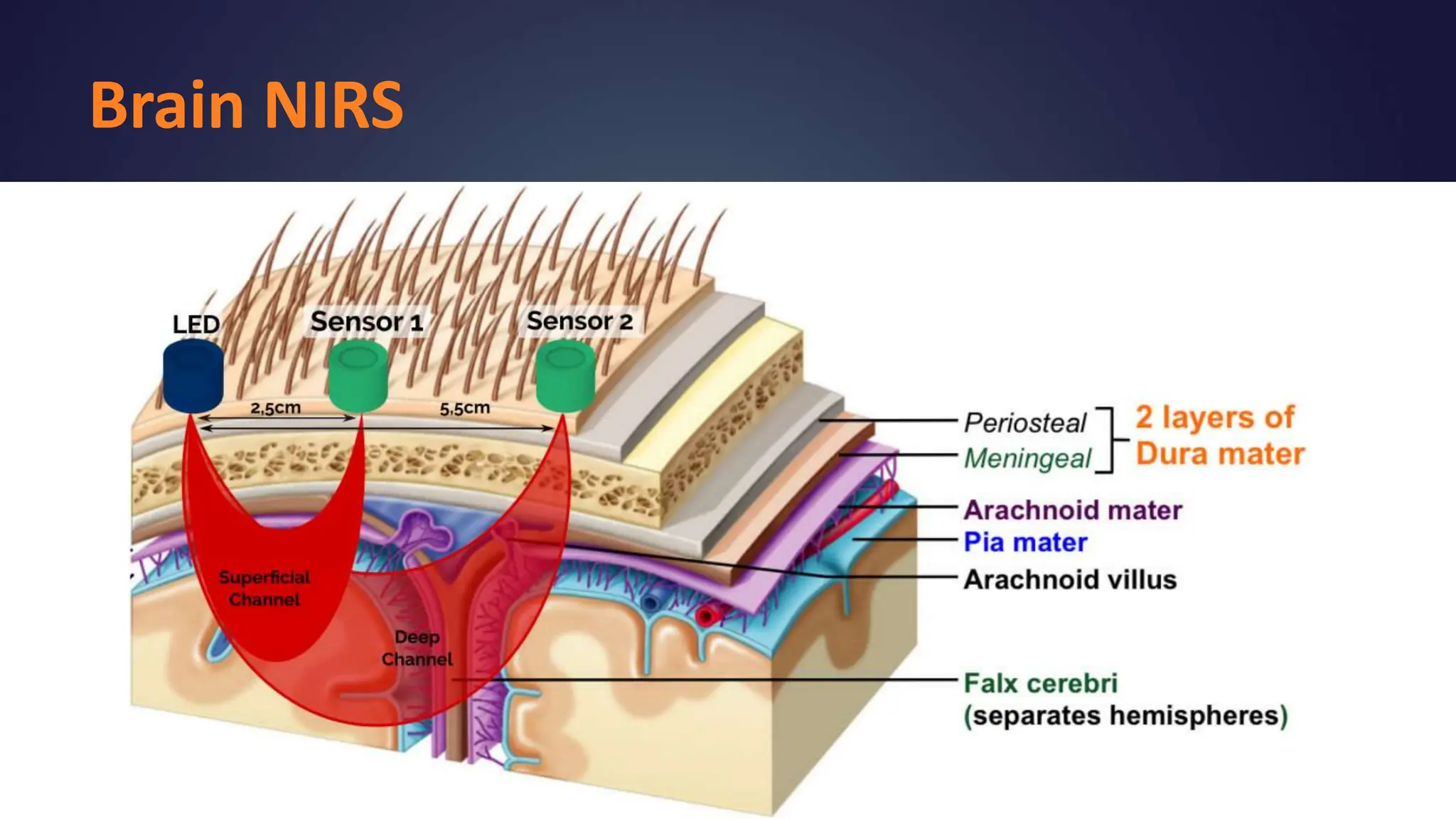
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a non-invasive optical method used to continuously measure tissue oxygenation and hemodynamics in the brain and muscle. It works by emitting light in the red and near-infrared region of the spectrum into the tissue, where it scatters due to refraction inside cells. Oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin have different absorbance spectra in this region, allowing their concentrations to be measured. For muscle oxygen saturation (SmO2), light is emitted and detected at different distances from the emitter, and the ratio of oxygenated to total hemoglobin is reported as a percentage of SmO2. NIRS is useful for measuring oxygen supply and demand