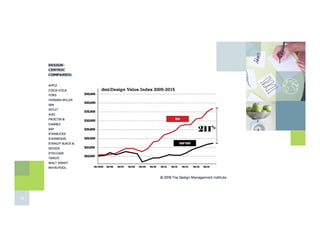
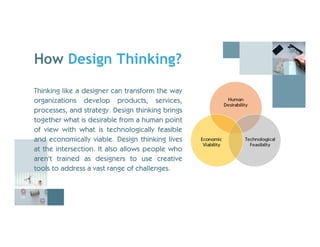
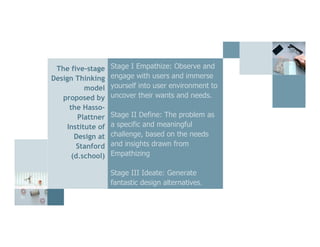
The document discusses design thinking, highlighting its importance and benefits, particularly in a business context using the Design Value Index that shows design-centric companies outperforming the S&P 500 by over 200%. It outlines the five-stage design thinking model proposed by the Stanford d.school, which includes empathizing with users, defining problems, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing. Emphasis is placed on the iterative nature of the design process, promoting continuous feedback and improvement.