describe communication systems in terms of
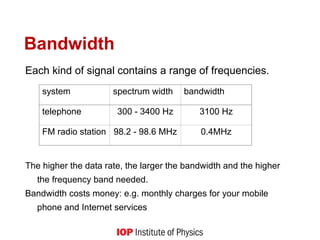
signal, carrier, noise, range, data transmission rate and bandwidth
a source – journey – detector model, with transmitter and receiver
modulation and demodulation (encoding and decoding)
calculate the critical angle for total internal reflection using Snell's law
describe advantages and limitations of optical fibre systems
identify UK radio wave bands used for wireless communications
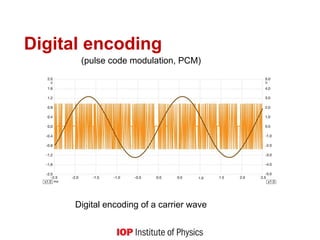
describe amplitude modulation (AM), frequency modulation (FM) and digital signals graphically and in words
use a variety of appropriate experiments and simulations when teaching about communications